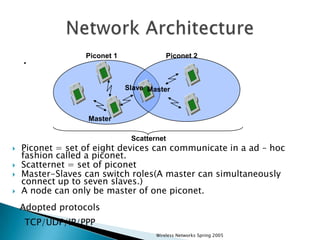
This document discusses Bluetooth technology. It provides a brief history, noting it was invented in 1994 and developed by an SIG comprising over 1000 companies. The document outlines the various Bluetooth specifications from versions 1.0 to 4.0. It describes how Bluetooth works using a piconet architecture with a master-slave structure. The document also lists some key advantages like wireless connectivity and ease of setup, and disadvantages such as short range and security issues. Finally, it discusses application areas and the future potential of Bluetooth.