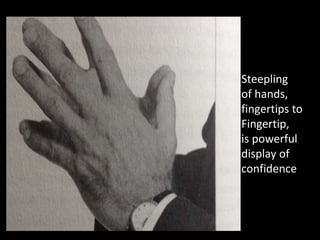
The document discusses nonverbal communication, highlighting its significance as it makes up 60-65% of interpersonal interactions and often reveals true thoughts and feelings. It outlines several body language signals, providing insights into interpreting physical cues and gestures that indicate comfort, discomfort, confidence, or insecurity. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of context and the ability to recognize and decode various nonverbal behaviors in social settings.






![The “turtle effect” [shoulder rise towards ears] is
often seen when people are humbled or suddenly
loose confidence](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bodylanguage-160115063218/85/Body-language-7-320.jpg)