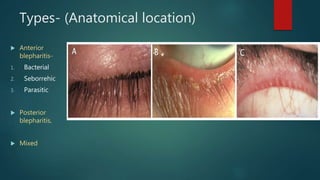
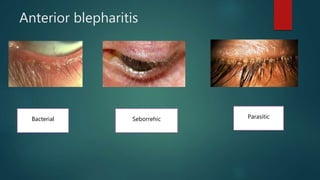
Blepharitis is an inflammatory eyelid condition with various types defined by location and cause. Anterior blepharitis includes bacterial, seborrheic, and parasitic forms. Bacterial blepharitis is caused by staphylococci and streptococci bacteria, presenting with glued eyelashes and irritation. Seborrheic blepharitis results from excess sebum, appearing as oily scales. Parasitic blepharitis involves eyelash mites. Posterior blepharitis or meibomitis involves inflamed meibomian glands, seen as streaks on eversion. Diagnosis involves tests like tear breakup time and treatment focuses on lid hy