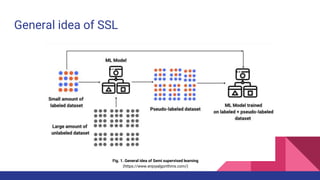
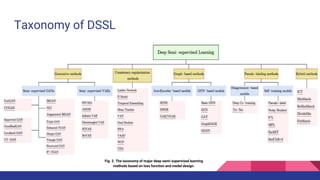
Deep semi-supervised learning (DSSL) uses a small amount of labeled data along with a large amount of unlabeled data. It works by using the labeled data to initially train a model, which is then used to label the unlabeled data, effectively increasing the training data. This document categorizes and describes various DSSL methods including generative models like GANs and VAEs, consistency regularization, graph-based methods using graphs and GNNs, pseudo-labeling using self-training or disagreement, and hybrid methods. Challenges include not fully understanding how DSSL works and potential performance issues with imbalanced or unrealistic data distributions.