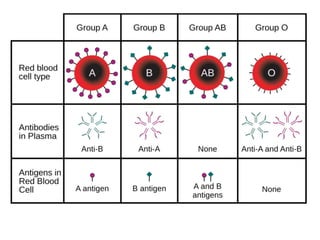
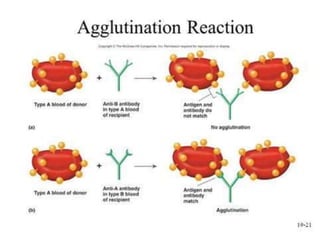
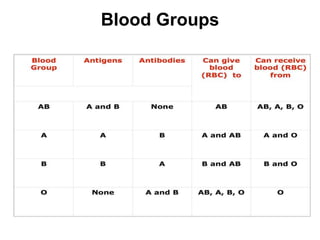
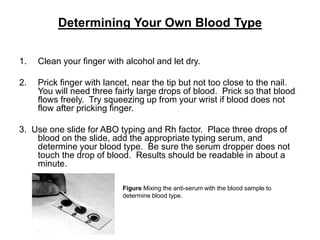
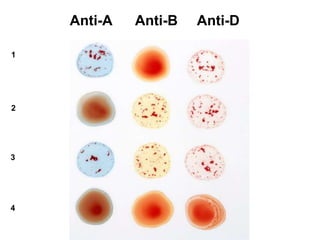
This document discusses blood typing and blood groups. It begins by explaining the purpose of blood typing before blood transfusions. It then covers the principles of blood groups based on antigens on red blood cells. The major blood groups are defined by the presence or absence of A and B antigens, resulting in types O, A, B, and AB. It also discusses the Rh factor and clinical significance of Rh-negative mothers carrying Rh-positive babies. The document provides details on determining blood types using different antiserums and preventing hemolytic disease of the newborn. It defines terms like universal donor and universal recipient.