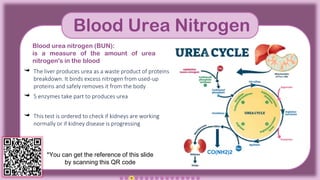
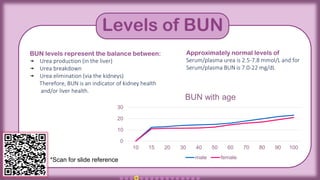
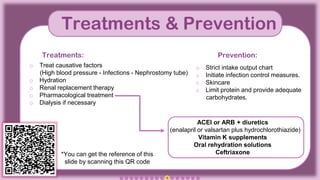
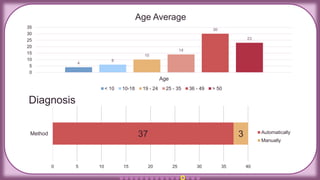
The document presents an overview of the Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN) test, including normal ranges, causes for abnormal levels, symptoms associated with high or low BUN, and diagnostic methods. It also discusses the BUN/creatinine ratio, treatment options for abnormal BUN levels, and presents a clinical case study. The information is supplemented with infographics and QR codes for further reference.