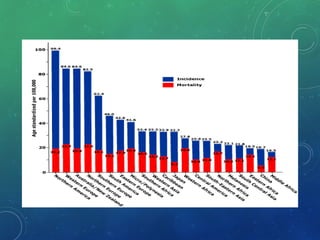
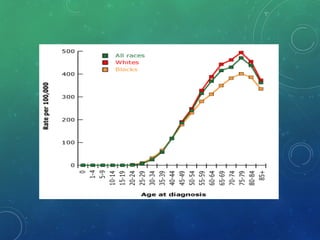
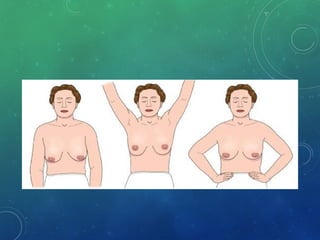
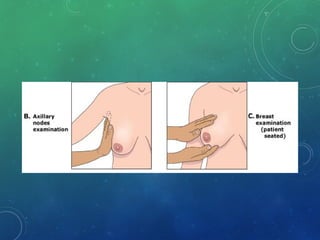
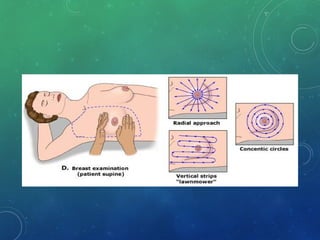
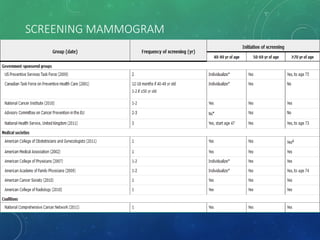
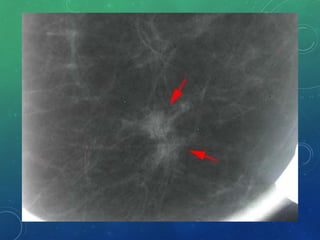
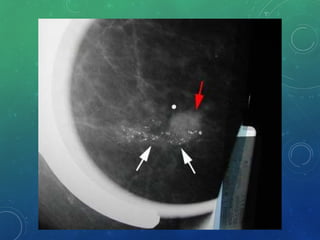
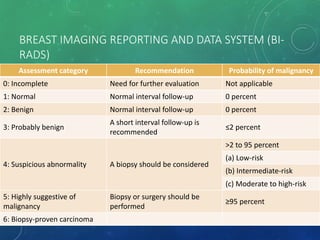
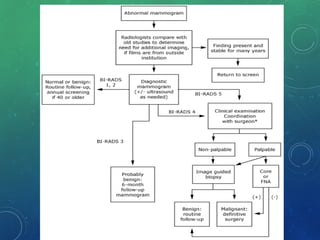
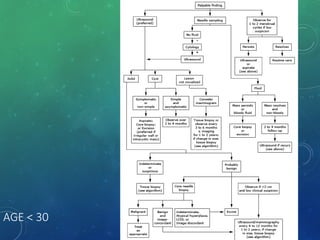
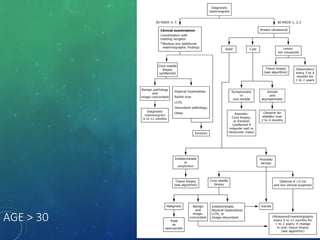
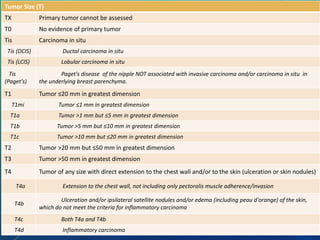
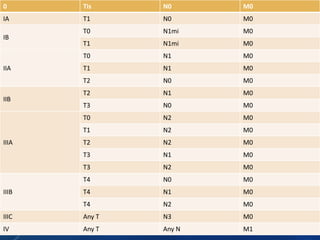
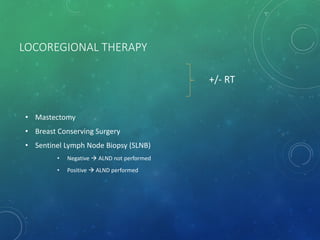
Breast cancer is the most common female cancer in the US and the second most common cause of cancer death in women. Risk factors include age, family history, lifestyle factors, and reproductive history. Evaluation of breast complaints requires a thorough history, physical exam including triple assessment with mammography, ultrasound and biopsy. Staging involves assessing tumor size, lymph node involvement and metastasis. Treatment may involve neoadjuvant chemotherapy, surgery such as mastectomy or lumpectomy with radiation, and adjuvant systemic therapy.