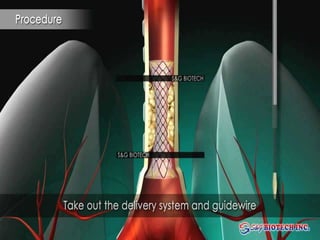
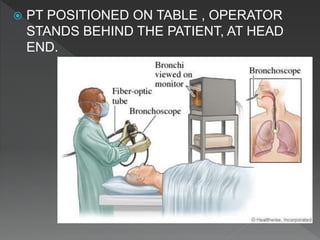
Bronchoscopy is a technique used to visually examine the inside of the airways. It can be performed using rigid or flexible scopes inserted through the nose, mouth or trachea. The first bronchoscopy was performed in 1897 using a rigid tube. Flexible fiberoptic bronchoscopes were developed in the 1960s, allowing better visualization of smaller airways. Bronchoscopy is used for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes such as evaluating lung abnormalities, taking biopsy samples, and treating conditions like airway tumors or bleeding. Complications can include pneumothorax, hemorrhage, or respiratory issues in high-risk patients.