The document defines several key terms and concepts in Boolean algebra:
- Boolean algebra uses binary operations to represent logical operations and deals with true/false values.
- Boolean variables represent true/false values using 0 and 1.
- Boolean functions are formed using Boolean variables and operators.
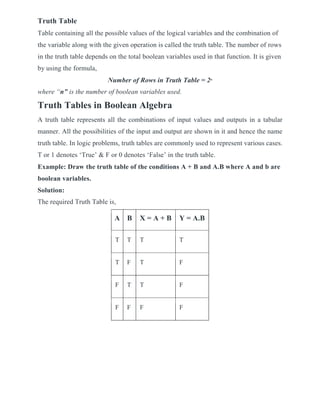
- Truth tables show all combinations of input and output values, and are used to represent logic problems.
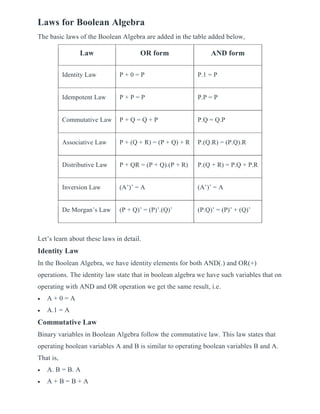
- Boolean algebra has basic laws like identity, commutative, associative, distributive, and De Morgan's laws.