The document discusses the evolution and methodologies of image processing, particularly through the use of Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) and advancements such as Residual Networks (ResNet). It covers historical perspectives, various CNN architectures (like AlexNet and VGGNet), and highlights the improvements in learning capacity over the years. Additionally, it acknowledges the challenges faced in deep neural networks and outlines future research directions in the field.

























![36
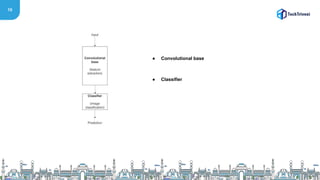
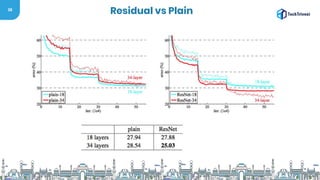
Residual Functions
● We explicitly reformulate the layers as learning residual functions
with reference to the layer inputs, instead of learning
unreferenced functions
● H[x] = F[x] + x](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tech-triveni-shubham-191127105422/85/Finding-the-best-solution-for-Image-Processing-36-320.jpg)













![54
References
● [1]. A. Krizhevsky, I. Sutskever, and G. E. Hinton. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional
neural networks. In Advances in neural information processing systems,pages 1097–1105,2012.
● [2]. K. He, X. Zhang, S. Ren, and J. Sun. Deep residual learning for image recognition. arXiv preprint
arXiv:1512.03385,2015.
● [3]. K. Simonyan and A. Zisserman. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image
recognition. arXiv preprint arXiv:1409.1556,2014.
● [4]. C. Szegedy, W. Liu, Y. Jia, P. Sermanet, S. Reed, D. Anguelov, D. Erhan, V. Vanhoucke, and A.
Rabinovich. Going deeper with convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on
Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition,pages 1–9,2015.
● https://arxiv.org/pdf/1901.06032.pdf](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tech-triveni-shubham-191127105422/85/Finding-the-best-solution-for-Image-Processing-54-320.jpg)
