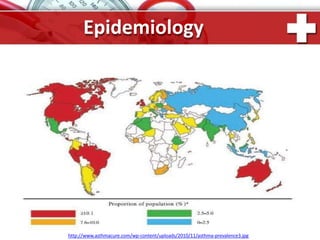
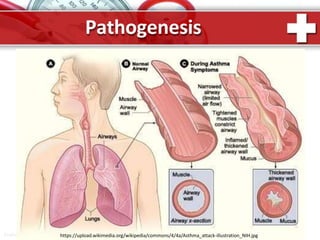
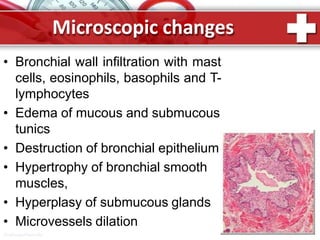
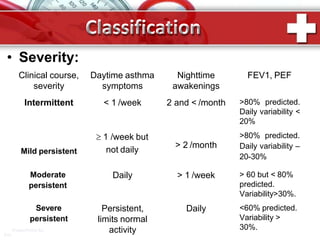
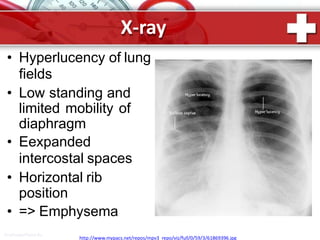
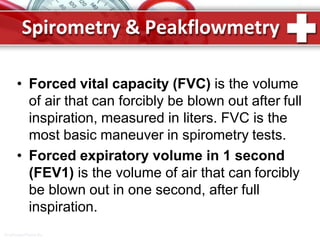
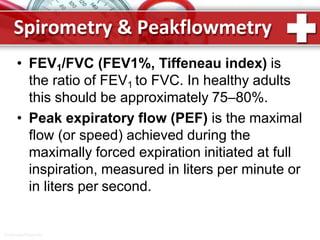
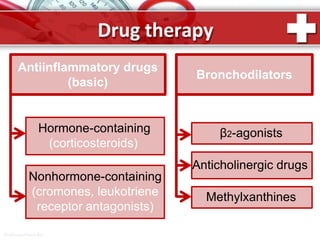
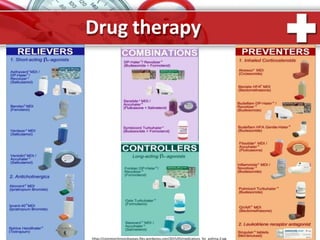
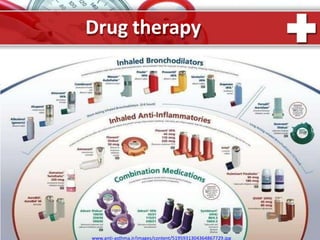
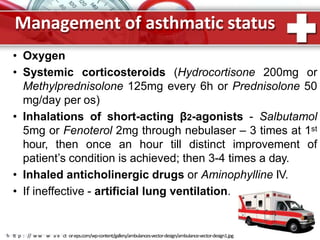
This document provides information on asthma, including its definition, epidemiology, etiology, pathogenesis, classification, symptoms, exacerbations, and atypical forms. Asthma is defined as a chronic inflammatory disease of the airways associated with bronchial hyperresponsiveness and reversible obstruction. It commonly involves eosinophilic inflammation and affects over 300 million people worldwide. Triggers include allergens, infections, pollution, and emotions. Pathogenesis typically involves a type I hypersensitivity reaction. Classification systems consider severity, control, and clinical course. Symptoms include wheezing, coughing, chest tightness, and shortness of breath. Exacerbations can be life-threatening without treatment.