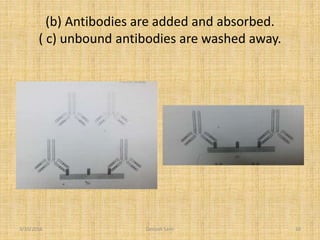
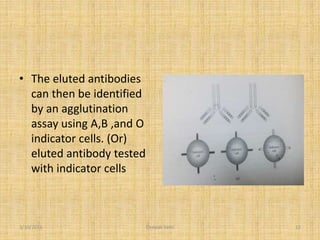
The document describes the absorption-elution technique for blood typing dried blood samples in forensic analysis. The absorption-elution assay indirectly detects blood type antigens in dried samples by binding antigens to specific antibodies which are later eluted and tested for agglutination with blood cells of known types. This sensitive method allows identification of blood types in severely dried samples where direct testing is not possible. The absorption and later elution of antibodies based on their binding to antigens in the dried sample enables typing of old blood evidence through antibody identification.