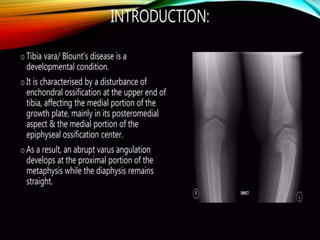
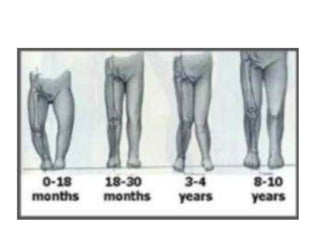
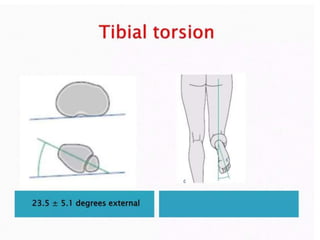
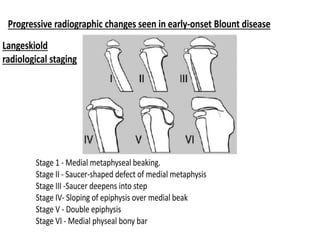
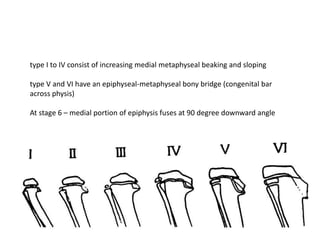
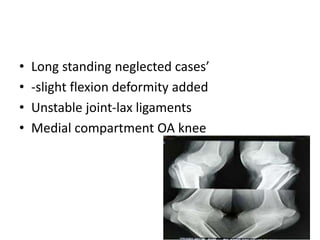
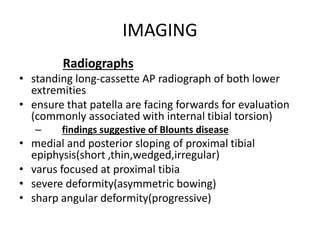
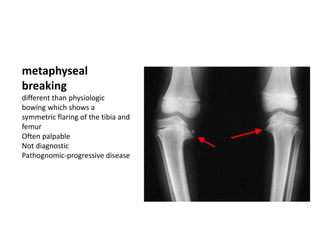
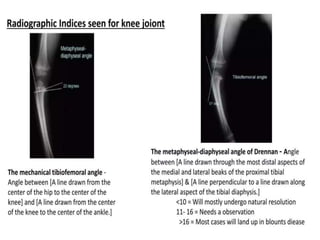
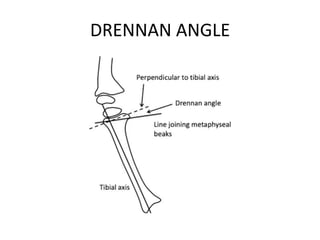
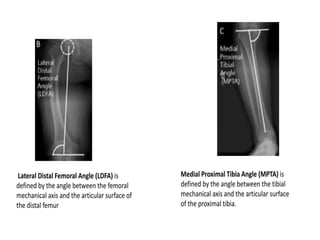
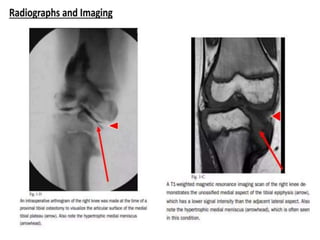
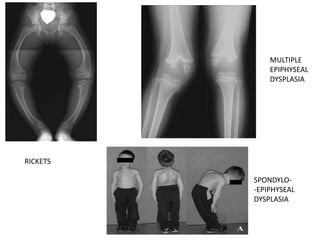
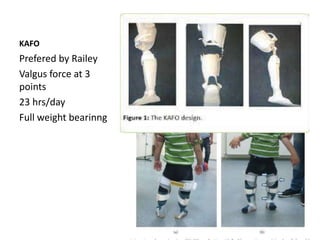
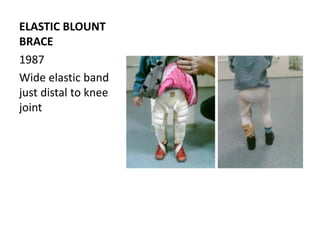
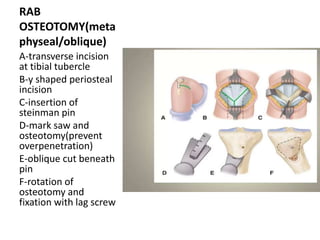
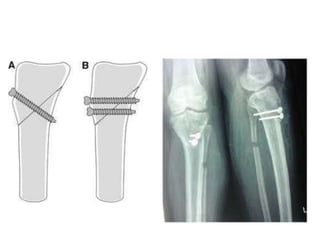
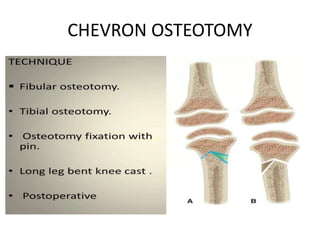
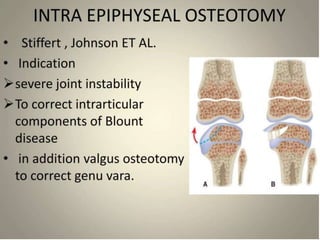
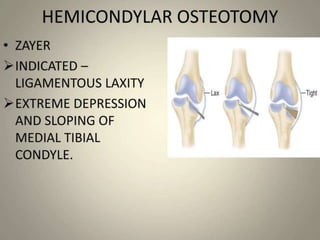
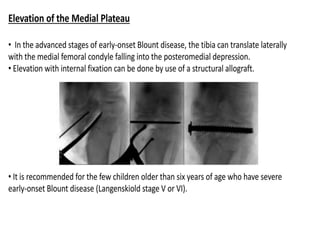
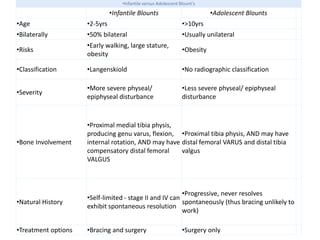
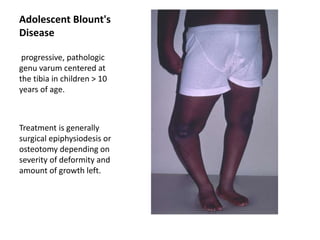
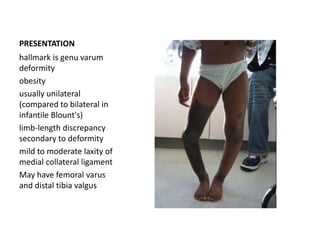
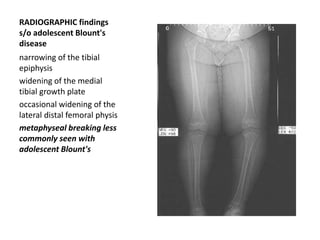
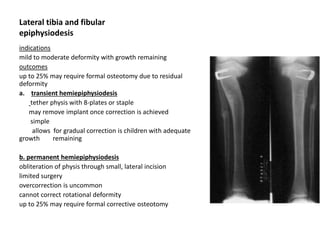
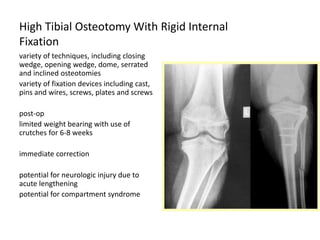
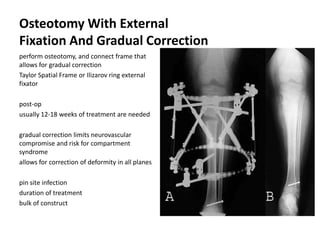
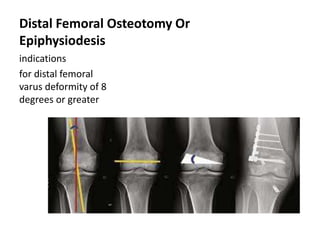
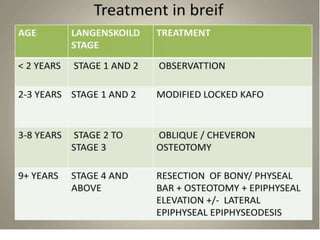
Blount's disease is a progressive deformity of the knee characterized by bowing of the legs (genu varum). It is classified into infantile and adolescent types. Infantile Blount's disease presents between ages 2-5 and is often bilateral, while adolescent Blount's disease presents after age 10 and is usually unilateral. Radiographs show abnormalities of the proximal tibial epiphysis. Treatment involves bracing for mild cases and osteotomy or epiphysiodesis surgery for more severe deformities, with the goal of correcting the varus alignment through a valgus procedure. Prognosis is best when treated early before significant bony changes occur.