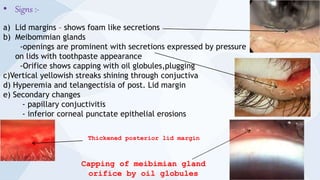
Blepharitis is inflammation of the eyelid margin that can be caused by bacteria, seborrhea, or parasites. Common symptoms include chronic irritation, itching, mild lacrimation, and worsening of symptoms in the morning. Signs include yellow crusts, small ulcers, hyperemia, and lash abnormalities. Treatment involves warm compresses, lid cleaning, antibiotics, and topical steroids. There are multiple types of blepharitis that can affect the anterior or posterior lid margin.