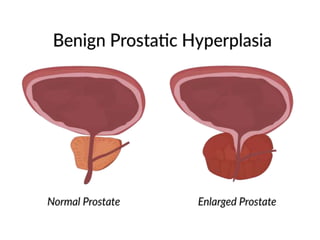
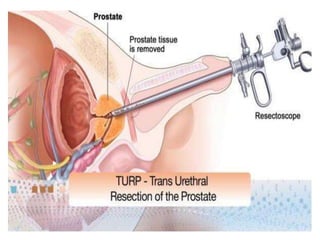
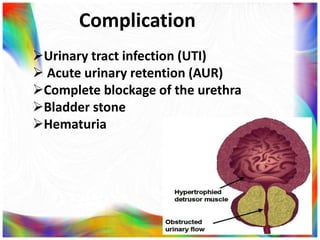
The document discusses benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), defined as an enlarged prostate gland. It affects men most commonly over age 50. Symptoms include frequent urination, urgency, and weak urine stream. Diagnosis involves digital rectal exam, lab tests, and prostate-specific antigen level. Treatment options include medications like alpha blockers and 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors, or surgical procedures like transurethral resection of the prostate. Nurses help manage symptoms, prevent complications like infection, and educate patients on BPH.