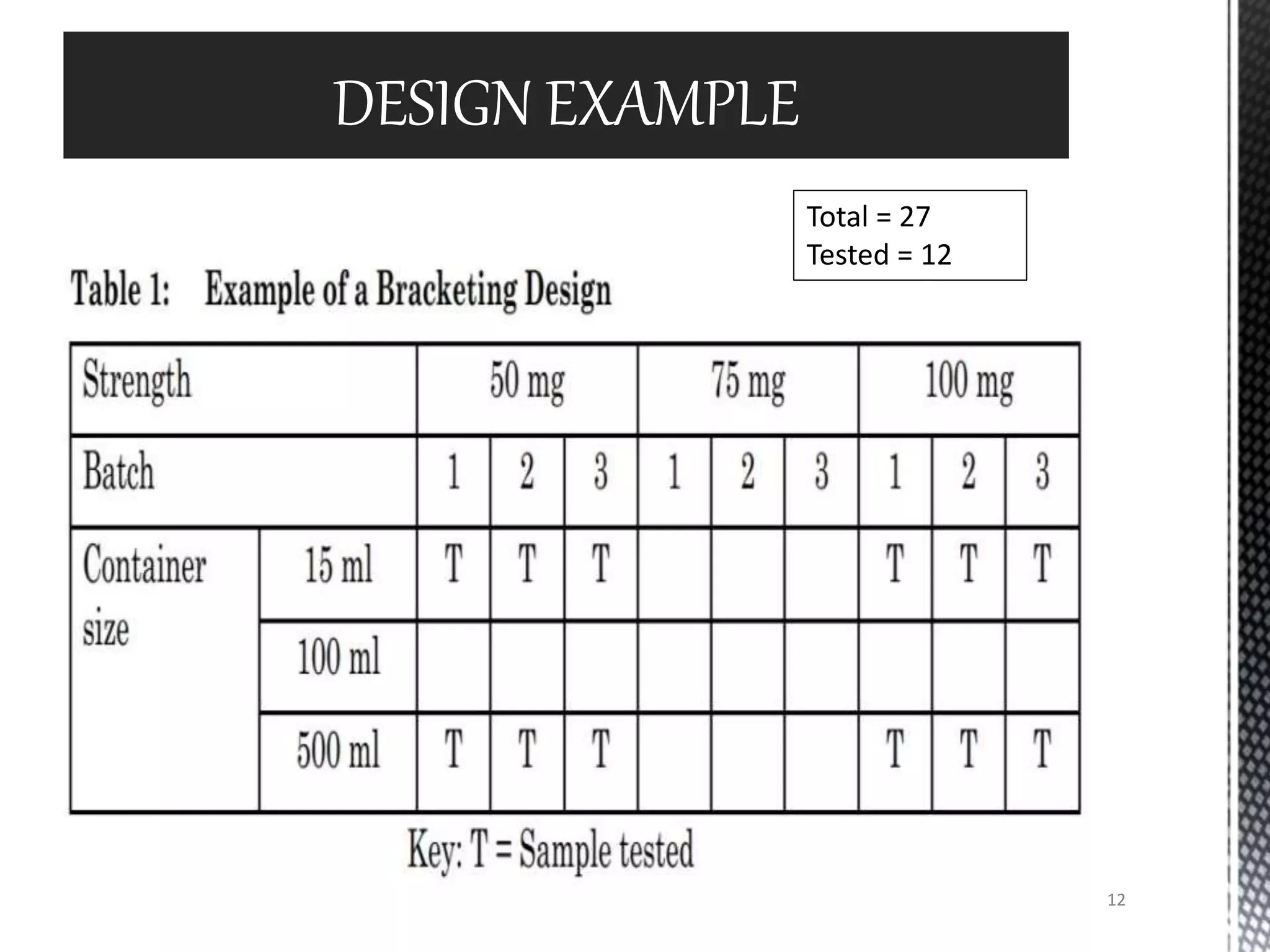
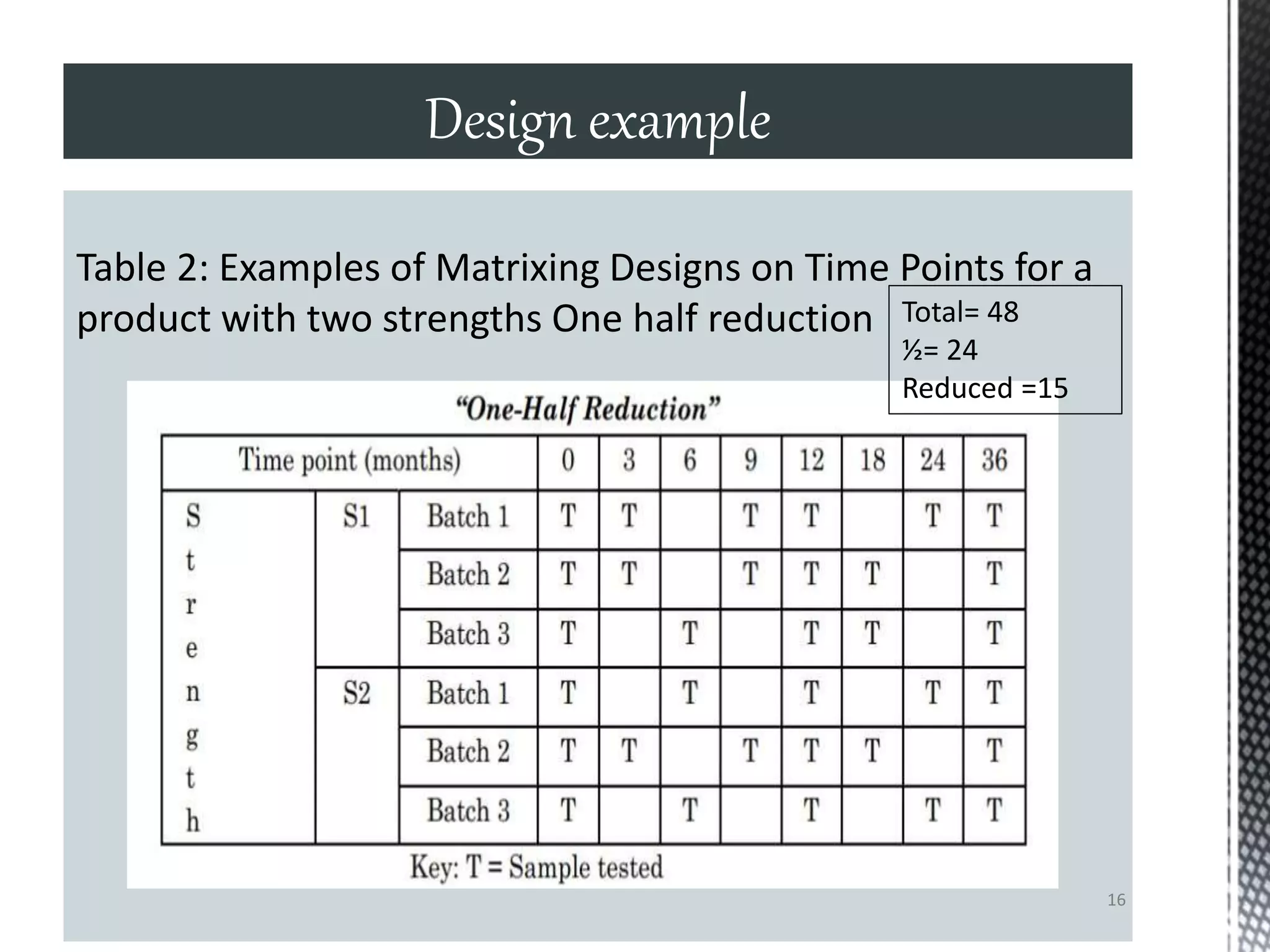
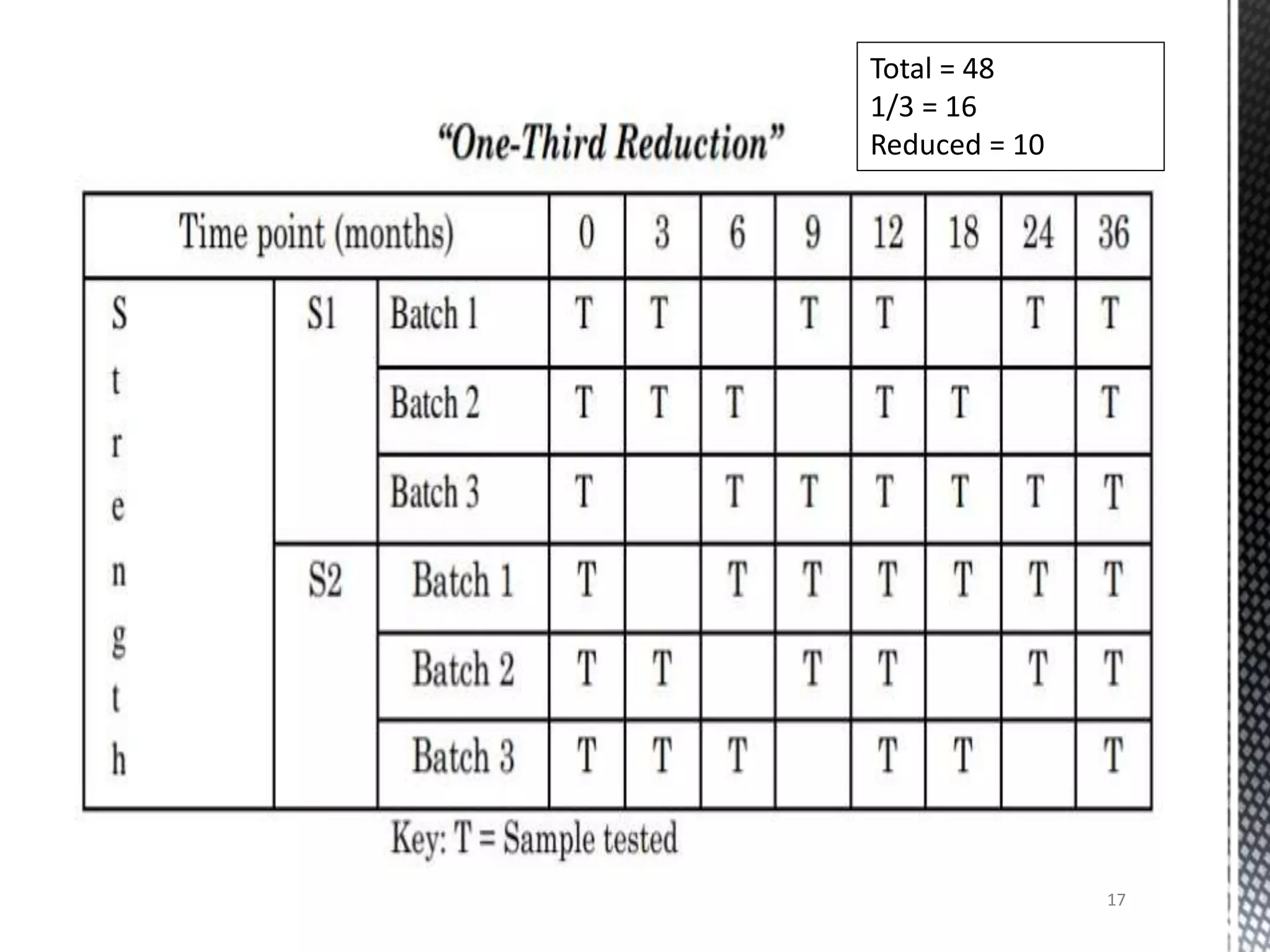
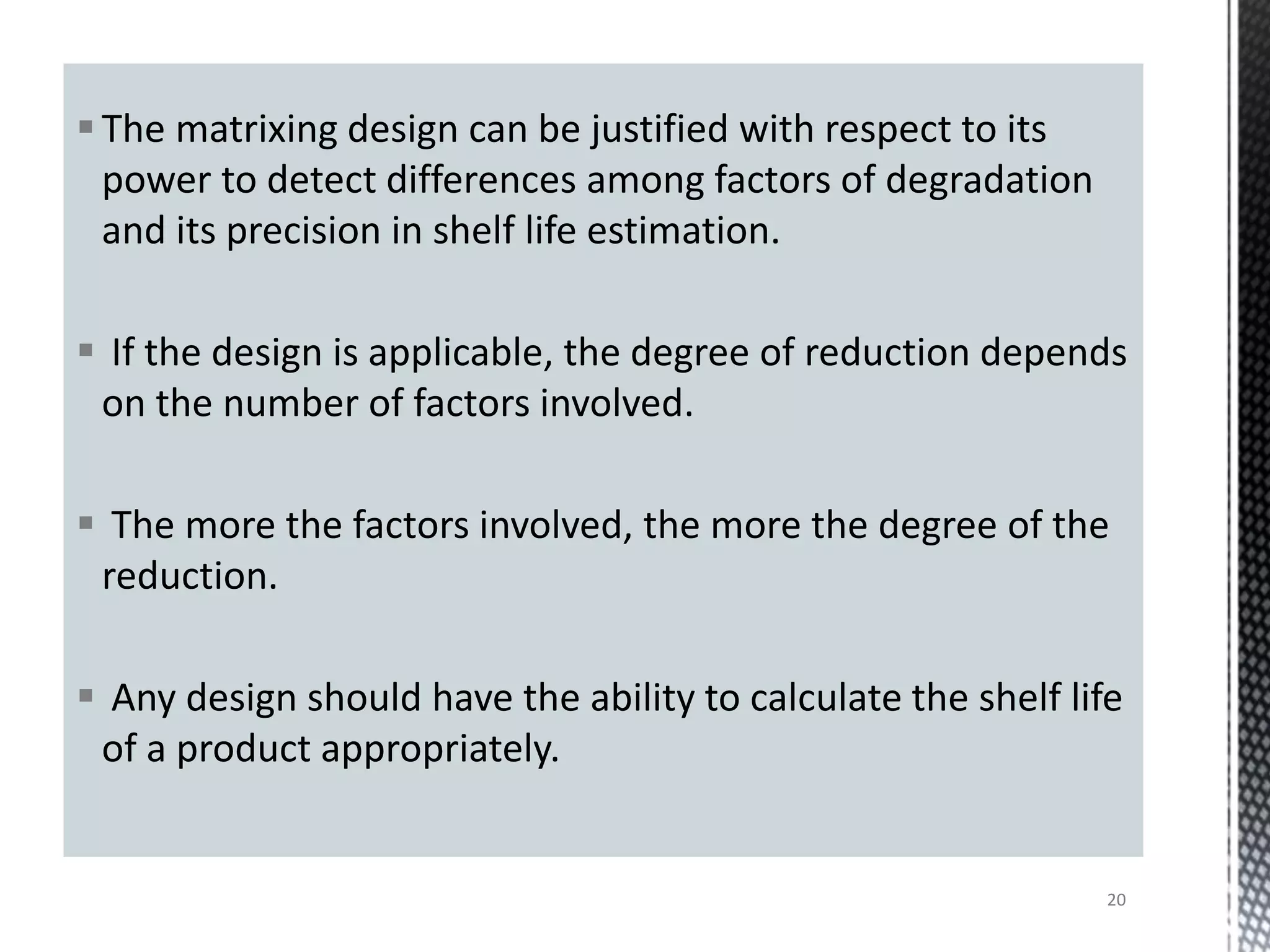
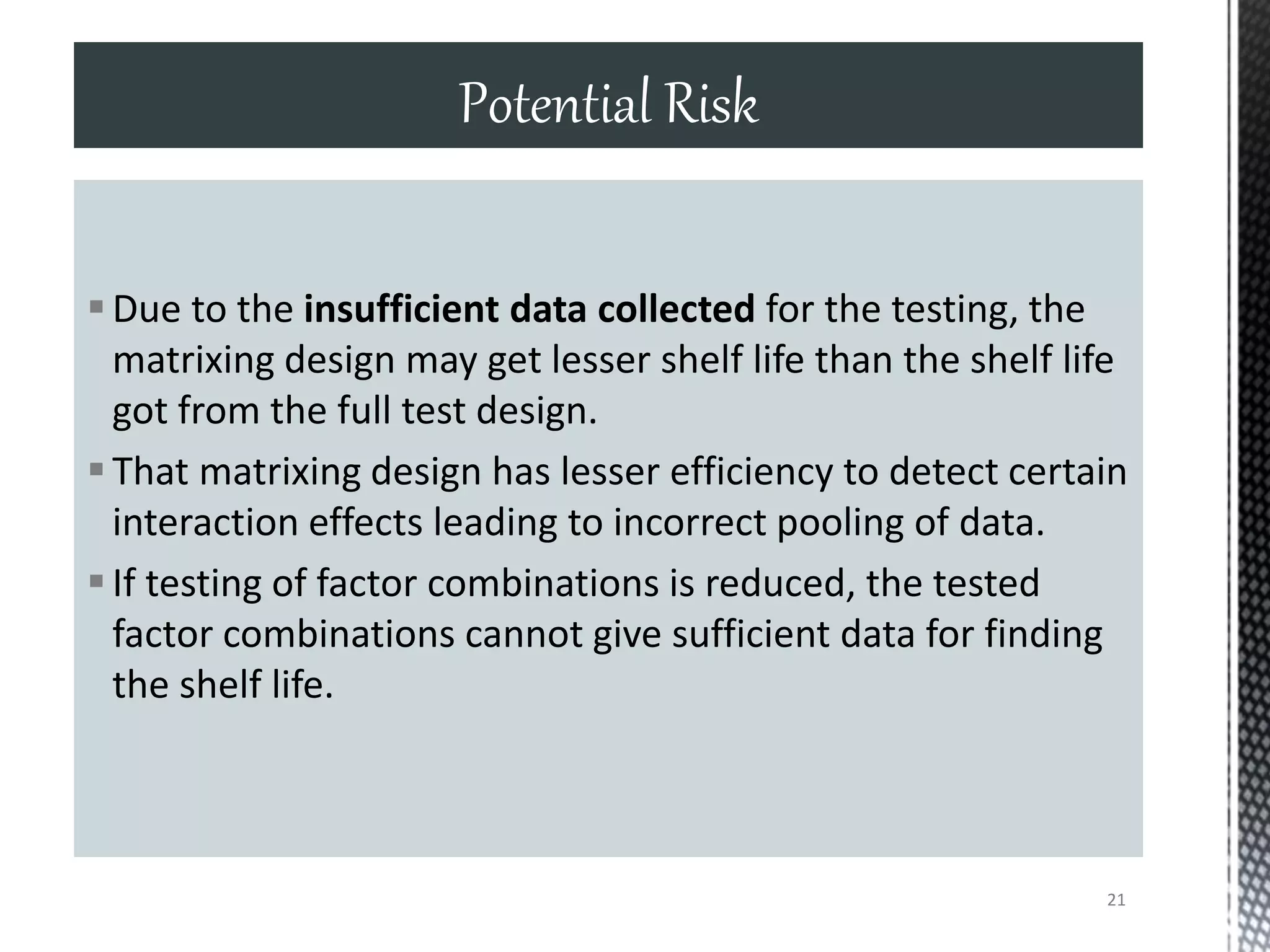
This document discusses guidelines for applying bracketing and matrixing designs to stability testing as outlined in ICH Q1A. Bracketing involves testing only the extremes of design factors like strength, while assuming stability of intermediates is represented by the extremes. Matrixing involves testing selected samples of all combinations at time points. Reduced designs can shorten testing if justified based on supporting data variability and product stability. However, reduced designs may underestimate shelf life compared to full testing and miss some degradation interactions. Data from reduced designs should still be evaluated statistically.