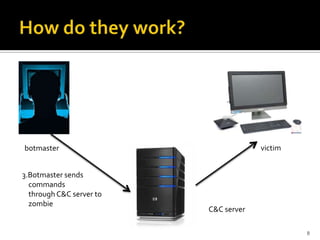
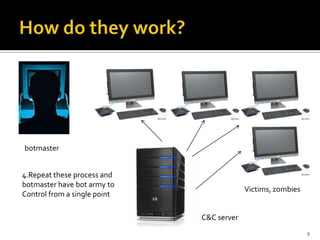
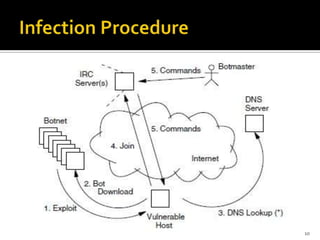
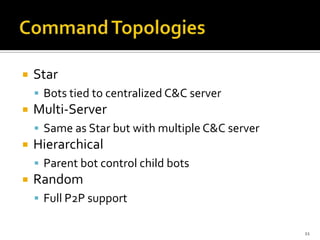
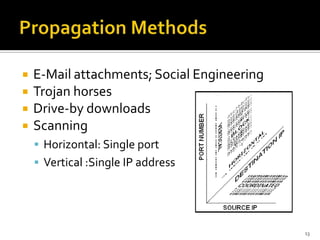
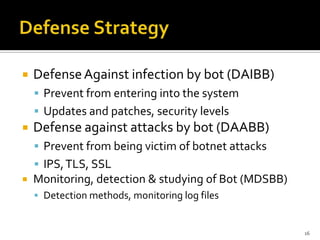
Botnets are collections of internet-connected programs that communicate together to perform tasks for their operators. They originated as tools to automate tasks but evolved into tools for malicious attacks like spam and DDoS. Botnets infect victims through various means and form centralized or hierarchical structures controlled through command and control servers using protocols like HTTP and IRC. They are used to carry out spam, phishing, and DDoS attacks. Detection relies on analyzing network traffic, application logs, and using honeypots while defense focuses on prevention, monitoring, and user education.