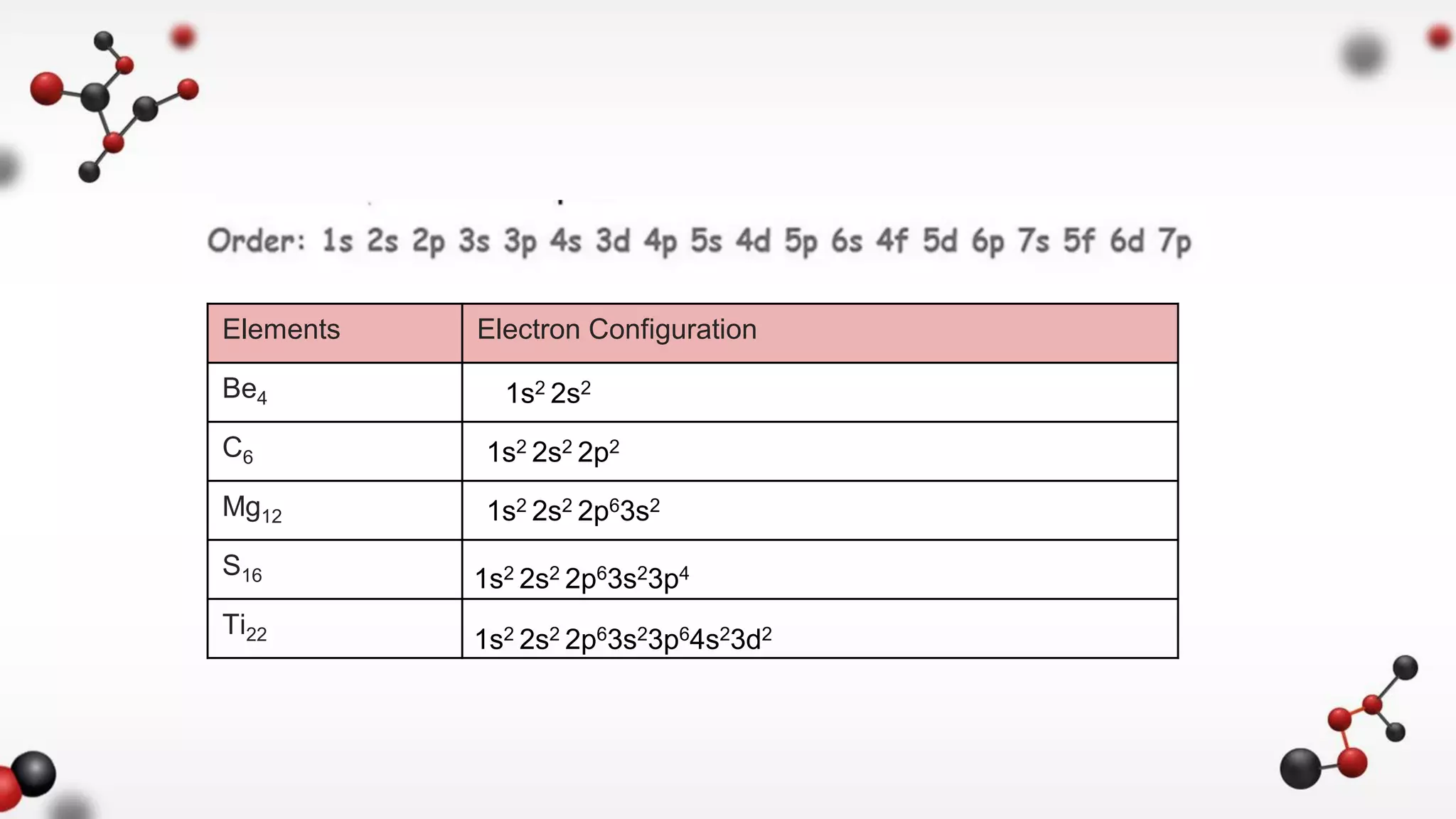
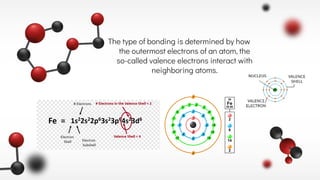
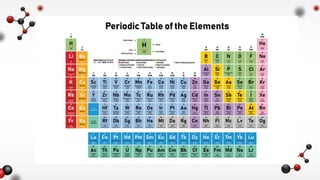
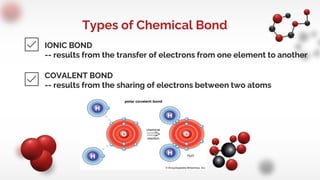
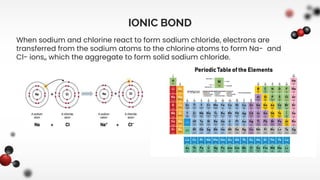
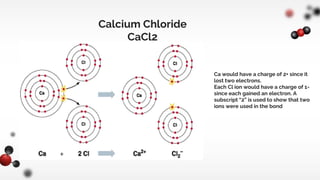
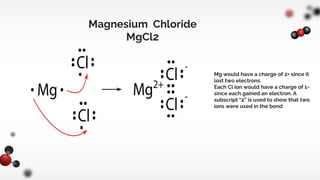
The document discusses different types of chemical bonds including ionic and covalent bonds. Ionic bonds form between metals and nonmetals through the transfer of electrons from the metal to the nonmetal. Covalent bonds form between nonmetals through the sharing of electrons between atoms. The document provides examples of ionic compounds calcium chloride (CaCl2) and magnesium chloride (MgCl2) to illustrate how ions are formed when electrons are transferred between the atoms.