Bone disorders
•Download as PPT, PDF•
27 likes•9,737 views
Biochemical tests are used to diagnose bone diseases. Serum tests measure calcium, phosphate, alkaline phosphatase, parathyroid hormone, and vitamin D levels. Urine tests measure calcium, phosphate, and bone turnover markers. Common bone diseases include arthritis, osteoporosis, rickets/osteomalacia, and Paget's disease. Arthritis causes joint symptoms. Osteoporosis weakens bones and increases fracture risk. Rickets/osteomalacia cause soft bones from vitamin D deficiency. Paget's disease involves abnormal bone remodeling.
Report
Share
Report
Share
Recommended
Introduction to Common Bone Disorders

This document provides an introduction to common bone disorders. It begins by defining bone and its importance in providing structure, protection, and a site for blood cell production. Bone disorders are divided into congenital and acquired categories. Congenital disorders include Osteogenesis Imperfecta, Achondroplasia, and Osteopetrosis. Acquired or metabolic bone diseases are caused by abnormalities in minerals, vitamins, bone mass or structure and include Osteoporosis, Paget's Disease, Rickets/Osteomalacia, and Hyperparathyroidism. Each condition is briefly characterized in terms of symptoms and causes of abnormal bone structure or composition.
paget's disease of bone

1. Paget's disease of bone is a disorder characterized by excessive and disorganized bone remodeling, leading to bone deformities and potential fractures.
2. It most commonly affects older individuals, with a higher prevalence in males. The exact cause is unclear but may be triggered by viral infections or genetic mutations.
3. The disease involves three phases: lytic, mixed, and sclerotic. In the lytic phase, overly active osteoclasts aggressively demineralize bone. In the mixed phase, rapid new bone formation occurs. In the sclerotic phase, new bone formation exceeds resorption.
4. Diagnosis involves biochemical tests showing elevated markers of bone formation and resorption, as
Osteoporosis

Osteoporosis is a metabolic bone disorder characterized by decreased bone mass and density, leading to porous and brittle bones that are prone to fracture. It is classified as either primary or secondary osteoporosis. Primary osteoporosis includes type I, which usually affects postmenopausal women, and type II, which occurs most commonly in those ages 70-85. Symptoms may include fractures after minor trauma. Diagnosis involves imaging tests to measure bone mineral density. Treatment focuses on controlling bone loss and preventing fractures through exercise, medication, supplements, and lifestyle changes. Nursing care emphasizes safety, mobility, nutrition, pain management, and education.
Atrophy

This document defines atrophy and discusses its causes and prevention. It begins by defining atrophy as a decrease in size of an organ resulting from a decrease in both the number and size of cells. It then discusses the microscopic and macroscopic signs of atrophy and the cellular changes that occur. The document classifies atrophy into physiological types, such as the natural atrophy of certain organs with age, and pathological types caused by factors like starvation, loss of innervation, pressure, ischemia, or decreased workload. It concludes by recommending a healthy diet, regular exercise, avoiding smoking, and changing positions frequently to prevent atrophic changes.
Osteomalacia

This document discusses metabolic bone diseases including osteomalacia and rickets. It provides details on bone histology, calcium homeostasis, vitamin D metabolism, and the roles of parathyroid hormone and calcitonin in regulating calcium levels. It describes the causes, clinical features, investigations and treatments of osteomalacia and rickets. Osteomalacia is characterized by softening of bones from defective mineralization in adults, while rickets causes softening of bones and growth plate abnormalities in children, often due to vitamin D or calcium deficiencies.
Metaplasia

Hyperplasia is an increase in the number of cells in an organ or tissue. It can be physiologic, such as during pregnancy, or pathologic, such as with excessive hormone stimulation. Hypertrophy is an increase in cell size within an organ or tissue, often due to increased functional demands. Atrophy is a decrease in cell and organ size due to loss of cell substance from factors like disuse or inadequate nutrition. Metaplasia is a reversible change where one adult cell type replaces another, such as squamous replacing columnar epithelium from chronic irritation. These changes can sometimes progress to cancer if the predisposing stimuli persist long-term.
Pathologic Calcification

Pathological calcification involves the abnormal deposition of calcium salts in tissues other than bone. There are two main types: dystrophic calcification occurs in dead or damaged tissue with normal calcium levels, while metastatic calcification affects normal tissues and results from disorders that increase calcium levels in the blood (hypercalcemia). Dystrophic calcification is seen in areas of necrosis, atherosclerotic plaques, and infarcts. Metastatic calcification commonly involves the kidneys, lungs, blood vessels, and stomach, and is caused by hyperparathyroidism, bone destruction, or excessive vitamin D intake.
Pathophysiology of Gout

Gout is caused by deposition of monosodium urate crystals in joints due to hyperuricemia or high levels of uric acid in the blood. It most commonly affects the big toe joint, causing sudden and severe pain. Over time, if untreated, it can progress to a chronic arthritis and formation of tophi or urate deposits in other tissues. Hyperuricemia occurs due to increased production or decreased excretion of uric acid, which can be due to diet, genetics or medical conditions.
Recommended
Introduction to Common Bone Disorders

This document provides an introduction to common bone disorders. It begins by defining bone and its importance in providing structure, protection, and a site for blood cell production. Bone disorders are divided into congenital and acquired categories. Congenital disorders include Osteogenesis Imperfecta, Achondroplasia, and Osteopetrosis. Acquired or metabolic bone diseases are caused by abnormalities in minerals, vitamins, bone mass or structure and include Osteoporosis, Paget's Disease, Rickets/Osteomalacia, and Hyperparathyroidism. Each condition is briefly characterized in terms of symptoms and causes of abnormal bone structure or composition.
paget's disease of bone

1. Paget's disease of bone is a disorder characterized by excessive and disorganized bone remodeling, leading to bone deformities and potential fractures.
2. It most commonly affects older individuals, with a higher prevalence in males. The exact cause is unclear but may be triggered by viral infections or genetic mutations.
3. The disease involves three phases: lytic, mixed, and sclerotic. In the lytic phase, overly active osteoclasts aggressively demineralize bone. In the mixed phase, rapid new bone formation occurs. In the sclerotic phase, new bone formation exceeds resorption.
4. Diagnosis involves biochemical tests showing elevated markers of bone formation and resorption, as
Osteoporosis

Osteoporosis is a metabolic bone disorder characterized by decreased bone mass and density, leading to porous and brittle bones that are prone to fracture. It is classified as either primary or secondary osteoporosis. Primary osteoporosis includes type I, which usually affects postmenopausal women, and type II, which occurs most commonly in those ages 70-85. Symptoms may include fractures after minor trauma. Diagnosis involves imaging tests to measure bone mineral density. Treatment focuses on controlling bone loss and preventing fractures through exercise, medication, supplements, and lifestyle changes. Nursing care emphasizes safety, mobility, nutrition, pain management, and education.
Atrophy

This document defines atrophy and discusses its causes and prevention. It begins by defining atrophy as a decrease in size of an organ resulting from a decrease in both the number and size of cells. It then discusses the microscopic and macroscopic signs of atrophy and the cellular changes that occur. The document classifies atrophy into physiological types, such as the natural atrophy of certain organs with age, and pathological types caused by factors like starvation, loss of innervation, pressure, ischemia, or decreased workload. It concludes by recommending a healthy diet, regular exercise, avoiding smoking, and changing positions frequently to prevent atrophic changes.
Osteomalacia

This document discusses metabolic bone diseases including osteomalacia and rickets. It provides details on bone histology, calcium homeostasis, vitamin D metabolism, and the roles of parathyroid hormone and calcitonin in regulating calcium levels. It describes the causes, clinical features, investigations and treatments of osteomalacia and rickets. Osteomalacia is characterized by softening of bones from defective mineralization in adults, while rickets causes softening of bones and growth plate abnormalities in children, often due to vitamin D or calcium deficiencies.
Metaplasia

Hyperplasia is an increase in the number of cells in an organ or tissue. It can be physiologic, such as during pregnancy, or pathologic, such as with excessive hormone stimulation. Hypertrophy is an increase in cell size within an organ or tissue, often due to increased functional demands. Atrophy is a decrease in cell and organ size due to loss of cell substance from factors like disuse or inadequate nutrition. Metaplasia is a reversible change where one adult cell type replaces another, such as squamous replacing columnar epithelium from chronic irritation. These changes can sometimes progress to cancer if the predisposing stimuli persist long-term.
Pathologic Calcification

Pathological calcification involves the abnormal deposition of calcium salts in tissues other than bone. There are two main types: dystrophic calcification occurs in dead or damaged tissue with normal calcium levels, while metastatic calcification affects normal tissues and results from disorders that increase calcium levels in the blood (hypercalcemia). Dystrophic calcification is seen in areas of necrosis, atherosclerotic plaques, and infarcts. Metastatic calcification commonly involves the kidneys, lungs, blood vessels, and stomach, and is caused by hyperparathyroidism, bone destruction, or excessive vitamin D intake.
Pathophysiology of Gout

Gout is caused by deposition of monosodium urate crystals in joints due to hyperuricemia or high levels of uric acid in the blood. It most commonly affects the big toe joint, causing sudden and severe pain. Over time, if untreated, it can progress to a chronic arthritis and formation of tophi or urate deposits in other tissues. Hyperuricemia occurs due to increased production or decreased excretion of uric acid, which can be due to diet, genetics or medical conditions.
Pathology of Skeletal Muscle

Neurogenic changes in denervated skeletal muscle include angulated fibers, increased nuclei, and an absence of necrosis or fibrosis. Reinnervation results in fiber type grouping and target fibers. The reading frame hypothesis explains how in-frame deletions in the dystrophin gene cause Becker muscular dystrophy by producing an abnormally short, but present, dystrophin protein. Routine muscle biopsy has limitations in diagnosing some muscular dystrophies and mitochondrial diseases due to heterogeneity and sampling issues. Dermatomyositis is distinguished from polymyositis by features of a complement-mediated small vessel vasculitis, while inclusion body myositis shows vacuolated fibers, mononuclear inflammation, and intracellular protein
Osteoporosis

The document discusses osteoporosis, which is a disease characterized by low bone mass and fragile bones that break easily. It defines osteoporosis and describes that typical fractures occur in the vertebrae, ribs, hip and wrist. While it has no symptoms, its main consequence is an increased risk of bone fractures. The document outlines exams and tests used to diagnose osteoporosis, as well as lifestyle changes and medications used to treat and prevent the disease.
Disorders Of The Bone By Yapa Wijeratne

Presentation on disorders of the bone which explains the biochemical & physiological aspects with illustrations.
Osteoporosis-pathogenesis, diagnosis, management and prevention

Osteoporosis is a disease characterized by low bone mass and deterioration of bone tissue, leading to fragile bones and increased risk of fractures. It is defined by the World Health Organization as a bone mineral density score of -2.5 or below. Those at highest risk include older adults, especially post-menopausal women, and those with low calcium/vitamin D intake or other risk factors such as smoking. Symptoms include back pain from fractured or collapsed vertebrae. Diagnosis involves bone mineral density tests and other lab tests. Treatment focuses on calcium, vitamin D, bisphosphonates, and lifestyle changes to build strong bones early in life and prevent bone loss later in life.
Cell injury and hypertrophy

This document discusses cell injury, adaptation, and death. It explains that cells can undergo adaptation to physiologic or pathologic stresses to maintain homeostasis. Adaptation allows cells to modify their structure and function to avoid injury. If stresses exceed a cell's adaptive capacity, injury occurs. Adaptations include hypertrophy, where cells increase in size rather than number. Hypertrophy can be physiologic, like uterine enlargement during pregnancy, or pathologic, like cardiac enlargement from hypertension. The document then focuses on hypertrophy in more detail.
Osteoporosis

This document discusses osteoporosis, including its definitions, epidemiology, risk factors, pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, diagnosis, and treatment options. Osteoporosis is a disease characterized by low bone mass and deterioration of bone tissue, leading to fragile bones and increased risk of fractures. It affects millions of people worldwide, especially postmenopausal women, and can be caused by aging, genetics, lifestyle factors, and certain medical conditions or medications. Treatment involves lifestyle modifications like diet, exercise and fall prevention as well as pharmacologic options like calcium, vitamin D, bisphosphonates, and drugs that modify bone metabolism.
Metabolic bone diseases, pathology dept

This document discusses metabolic bone diseases. It begins by describing the basic structure and function of bone, including its cellular components like osteoblasts and osteoclasts. It then discusses the constituents of bone matrix, including collagen, proteoglycans, and minerals. Bone development and homeostasis are explained, involving processes like remodeling. Specific metabolic bone diseases are then outlined in more detail, including osteogenesis imperfecta (brittle bone disease), osteomalacia/rickets due to abnormal mineralization, and hypophosphatasia due to a genetic disturbance in alkaline phosphatase synthesis. Throughout, the document provides microscopic and radiographic characteristics of these conditions.
Osteoporosis

All you need to know about this disease of bones called Osteoporosis.
Subject: Pathophysiology, B.Pharma. Semester 3
paget's disease

Paget's disease is a chronic bone disorder caused by abnormal bone remodeling. The cause is unknown but may involve viruses or genetic predisposition. It is characterized by increased and disorderly bone breakdown followed by rapid bone formation, resulting in abnormal bone structure. Common symptoms include bone pain, fractures, and skeletal deformities. Diagnosis involves blood tests showing elevated alkaline phosphatase levels and imaging tests revealing abnormal bone structure. While there is no cure, treatment focuses on reducing symptoms.
Skeletal muscles disease and disorder

Skeletal muscles disorder is disease and damage the brain or nerves that stimulate muscles and disorders of muscle fibers.
Types of that are :
1- Muscular Atrophy.
2- Muscular Dystrophy.
3- Inflammation of muscle (Myositis).
4- Disorders of Neuromuscular Transmission.
Osteomalacia

This document discusses osteomalacia, a disease characterized by softening of the bones due to defective mineralization. It is caused by vitamin D deficiency and/or phosphate deficiency. Signs include diffuse body pains, muscle weakness, and fragile bones. Laboratory findings show low calcium and phosphate levels as well as elevated alkaline phosphatase and parathyroid hormone levels. Treatment involves vitamin D and calcium supplementation. Exercise and sunlight exposure can also help strengthen bones affected by osteomalacia.
Osteoporosis

This document provides information on osteoporosis from Dr. Ashutosh. It defines osteoporosis as a reduction in bone strength that increases fracture risk. The WHO defines it as a bone density 2.5 standard deviations below young adults of the same sex. Postmenopausal women with bone density between -1 and -2.5 SD also have increased fracture risk. Non-pharmacological prevention includes nutrition, lifestyle modifications, fall prevention, and hip protectors. Pharmacological management includes calcium and vitamin D supplementation, hormonal therapy, antiresorptive drugs, anabolic drugs, and drugs with dual actions.
Muscle disorders

This document discusses various muscle disorders including:
1) Diseases affecting the neuromuscular junction such as myasthenia gravis and Lambert-Eaton syndrome.
2) Effects of denervation of muscle including fibrillation, fasciculation, muscle atrophy, and denervation hypersensitivity.
3) Muscle dystrophies which are degenerative diseases that cause progressive muscle weakness. The most common type is Duchenne muscular dystrophy which is often fatal by age 30.
Osteoporosis my ppt

This document defines osteoporosis and discusses its epidemiology, pathophysiology, risk factors, clinical features, diagnosis and treatment. Osteoporosis is defined as a systemic skeletal disease characterized by low bone density and deterioration of bone tissue, leading to increased bone fragility and fracture risk. It most commonly affects post-menopausal women and the elderly. Diagnosis involves assessing bone mineral density via DEXA scan and evaluating risk factors. Treatment focuses on lifestyle modifications and medications to prevent bone loss and fractures.
Pathology cell injury i

The document discusses cell injury and cell death. It explains that cells have a normal steady state of homeostasis but stress can force cells to adapt or become injured if the stress exceeds their capacity. Cell injury can be reversible or irreversible and leads to cell death if irreversible. Key systems vulnerable to injury are membranes, respiration, protein synthesis and the genetic apparatus. Causes of injury include hypoxia, toxins, infections and more. Reversible injury disrupts mitochondria while irreversible injury causes mitochondrial and lysosomal damage leading to cell death.
Paget’s disease of the bone

Paget's disease is a condition where there is excessive and disorganized bone remodeling, leading to thickened and deformed bones. It was first described in 1877 and typically involves the pelvis, femur, skull and spine. The cause is unknown but genetic and viral factors may play a role. It progresses through lytic, mixed, and sclerotic phases with abnormal osteoclast and osteoblast activity. Complications include fractures, arthritis, and neurological or vascular issues. Diagnosis involves elevated alkaline phosphatase and imaging showing thickened bones. Treatment focuses on suppressing active disease with bisphosphonates or calcitonin to reduce pain, deformity, and complications.
Immunopathology 1

This document summarizes different types of immunity and hypersensitivity reactions. It describes two broad categories of immunity: innate immunity which provides a first line of defense, and adaptive immunity which develops after exposure and recognizes specific antigens. It then discusses four types of hypersensitivity reactions (Type I-IV) mediated by different immune mechanisms in response to various antigens, providing examples of diseases associated with each type.
Metabolic bone disease

metabolic disease from physiotherapy point of view. in detailed description along with imaging and assessment techniques of the same.
Blood Disorders

Common blood disorders include anemia, bleeding disorders such as hemophilia, blood clots, and blood cancers such as leukemia, lymphoma, and myeloma.
Cell injury etiology and pathogenesis

This document discusses etiology and pathogenesis of cell injury. It defines cell injury as changes in a cell's internal and external environment due to various stresses from etiological agents. The cellular response depends on host factors like cell type and extent of injury. Injury can result in reversible or irreversible cell injury depending on factors like agent type/duration and cell adaptability. Common causes of cell injury include hypoxia, ischemia, toxins, microbes, nutrition imbalances, and aging. Ischemia and hypoxia are the most frequent causes of cell injury in humans. Reversible injury involves ATP depletion and membrane changes, while irreversible injury brings further damage including to mitochondria and nuclei, leading to cell death.
case microscopic polyangiitis

This document summarizes the case of a 56-year-old Thai woman who presented with hemoptysis and renal failure. She has a history of tuberculosis as a child and rheumatoid arthritis. On examination, she had coarse lung crepitations and signs of renal impairment. Tests showed p-ANCA positivity. She was diagnosed with microscopic polyangiitis and treated with plasma exchange, antibiotics, and steroids. Her condition gradually improved with treatment.
medicine.CRF2.(dr.kawa)

Chronic renal failure refers to the irreversible deterioration of renal function over years. It initially presents as biochemical abnormalities and eventually leads to uraemic symptoms as the excretory, metabolic and endocrine functions of the kidneys fail. Common causes include diabetes, hypertension, and glomerulonephritis. Management involves identifying and treating the underlying disease, slowing progression, managing complications, and renal replacement therapy for end-stage disease.
More Related Content
What's hot
Pathology of Skeletal Muscle

Neurogenic changes in denervated skeletal muscle include angulated fibers, increased nuclei, and an absence of necrosis or fibrosis. Reinnervation results in fiber type grouping and target fibers. The reading frame hypothesis explains how in-frame deletions in the dystrophin gene cause Becker muscular dystrophy by producing an abnormally short, but present, dystrophin protein. Routine muscle biopsy has limitations in diagnosing some muscular dystrophies and mitochondrial diseases due to heterogeneity and sampling issues. Dermatomyositis is distinguished from polymyositis by features of a complement-mediated small vessel vasculitis, while inclusion body myositis shows vacuolated fibers, mononuclear inflammation, and intracellular protein
Osteoporosis

The document discusses osteoporosis, which is a disease characterized by low bone mass and fragile bones that break easily. It defines osteoporosis and describes that typical fractures occur in the vertebrae, ribs, hip and wrist. While it has no symptoms, its main consequence is an increased risk of bone fractures. The document outlines exams and tests used to diagnose osteoporosis, as well as lifestyle changes and medications used to treat and prevent the disease.
Disorders Of The Bone By Yapa Wijeratne

Presentation on disorders of the bone which explains the biochemical & physiological aspects with illustrations.
Osteoporosis-pathogenesis, diagnosis, management and prevention

Osteoporosis is a disease characterized by low bone mass and deterioration of bone tissue, leading to fragile bones and increased risk of fractures. It is defined by the World Health Organization as a bone mineral density score of -2.5 or below. Those at highest risk include older adults, especially post-menopausal women, and those with low calcium/vitamin D intake or other risk factors such as smoking. Symptoms include back pain from fractured or collapsed vertebrae. Diagnosis involves bone mineral density tests and other lab tests. Treatment focuses on calcium, vitamin D, bisphosphonates, and lifestyle changes to build strong bones early in life and prevent bone loss later in life.
Cell injury and hypertrophy

This document discusses cell injury, adaptation, and death. It explains that cells can undergo adaptation to physiologic or pathologic stresses to maintain homeostasis. Adaptation allows cells to modify their structure and function to avoid injury. If stresses exceed a cell's adaptive capacity, injury occurs. Adaptations include hypertrophy, where cells increase in size rather than number. Hypertrophy can be physiologic, like uterine enlargement during pregnancy, or pathologic, like cardiac enlargement from hypertension. The document then focuses on hypertrophy in more detail.
Osteoporosis

This document discusses osteoporosis, including its definitions, epidemiology, risk factors, pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, diagnosis, and treatment options. Osteoporosis is a disease characterized by low bone mass and deterioration of bone tissue, leading to fragile bones and increased risk of fractures. It affects millions of people worldwide, especially postmenopausal women, and can be caused by aging, genetics, lifestyle factors, and certain medical conditions or medications. Treatment involves lifestyle modifications like diet, exercise and fall prevention as well as pharmacologic options like calcium, vitamin D, bisphosphonates, and drugs that modify bone metabolism.
Metabolic bone diseases, pathology dept

This document discusses metabolic bone diseases. It begins by describing the basic structure and function of bone, including its cellular components like osteoblasts and osteoclasts. It then discusses the constituents of bone matrix, including collagen, proteoglycans, and minerals. Bone development and homeostasis are explained, involving processes like remodeling. Specific metabolic bone diseases are then outlined in more detail, including osteogenesis imperfecta (brittle bone disease), osteomalacia/rickets due to abnormal mineralization, and hypophosphatasia due to a genetic disturbance in alkaline phosphatase synthesis. Throughout, the document provides microscopic and radiographic characteristics of these conditions.
Osteoporosis

All you need to know about this disease of bones called Osteoporosis.
Subject: Pathophysiology, B.Pharma. Semester 3
paget's disease

Paget's disease is a chronic bone disorder caused by abnormal bone remodeling. The cause is unknown but may involve viruses or genetic predisposition. It is characterized by increased and disorderly bone breakdown followed by rapid bone formation, resulting in abnormal bone structure. Common symptoms include bone pain, fractures, and skeletal deformities. Diagnosis involves blood tests showing elevated alkaline phosphatase levels and imaging tests revealing abnormal bone structure. While there is no cure, treatment focuses on reducing symptoms.
Skeletal muscles disease and disorder

Skeletal muscles disorder is disease and damage the brain or nerves that stimulate muscles and disorders of muscle fibers.
Types of that are :
1- Muscular Atrophy.
2- Muscular Dystrophy.
3- Inflammation of muscle (Myositis).
4- Disorders of Neuromuscular Transmission.
Osteomalacia

This document discusses osteomalacia, a disease characterized by softening of the bones due to defective mineralization. It is caused by vitamin D deficiency and/or phosphate deficiency. Signs include diffuse body pains, muscle weakness, and fragile bones. Laboratory findings show low calcium and phosphate levels as well as elevated alkaline phosphatase and parathyroid hormone levels. Treatment involves vitamin D and calcium supplementation. Exercise and sunlight exposure can also help strengthen bones affected by osteomalacia.
Osteoporosis

This document provides information on osteoporosis from Dr. Ashutosh. It defines osteoporosis as a reduction in bone strength that increases fracture risk. The WHO defines it as a bone density 2.5 standard deviations below young adults of the same sex. Postmenopausal women with bone density between -1 and -2.5 SD also have increased fracture risk. Non-pharmacological prevention includes nutrition, lifestyle modifications, fall prevention, and hip protectors. Pharmacological management includes calcium and vitamin D supplementation, hormonal therapy, antiresorptive drugs, anabolic drugs, and drugs with dual actions.
Muscle disorders

This document discusses various muscle disorders including:
1) Diseases affecting the neuromuscular junction such as myasthenia gravis and Lambert-Eaton syndrome.
2) Effects of denervation of muscle including fibrillation, fasciculation, muscle atrophy, and denervation hypersensitivity.
3) Muscle dystrophies which are degenerative diseases that cause progressive muscle weakness. The most common type is Duchenne muscular dystrophy which is often fatal by age 30.
Osteoporosis my ppt

This document defines osteoporosis and discusses its epidemiology, pathophysiology, risk factors, clinical features, diagnosis and treatment. Osteoporosis is defined as a systemic skeletal disease characterized by low bone density and deterioration of bone tissue, leading to increased bone fragility and fracture risk. It most commonly affects post-menopausal women and the elderly. Diagnosis involves assessing bone mineral density via DEXA scan and evaluating risk factors. Treatment focuses on lifestyle modifications and medications to prevent bone loss and fractures.
Pathology cell injury i

The document discusses cell injury and cell death. It explains that cells have a normal steady state of homeostasis but stress can force cells to adapt or become injured if the stress exceeds their capacity. Cell injury can be reversible or irreversible and leads to cell death if irreversible. Key systems vulnerable to injury are membranes, respiration, protein synthesis and the genetic apparatus. Causes of injury include hypoxia, toxins, infections and more. Reversible injury disrupts mitochondria while irreversible injury causes mitochondrial and lysosomal damage leading to cell death.
Paget’s disease of the bone

Paget's disease is a condition where there is excessive and disorganized bone remodeling, leading to thickened and deformed bones. It was first described in 1877 and typically involves the pelvis, femur, skull and spine. The cause is unknown but genetic and viral factors may play a role. It progresses through lytic, mixed, and sclerotic phases with abnormal osteoclast and osteoblast activity. Complications include fractures, arthritis, and neurological or vascular issues. Diagnosis involves elevated alkaline phosphatase and imaging showing thickened bones. Treatment focuses on suppressing active disease with bisphosphonates or calcitonin to reduce pain, deformity, and complications.
Immunopathology 1

This document summarizes different types of immunity and hypersensitivity reactions. It describes two broad categories of immunity: innate immunity which provides a first line of defense, and adaptive immunity which develops after exposure and recognizes specific antigens. It then discusses four types of hypersensitivity reactions (Type I-IV) mediated by different immune mechanisms in response to various antigens, providing examples of diseases associated with each type.
Metabolic bone disease

metabolic disease from physiotherapy point of view. in detailed description along with imaging and assessment techniques of the same.
Blood Disorders

Common blood disorders include anemia, bleeding disorders such as hemophilia, blood clots, and blood cancers such as leukemia, lymphoma, and myeloma.
Cell injury etiology and pathogenesis

This document discusses etiology and pathogenesis of cell injury. It defines cell injury as changes in a cell's internal and external environment due to various stresses from etiological agents. The cellular response depends on host factors like cell type and extent of injury. Injury can result in reversible or irreversible cell injury depending on factors like agent type/duration and cell adaptability. Common causes of cell injury include hypoxia, ischemia, toxins, microbes, nutrition imbalances, and aging. Ischemia and hypoxia are the most frequent causes of cell injury in humans. Reversible injury involves ATP depletion and membrane changes, while irreversible injury brings further damage including to mitochondria and nuclei, leading to cell death.
What's hot (20)
Osteoporosis-pathogenesis, diagnosis, management and prevention

Osteoporosis-pathogenesis, diagnosis, management and prevention
Viewers also liked
case microscopic polyangiitis

This document summarizes the case of a 56-year-old Thai woman who presented with hemoptysis and renal failure. She has a history of tuberculosis as a child and rheumatoid arthritis. On examination, she had coarse lung crepitations and signs of renal impairment. Tests showed p-ANCA positivity. She was diagnosed with microscopic polyangiitis and treated with plasma exchange, antibiotics, and steroids. Her condition gradually improved with treatment.
medicine.CRF2.(dr.kawa)

Chronic renal failure refers to the irreversible deterioration of renal function over years. It initially presents as biochemical abnormalities and eventually leads to uraemic symptoms as the excretory, metabolic and endocrine functions of the kidneys fail. Common causes include diabetes, hypertension, and glomerulonephritis. Management involves identifying and treating the underlying disease, slowing progression, managing complications, and renal replacement therapy for end-stage disease.
Imaging findings of metabolic bone diseases 

This document discusses various metabolic bone diseases including osteoporosis, rickets, osteomalacia, and others. It provides details on:
- The definition and causes of osteoporosis as well as how it leads to loss of horizontal trabecular bone.
- The differences between rickets, which affects growth plates, and osteomalacia, which affects mineralization of bone. Causes include vitamin D deficiency and other disorders.
- Features of various other metabolic bone diseases like hypophosphatasia, hyperparathyroidism, and their effects on bone structure and mineralization.
Bone Care Basics (CRF)

The document provides an outline and overview of kidney function, hormone production, secondary hyperparathyroidism (SHPT), and treatment with vitamin D in chronic kidney disease patients. It discusses how kidney failure leads to SHPT through vitamin D deficiency and other factors. SHPT can cause bone disease and other complications. Treatment focuses on vitamin D supplementation to control PTH levels and symptoms of SHPT.
metabolic bone diseases

This document discusses several metabolic bone diseases including hyperparathyroidism, Paget's disease, and rickets. It provides details on:
- The processes of bone remodeling and how disorders can disrupt mineralization or formation/resorption, leading to conditions like rickets.
- Hyperparathyroidism, which can be primary due to parathyroid adenomas, secondary due to hypocalcemia, or tertiary if secondary is longstanding. This causes high calcium and affects bones, kidneys, and other organs.
- Paget's disease, which involves abnormal bone remodeling from viral infection, leading to deformity, fractures, and other complications. It typically involves the pelvis, spine,
Metabolic bone disease

This document discusses metabolic bone diseases, including their composition, calcium and phosphate metabolism, and specific diseases. It provides details on osteoporosis, rickets/osteomalacia, Paget's disease, and renal osteodystrophy. The composition of bone includes collagen, proteoglycans, and hydroxyapatite. Calcium and vitamin D intake recommendations are outlined for different populations. PTH, calcitonin, vitamin D, and alkaline phosphatase roles in calcium regulation are summarized. Osteoporosis risk factors and management strategies are highlighted.
Disorders of parathyroid gland

This presentation is about Parathyroid Disorders which are hypo and hyperparathyroidism and their relationship to teeth and oral cavity including oral and dental manifestation of these disorders , and correct management patients seeking dental care with these disorders.
Hyperparathyroidism Presentation

The document discusses primary hyperparathyroidism, which is caused by elevated levels of parathyroid hormone due to a parathyroid adenoma. It causes high blood calcium levels, excessive calcium in the urine, and thinning of the bones. Diagnosis involves testing serum calcium and PTH levels, as well as parathyroid scans and ultrasounds. Treatment is removal of the parathyroid adenoma through a mini-incision parathyroidectomy guided by preoperative localization tests to reduce risks and improve outcomes. Aberrant adenoma locations and multiple adenomas can complicate the surgery.
Lab investig

This document provides information about various components that may be analyzed in urinalysis, urine sediment, and other body fluids and samples. It discusses normal ranges and clinical significance of findings for numerous tests, including urinalysis dipstick components, microscopic examination of urine sediment, cerebrospinal fluid analysis, culture of various clinical samples, and numerous serological tests. The document is intended as a reference for clinicians on interpreting results from these diagnostic tests.
Orthopedic Aspects Of Metabolic Bone Disease By Xiu

This document summarizes various metabolic bone diseases and their orthopedic manifestations and radiographic findings. It covers osteoporosis, rickets and osteomalacia, hyperparathyroidism, hypoparathyroidism, hyperthyroidism, and renal osteodystrophy. For each condition, it describes clinical presentation, pathogenesis, characteristic radiographic findings including areas of bone involvement and patterns of bone changes, and differential diagnoses.
Chronic renal failure 

This document discusses chronic kidney disease (CKD) in children, including definitions, stages, etiology, pathogenesis, clinical manifestations, complications, treatment, and strategies to slow progression. Key points include:
- CKD is defined as kidney damage or glomerular filtration rate <60 mL/min/1.73m2 for over 3 months.
- Etiology depends on age, and includes congenital abnormalities, glomerulonephritis, cystic kidney diseases.
- Pathogenesis involves hyperfiltration injury to surviving nephrons from loss of other nephrons.
- Treatment aims to replace renal function and slow progression, including fluid/electrolyte management, nutrition, growth supplements
Viewers also liked (11)
Orthopedic Aspects Of Metabolic Bone Disease By Xiu

Orthopedic Aspects Of Metabolic Bone Disease By Xiu
Similar to Bone disorders
Osteoporosis

osteoporosis i will talk about : definition &epidemiology& risk factor&psychopathology &classification & diagnosis&treatment &complication & prevention.
Osteoporosis

Osteoporosis is a condition characterized by low bone mass and quality, leading to an increased risk of bone fractures. It is most common in postmenopausal women over age 50 and men over age 80. Risk factors include female gender, advancing age, family history, hypogonadism, glucocorticoid use, low body mass index, smoking, and nutritional deficiencies. Diagnosis is made through bone density scans and confirmed by fragility fractures. Treatment focuses on lifestyle modifications, calcium and vitamin D supplementation, bisphosphonates, estrogen therapy, selective estrogen receptor modulators, parathyroid hormone, calcitonin, and surgery for fractures. Monitoring involves repeat bone density scans and biochemical markers to assess response to
Osteoporosis

This presentation includes four major topics:
1- reviews the essentials of osteoporosis including definition, pathophysiology, etiology, epidemiology, and prognosis
2- talks about the presentation of osteoporosis, including risk factors, symptoms and signs, radiologic manifestations, and complications
3- reviews the workup process to diagnose and define the severity of osteoporosis, including the lab. and radiologic procedures
4- reviews management tools of osteoporosis, including pharmacologic and non pharmacologic methods, with brief description for each pharmacologic or non pharmacologic tool.
Finally, some statements about the education and prevention of osteoporosis.
Manasil MBD.pptx

Osteoporosis is a systemic skeletal disease characterized by low bone mass and microarchitectural deterioration of bone tissue, leading to increased bone fragility and a consequent increase in fracture risk. It is a major public health threat. Key factors in the development of osteoporosis include peak bone mass attainment, bone loss, and bone quality. Dual energy X-ray absorptiometry is the gold standard test used to diagnose osteoporosis. Lifestyle modifications and pharmacological therapies including bisphosphonates, parathyroid hormone, and monoclonal antibodies are used for fracture prevention and treatment.
Chronic kidney disease associated mineral bone disorders

This document discusses chronic kidney disease-mineral and bone disorder (CKD-MBD), which represents a systemic disorder of mineral and bone metabolism that occurs as a complication of chronic kidney disease. As kidney function declines in CKD, there are progressive changes in the serum concentrations of calcium, phosphorus, vitamins D and PTH that lead to abnormalities in bone turnover, mineralization, and structure as well as soft tissue calcification. The document outlines the pathogenesis of CKD-MBD and its skeletal complications including renal osteodystrophy, and discusses treatment goals and management strategies to address abnormal mineral metabolism and bone disease in CKD.
osteoporosis

Osteoporosis is a disease where bones become fragile and more likely to break. It occurs when the body loses more bone than it forms, reducing bone density and bone mass. Key risk factors include a family history of osteoporosis, being Caucasian or Asian, smoking, excessive alcohol use, and low body weight. Diagnosis relies on bone mineral density tests to determine a T-score. Treatment focuses on lifestyle changes like exercise and nutrition, as well as medications to reduce bone loss and increase bone formation.
Metabolic and genetic disorders of bone

This document provides an overview of metabolic and genetic disorders of bone. It begins with introducing bone anatomy, histology, and physiology. It then discusses bone metabolism and the role of bones in general metabolism. The document classifies bone disorders and discusses several metabolic bone diseases in depth, including osteoporosis, rickets, osteomalacia, and hyperparathyroidism. For each, it covers etiology, clinical features, oral manifestations, histopathology, and treatment. The document thus provides a comprehensive review of key metabolic and genetic bone disorders.
Osteoporosis in Elderly People.pptx

Osteoporosis is a chronic, progressive skeletal disease characterized by low bone mass, microarchitecture deterioration of bone tissue, bone fragility, and a consequent increase in fracture risk.
Osteoporesis and Gout _RDP

Osteoporosis is a disease characterized by reduced bone density and strength, increasing the risk of fractures. It results from an imbalance between bone resorption and formation, with resorption exceeding formation. This can be due to age-related changes that reduce osteoblast function and bone quality over time, as well as other factors like reduced physical activity, nutritional deficiencies, genetics, and hormonal changes in women after menopause. Symptoms include fractures of the vertebrae, hips, and wrists. Treatment focuses on lifestyle changes and medications to reduce bone resorption and promote formation.
Calcium homeostasis

Control of calcium homeostasis involves parathyroid hormone, vitamin D, PTHrP, and calcitonin. Vitamin D is produced in skin and converted to its active form in liver and kidneys to regulate calcium absorption and bone mineralization. Disorders like rickets and osteomalacia can result from vitamin D deficiency. Primary hyperparathyroidism is a common cause of hypercalcemia where an overactive parathyroid gland increases bone resorption and renal calcium reabsorption. Hypocalcemia can occur in chronic kidney disease or hypoparathyroidism and cause neuromuscular symptoms. Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1 involves tumors of the parathyroid glands, pancreas
Osteoporosis

Osteoporosis is a disease characterized by low bone mass and structural defects that cause bone fragility and increased fracture risk. It is defined by the WHO as a bone density 2.5 standard deviations below the mean for young adults of the same sex. Bone is composed of a collagen matrix, mineral salts like calcium and phosphate, and bone cells including osteoblasts, osteocytes, and osteoclasts that are involved in bone formation and resorption. Diagnosis involves x-rays, bone mineral density tests, and laboratory tests of calcium, vitamin D, and biochemical markers of bone turnover. Treatment focuses on reducing risk factors, adequate nutrition, exercise, and pharmacologic therapies like bisphosphonates, SERMs,
OSTEOPOROSIS

Osteoporosis is a disease characterized by low bone mass and deterioration of bone structure. It increases the risk of fractures. The World Health Organization defines osteoporosis as a bone density 2.5 standard deviations or more below the mean bone density of healthy young adults. Dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DXA) is the gold standard test used to diagnose osteoporosis by measuring bone mineral density at sites like the hip and spine. Lifestyle factors like diet, exercise, smoking and alcohol as well as certain medical conditions and medications can impact bone health and increase the risk of osteoporosis.
Osteroporosis - clinical features and management

Osteoporosis is defined as low bone mass and deterioration of bone tissue, leading to increased bone fragility and fracture risk. It is diagnosed based on bone mineral density measurements. Risk factors include older age, female sex, family history, smoking, excessive alcohol, low body weight, and medications like glucocorticoids. The disease results from an imbalance between bone resorption by osteoclasts and bone formation by osteoblasts. Treatment involves lifestyle modifications like calcium, vitamin D, and exercise as well as pharmacologic therapies such as bisphosphonates, SERMs, calcitonin, PTH, and strontium which reduce resorption or stimulate formation to increase bone mineral density and reduce fractures.
osteoporosis.pdf

Osteoporosis
BY: Nader Amer al-assadi
Taiz university
1- Definition
2- Epidemiology
3- Risk factor
4-Pathophysiology
5-Classification
6- Osteoporosis Clinical Presentation.
7-Diagnosis
8-Treatment
9-Comblication
10-Prevention
what is Osteoporosis?
is a chronic, progressive disease of multifactorial etiology and it is the most common bone Metabolic disease in humans.
Characterized by:
Low bone mass
Microarchitectural deterioration
Compromised bone strength
Increased risk for fracture
normal minarlization
“Silent disease” until complicated by fractures.
incidence
Globally, osteoporosis is by far the most common metabolic bone disease, estimated to affect over 200 million people worldwide.
1.5 million osteoporotic fractures occur each year:
700,000 are vertebral fractures
300,000 are hip fractures
200,000 are wrist fracture
demographics
-The risk for osteoporosis increases with age as BMD declines. Senile osteoporosis is most common in persons aged 70 years or older.
-Secondary osteoporosis, however, can occur in persons of any age.
-male: female ratio is 1:4 postmenopausal woman
-Men have a higher prevalence of secondary osteoporosis, with an estimated 45-60% of cases being a consequence of hypogonadism, alcoholism, or glucocorticoid excess.
-Osteoporosis can occur in persons of all races and ethnicities. In general, however, whites (especially of northern European descent) and Asians are at increased risk .
The National Osteoporosis Foundation (NOF) has
categorized the risk factors into two categories: nonmodifiable and modifiable:
Nonmodifiable risk factors include the following:
- Personal history of fracture as an adult
- History of fracture in a first-degree relative
- White race
- Advanced age?
- Female sex
- Poor health or fragility
Medicine 5th year, 3rd lecture (Dr. Asso Fariadoon Ali Amin)

The document provides information on various bone diseases including osteoporosis, osteomalacia, osteoarthritis, Paget's disease, and hypercalcemia. It discusses the causes, clinical features, investigations, and treatment options for each condition. Risk factors for osteoporosis include age, gender, family history, smoking, alcohol, diet, medication use, and other medical conditions. DEXA scans are used to diagnose osteoporosis based on bone mineral density T-scores. Lifestyle changes, calcium/vitamin D supplements, and medications like bisphosphonates are used to treat osteoporosis.
MEtabolism+Ortho

The document provides an overview of normal bone structure and metabolism as well as common disorders of bone. It describes the typical composition of bone and how bone remodels over time. Key hormones involved in regulating calcium and phosphate levels like PTH, calcitonin, and vitamin D are discussed. Common disorders addressed include osteoporosis, osteomalacia, hyperparathyroidism, and Paget's disease. Presentation, investigations, and treatment are summarized for each condition.
Bone & Muscle disease biomarkers.ppt

The starting template material is RNA not DNA ( as in PCR assays for the diagnosis of viral infections)
RNA cannot serve as a template for PCR, (RNA is not a substrate for the Taq DNA polymerases commonly utilised in PCR.) Therefore reverse transcription is combined with PCR to convert RNA into a complementary DNA (cDNA)) suitable for PCR
The first step in this procedure is to convert the RNA molecules into single-stranded complementary DNA (cDNA) (Figure 9.20). Once this preliminary step has been carried out, the PCR primers and Taq polymerase are added and the experiment proceeds exactly as in the standard technique
1933864184

This document discusses osteoporosis and provides information about its characteristics, risk factors, epidemiology, and classification. Some key points:
- Osteoporosis is a disease characterized by low bone mass and deterioration of bone structure, leading to an increased risk of fractures. It is caused by an imbalance between bone formation and resorption.
- Risk factors include being Caucasian or Asian, female sex, advanced age, family history, smoking, excess alcohol, low body weight, and loss of sex hormones.
- It affects many older adults, especially women past menopause. Hip fractures from osteoporosis can significantly increase mortality and disability.
- Osteoporosis is
Basic science of bone

This document provides an overview of basic bone science, including:
1. The histologic features and types of bone tissue.
2. The cellular biology of osteoblasts, osteocytes, and osteoclasts involved in bone formation and resorption.
3. The organic and inorganic components of the bone matrix.
4. The processes of bone remodeling, circulation, injury and repair.
5. Conditions affecting bone mineralization, mineral density, and viability such as osteoporosis, rickets, and fractures.
Osteoporosis

This document discusses the pathophysiology, epidemiology, presentation, diagnosis, and treatment of osteoporosis. It notes that bone undergoes constant remodeling by osteoblasts and osteoclasts. Estrogen deficiency accelerates bone loss via increased osteoclast activity. Risk factors include female gender, older age, family history, smoking, low calcium intake, and certain medications. Vertebral fractures often cause back pain and kyphosis. Treatment involves lifestyle modifications, calcium/vitamin D supplementation, and pharmacotherapy like bisphosphonates, denosumab, teriparatide, calcitonin, and SERMs. Medication choice depends on factors like fracture risk, side effect profile, and cost.
Similar to Bone disorders (20)
Chronic kidney disease associated mineral bone disorders

Chronic kidney disease associated mineral bone disorders
Medicine 5th year, 3rd lecture (Dr. Asso Fariadoon Ali Amin)

Medicine 5th year, 3rd lecture (Dr. Asso Fariadoon Ali Amin)
Recently uploaded
Does Over-Masturbation Contribute to Chronic Prostatitis.pptx

In some case, your chronic prostatitis may be related to over-masturbation. Generally, natural medicine Diuretic and Anti-inflammatory Pill can help mee get a cure.
Top Effective Soaps for Fungal Skin Infections in India

Swisschem Dermacare has mentioned the List of The Best Antifungal Soap In India 2022. All of these soaps are trusted by various Dermatology Experts.
Part II - Body Grief: Losing parts of ourselves and our identity before, duri...

Learn about body grief and ways to cope with it. We will also explore methods to heal from this challenging experience.
ABDOMINAL TRAUMA in pediatrics part one.

Abdominal trauma in pediatrics refers to injuries or damage to the abdominal organs in children. It can occur due to various causes such as falls, motor vehicle accidents, sports-related injuries, and physical abuse. Children are more vulnerable to abdominal trauma due to their unique anatomical and physiological characteristics. Signs and symptoms include abdominal pain, tenderness, distension, vomiting, and signs of shock. Diagnosis involves physical examination, imaging studies, and laboratory tests. Management depends on the severity and may involve conservative treatment or surgical intervention. Prevention is crucial in reducing the incidence of abdominal trauma in children.
#cALL# #gIRLS# In Dehradun ꧁❤8107221448❤꧂#cALL# #gIRLS# Service In Dehradun W...

#cALL# #gIRLS# In Dehradun ꧁❤8107221448❤꧂#cALL# #gIRLS# Service In Dehradun W...chandankumarsmartiso
#cALL# #gIRLS# In Dehradun ꧁❤8107221448❤꧂#cALL# #gIRLS# Service In Dehradun Women Seeking Service
Basavarajeeyam - Ayurvedic heritage book of Andhra pradesh

Basavarajeeyam is an important text for ayurvedic physician belonging to andhra pradehs. It is a popular compendium in various parts of our country as well as in andhra pradesh. The content of the text was presented in sanskrit and telugu language (Bilingual). One of the most famous book in ayurvedic pharmaceutics and therapeutics. This book contains 25 chapters called as prakaranas. Many rasaoushadis were explained, pioneer of dhatu druti, nadi pareeksha, mutra pareeksha etc. Belongs to the period of 15-16 century. New diseases like upadamsha, phiranga rogas are explained.
Osteoporosis - Definition , Evaluation and Management .pdf

Osteoporosis is an increasing cause of morbidity among the elderly.
In this document , a brief outline of osteoporosis is given , including the risk factors of osteoporosis fractures , the indications for testing bone mineral density and the management of osteoporosis
The Electrocardiogram - Physiologic Principles

These lecture slides, by Dr Sidra Arshad, offer a quick overview of the physiological basis of a normal electrocardiogram.
Learning objectives:
1. Define an electrocardiogram (ECG) and electrocardiography
2. Describe how dipoles generated by the heart produce the waveforms of the ECG
3. Describe the components of a normal electrocardiogram of a typical bipolar lead (limb II)
4. Differentiate between intervals and segments
5. Enlist some common indications for obtaining an ECG
6. Describe the flow of current around the heart during the cardiac cycle
7. Discuss the placement and polarity of the leads of electrocardiograph
8. Describe the normal electrocardiograms recorded from the limb leads and explain the physiological basis of the different records that are obtained
9. Define mean electrical vector (axis) of the heart and give the normal range
10. Define the mean QRS vector
11. Describe the axes of leads (hexagonal reference system)
12. Comprehend the vectorial analysis of the normal ECG
13. Determine the mean electrical axis of the ventricular QRS and appreciate the mean axis deviation
14. Explain the concepts of current of injury, J point, and their significance
Study Resources:
1. Chapter 11, Guyton and Hall Textbook of Medical Physiology, 14th edition
2. Chapter 9, Human Physiology - From Cells to Systems, Lauralee Sherwood, 9th edition
3. Chapter 29, Ganong’s Review of Medical Physiology, 26th edition
4. Electrocardiogram, StatPearls - https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK549803/
5. ECG in Medical Practice by ABM Abdullah, 4th edition
6. Chapter 3, Cardiology Explained, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK2214/
7. ECG Basics, http://www.nataliescasebook.com/tag/e-c-g-basics
Identification and nursing management of congenital malformations .pptx

Identification and nursing management of congenital malformations .pptxMGM SCHOOL/COLLEGE OF NURSING
Identification and nursing management of congenital malformations Dehradun #ℂall #gIRLS Oyo Hotel 8107221448 #ℂall #gIRL in Dehradun

Dehradun #ℂall #gIRLS Oyo Hotel 8107221448 #ℂall #gIRL in Dehradun
Histololgy of Female Reproductive System.pptx

Dive into an in-depth exploration of the histological structure of female reproductive system with this comprehensive lecture. Presented by Dr. Ayesha Irfan, Assistant Professor of Anatomy, this presentation covers the Gross anatomy and functional histology of the female reproductive organs. Ideal for students, educators, and anyone interested in medical science, this lecture provides clear explanations, detailed diagrams, and valuable insights into female reproductive system. Enhance your knowledge and understanding of this essential aspect of human biology.
Integrating Ayurveda into Parkinson’s Management: A Holistic Approach

Explore the benefits of combining Ayurveda with conventional Parkinson's treatments. Learn how a holistic approach can manage symptoms, enhance well-being, and balance body energies. Discover the steps to safely integrate Ayurvedic practices into your Parkinson’s care plan, including expert guidance on diet, herbal remedies, and lifestyle modifications.
share - Lions, tigers, AI and health misinformation, oh my!.pptx

• Pitfalls and pivots needed to use AI effectively in public health
• Evidence-based strategies to address health misinformation effectively
• Building trust with communities online and offline
• Equipping health professionals to address questions, concerns and health misinformation
• Assessing risk and mitigating harm from adverse health narratives in communities, health workforce and health system
Recently uploaded (20)
Does Over-Masturbation Contribute to Chronic Prostatitis.pptx

Does Over-Masturbation Contribute to Chronic Prostatitis.pptx
Top Effective Soaps for Fungal Skin Infections in India

Top Effective Soaps for Fungal Skin Infections in India
Thyroid Gland- Gross Anatomy by Dr. Rabia Inam Gandapore.pptx

Thyroid Gland- Gross Anatomy by Dr. Rabia Inam Gandapore.pptx
Part II - Body Grief: Losing parts of ourselves and our identity before, duri...

Part II - Body Grief: Losing parts of ourselves and our identity before, duri...
#cALL# #gIRLS# In Dehradun ꧁❤8107221448❤꧂#cALL# #gIRLS# Service In Dehradun W...

#cALL# #gIRLS# In Dehradun ꧁❤8107221448❤꧂#cALL# #gIRLS# Service In Dehradun W...
Basavarajeeyam - Ayurvedic heritage book of Andhra pradesh

Basavarajeeyam - Ayurvedic heritage book of Andhra pradesh
Muscles of Mastication by Dr. Rabia Inam Gandapore.pptx

Muscles of Mastication by Dr. Rabia Inam Gandapore.pptx
Osteoporosis - Definition , Evaluation and Management .pdf

Osteoporosis - Definition , Evaluation and Management .pdf
Identification and nursing management of congenital malformations .pptx

Identification and nursing management of congenital malformations .pptx
Dehradun #ℂall #gIRLS Oyo Hotel 8107221448 #ℂall #gIRL in Dehradun

Dehradun #ℂall #gIRLS Oyo Hotel 8107221448 #ℂall #gIRL in Dehradun
Integrating Ayurveda into Parkinson’s Management: A Holistic Approach

Integrating Ayurveda into Parkinson’s Management: A Holistic Approach
CHEMOTHERAPY_RDP_CHAPTER 6_Anti Malarial Drugs.pdf

CHEMOTHERAPY_RDP_CHAPTER 6_Anti Malarial Drugs.pdf
share - Lions, tigers, AI and health misinformation, oh my!.pptx

share - Lions, tigers, AI and health misinformation, oh my!.pptx
Bone disorders
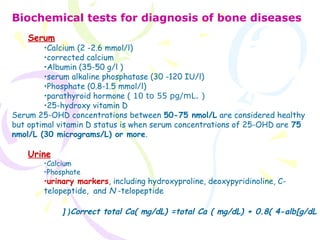
- 1. Biochemical tests for diagnosis of bone diseases Serum •Calcium (2 -2.6 mmol/l) •corrected calcium •Albumin (35-50 g/l ) •serum alkaline phosphatase (30 -120 IU/l) •Phosphate (0.8-1.5 mmol/l) •parathyroid hormone ( 10 to 55 pg/mL. ) •25-hydroxy vitamin D Serum 25-OHD concentrations between 50-75 nmol/L are considered healthy but optimal vitamin D status is when serum concentrations of 25-OHD are 75 nmol/L (30 micrograms/L) or more. Urine •Calcium •Phosphate •urinary markers, including hydroxyproline, deoxypyridinoline, C- telopeptide, and N -telopeptide Correct total Ca( mg/dL) =total Ca ( mg/dL) + 0.8( 4-alb[g/dL[ (
- 4. Arthritis is not a single disease; it is an informal way of referring to joint pain or joint disease. There are more than 100 different types of arthritis and related conditions. TYPES OF ARTHRITISTYPES OF ARTHRITIS • Degenerative Arthritis (Osteoarthritis) • Inflammatory Arthritis (rheumatoid ) • Infectious (Septic) Arthritis • Metabolic (Gouty) Arthritis symptoms Common arthritis joint symptoms include swelling, pain, stiffness and decreased range of motion. Symptoms may be mild, moderate or severe
- 6. Osteoporosis is a bone disease that occurs when the body loses too much bone, makes too little bone, or both. Osteoporosis means “porous bone”. Osteoporotic bones have lost density or mass and contain abnormal tissue structure. As bones become less dense, they weaken and are more likely to break
- 7. Postmenopausal osteoporosis occurs in 5% to 20% of women, with a peak incidence in the 60s.The incidence in women is eight times higher than that in men. Estrogen deficiency is thought to underlie this form of osteoporosis, rendering the skeleton more sensitive to parathyroid hormone (PTH), resulting in increased calcium resorption from bone. This in turn decreases PTH secretion, 1,25- dihydroxyvitamin D production, and calcium absorption and ultimately causes loss of trabecular bone, leading to vertebral crush fractures and Colles' fractures. Senile osteoporosis occurs in women or men more than 70 years of age and usually is associated with decreased bone formation along with decreased ability of the kidney to produce 1,25(OH)2D3. The vitamin D deficiency results in decreased calcium absorption, which increases the PTH level and therefore bone resorption. In type 2 osteoporosis, cortical and trabecular bone is lost, primarily leading to increased risk of hip, long bone, and vertebral fractures.
- 8. Treatment of symptomatic osteoporosis has had limited success. Prevention is preferable to treatment, since no therapy fully restores lost bone mass. •PHARMACOLOGIC TREATMENT:PHARMACOLOGIC TREATMENT: •Hormonal Replacement Therapy (HRT) such as Estrogen •Non-hormonal Replacement Therapy (NHRT) such as biphosphonates (alendronate), calcitonin, selective estrogen-receptor modulators (raloxifene), and fluoride •Others ( testosterone, human parathyroid hormone & analougs(Teriparatide), and growth hormone) (NON-PHARMACOLOGIC(NON-PHARMACOLOGIC PREVENTION)PREVENTION) • The combination of calcium (1.2 g/day) with vitamin D3 (800 IU/day) • Exercise regularly • Prevent falls • Avoid smoking & excessive alcohol • Maintain an appropriate body weight
- 9. This type of osteoporosis is associated with a variety of conditions, including: Hormonal imbalances (eg, cushing's syndrome); Cancer (notably multiple myeloma); Gastrointestinal disorders (especially IBD causing malabsorption); Drug use (eg, corticosteroids, cancer chemotherapy, anticonvulsants, heparin, barbiturates, valporic acid, gonadotropin-releasing hormone excessive use of aluminum- containing antacids); Pathological conditions: chronic renal failure; hyperthyroidism; hypogonadism in men; immobilization,rheumatoid arthritis); and Poor nutrition (including malnutrition due to eating disorders).
- 10. Osteomalacia is a disorder marked by inadequate or defective mineralization of the skeleton, resulting in soft or fragile bones. When the disease occurs in children before the growth plates have closed, it is known as rickets and tends to produce obvious skeletal deformities. It typically occurs either when there are insufficient amounts of vitamin D in the diet or, when the body is unable to properly absorb and metabolize vitamin D, which is essential for the absorption of the calcium needed to maintain strong, healthy bones. It can also occur with calcium and phosphorus deficiency plus other genetics disorders Vitamin D deficiency is most often caused •insufficient exposure to sunlight and nutritional deficiency •Gastrointestinal malabsorption •Liver and kidney disease * drugs
- 11. Hypocalcaemic seizures or tetany, particularly in the neonatal period. From the age of 6 months, children often present with bony deformities of the chest, pelvis and skull, delayed dentition, and bone pain. Children may be irritable and manifest impaired growth of all body organs. Increased susceptibility to infections and respiratory symptoms. Severe vitamin D deficiency can result in cardiomyopathy and potentially fatal heart failure. Widespread bone pain and tenderness (especially low back pain and in the hips), proximal muscle weakness & lethargy are the main features of vitamin D deficiency in adults. Skeletal deformity The patient may experience signs of hypocalcaemia & multiple fractures which are bilateral and symmetrical Low bone density on dual-energy X-ray rickets osteomalacia
- 12. • BIOCHEMICAL FINDINGS Blood biochemistry: renal function, electrolytes (including serum calcium and phosphate), LFTs, parathyroid hormone level: More than 80% of adults with osteomalacia have a high concentration of serum alkaline phosphatase. Hypocalcaemia (NV:9-11mg/dl), hypomagnesaemia and hypophosphataemia (NV: 5-7mg/dl) may be present, depending on the severity and chronicity of the disease and the patient's dietary calcium intake. Secondary hyperparathyroidism is typical in hypocalcemic rickets. Full Blood Count: Anaemia suggests possible malabsorption. Urine microscopy to help determine whether the patient has underlying chronic kidney disease. Vitamin D status is most reliably determined by assay of serum 25- hydroxyvitamin D (25-OHD): Vitamin D deficiency: individuals with symptomatic osteomalacia or rickets have serum 25-OHD of less than 25 nmol/L (10 micrograms/L)
- 13. TREATMENT General management Education: dietary advice (refer to a dietician). Encourage exposure to sunlight. Vitamin D supplementation. Calcium supplementation. Treatment of any underlying condition. Treatment of pain. Orthopaedic intervention may be required. Children Oral calciferol in the form of either ergocalciferol or colecalciferol is the treatment of choice for children with rickets (6000 IU( Calcium supplementation is advisable during the first weeks of therapy. Adult Calciferol in a daily dose of 10000 IU
- 14. CAUSES The cause of Paget disease is unknown. Both genetic and environmental factors have been implicated. SYMPTOMS •Most people who have Paget's disease of bone have no symptoms. When symptoms occur, the most common complaint is • bone pain. •Joint pain Nerve problems:
- 15. • PATHOGENESIS Three phases of Paget disease have been described: lytic, mixed lytic&blastic, and sclerotic. Paget disease begins with the lytic phase, in which normal bone is resorbed by osteoclasts that are more numerous and larger than normal osteoclasts. Bone turnover rates increase to as much as 20 times normal. The second phase, the mixed phase, is characterized by rapid increases in bone formation from numerous osteoblasts. Although increased in number, the osteoblasts remain morphologically normal. The newly made bone is abnormal, however, with collagen fibers deposited in a haphazard fashion rather than linearly, as with normal bone formation. In the final phase of Paget disease, the sclerotic phase, bone formation dominates and the bone that is formed has a disorganized pattern (woven bone) and is weaker than normal adult bone. This woven bone pattern allows the bone marrow to be infiltrated by excessive fibrous connective tissue and blood vessels, leading to a hypervascular bone state.
- 16. • BIOCHEMICAL DIAGNOSIS Measurement of serum alkaline phosphatase—in some cases, bone- specific alkaline phosphatase (BSAP)—can be useful in the diagnosis of Paget disease. Elevated levels of urinary markers, including hydroxyproline, deoxypyridinoline, C-telopeptide, and N -telopeptide, may help identify patients with Paget disease. Procollagen I N -terminal peptide (PINP) has emerged as a sensitive serum marker for bone formation. Hypercalcemia or hypercalciuria may develop with immobilization or coincident primary hyperparathyroidism. Hyperuricemia from Paget disease is more common in men than women and appears to be caused by the increased turnover of nucleic acids from high bone turnover. Serum total acid phosphatase is an osteoclastic enzyme that may be elevated in active Paget disease.