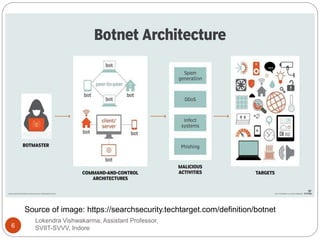
The document discusses botnets, which are networks of infected devices controlled by cybercriminals and used for various malicious activities, including identity theft and election interference. It outlines the mechanisms of infection, common tasks performed by botnets, and notable examples of their operations, such as the Zeus and Mirai botnets. Additionally, the document provides preventive measures individuals can take to protect their devices from becoming part of a botnet.