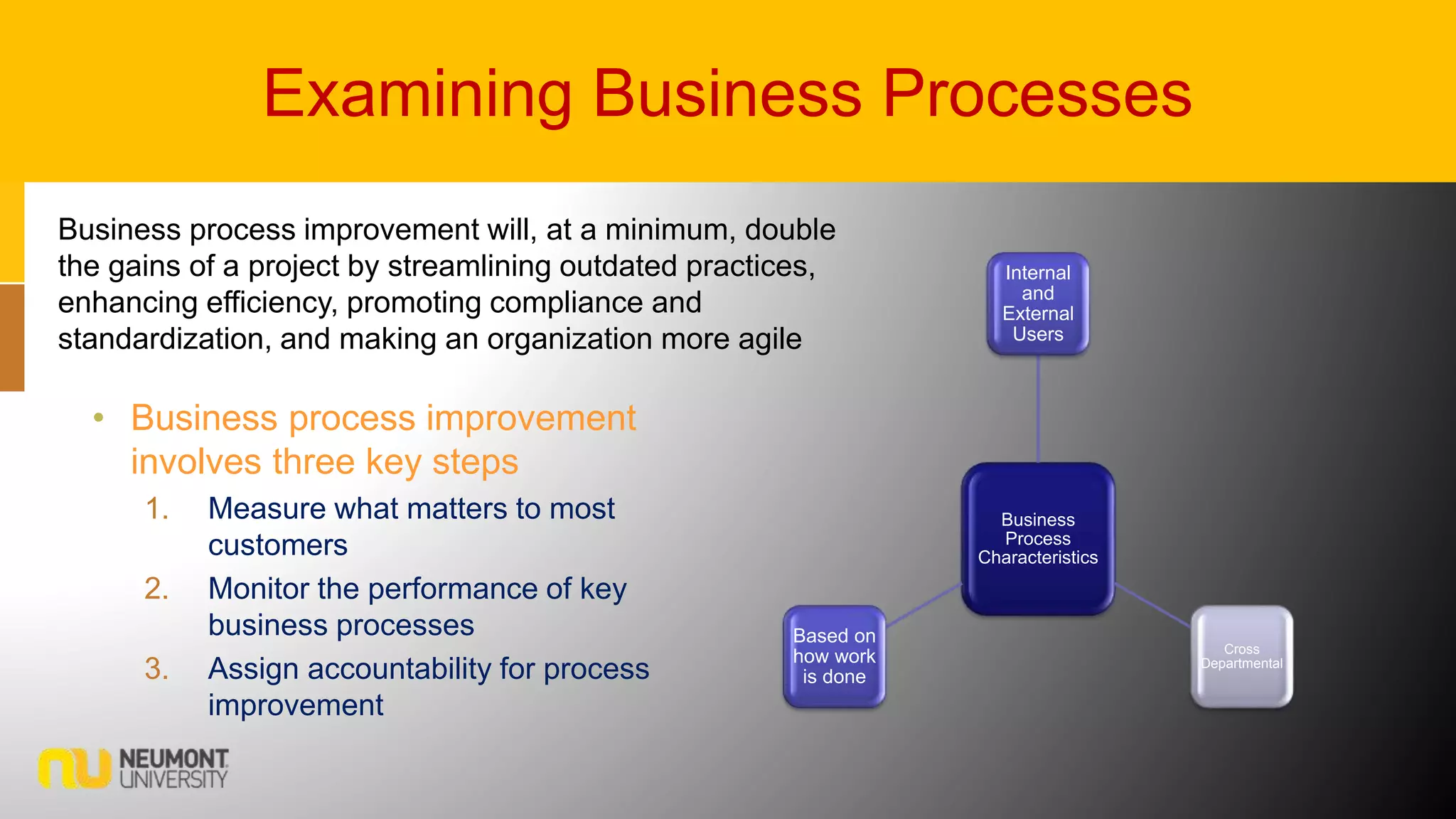
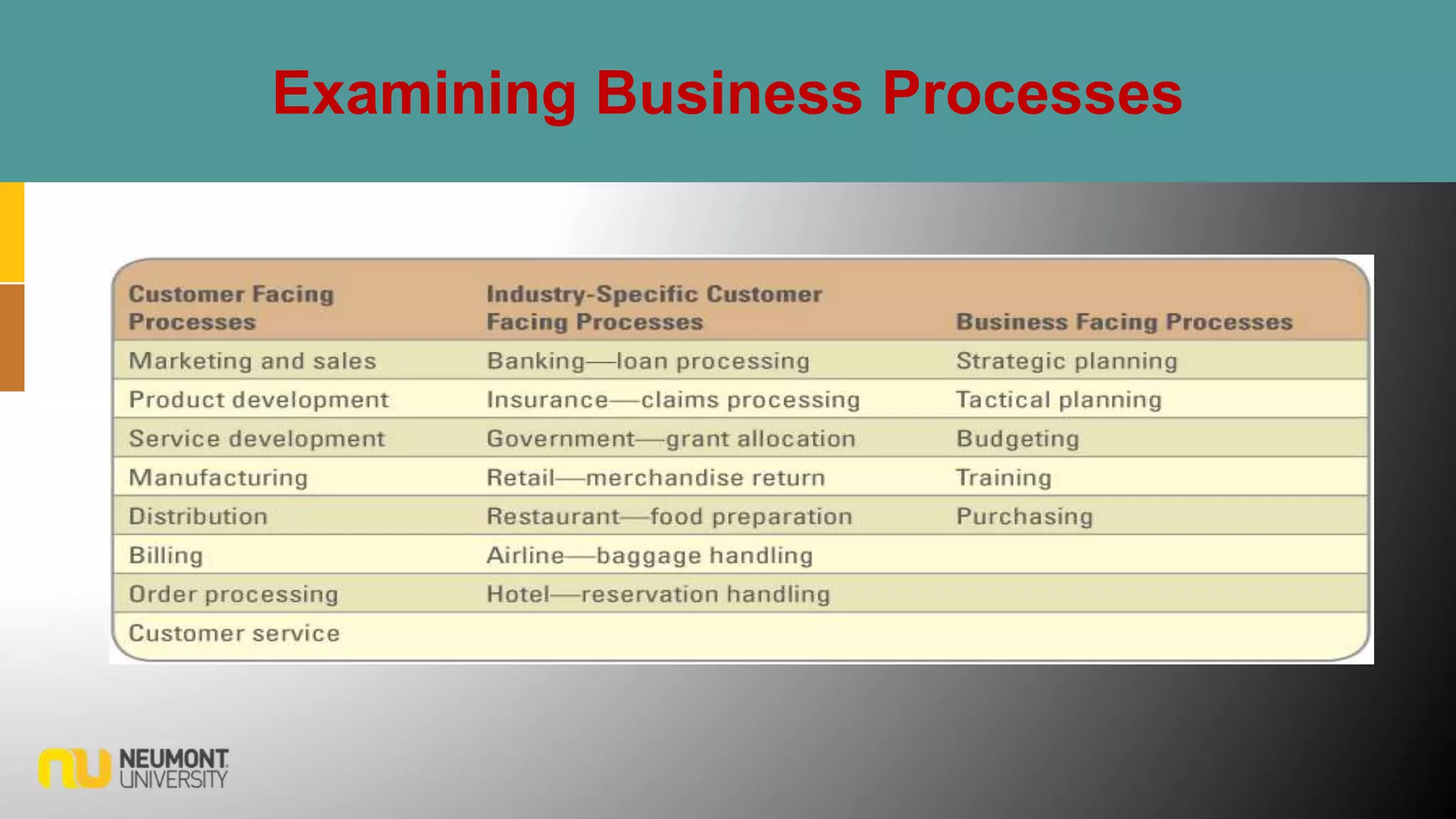
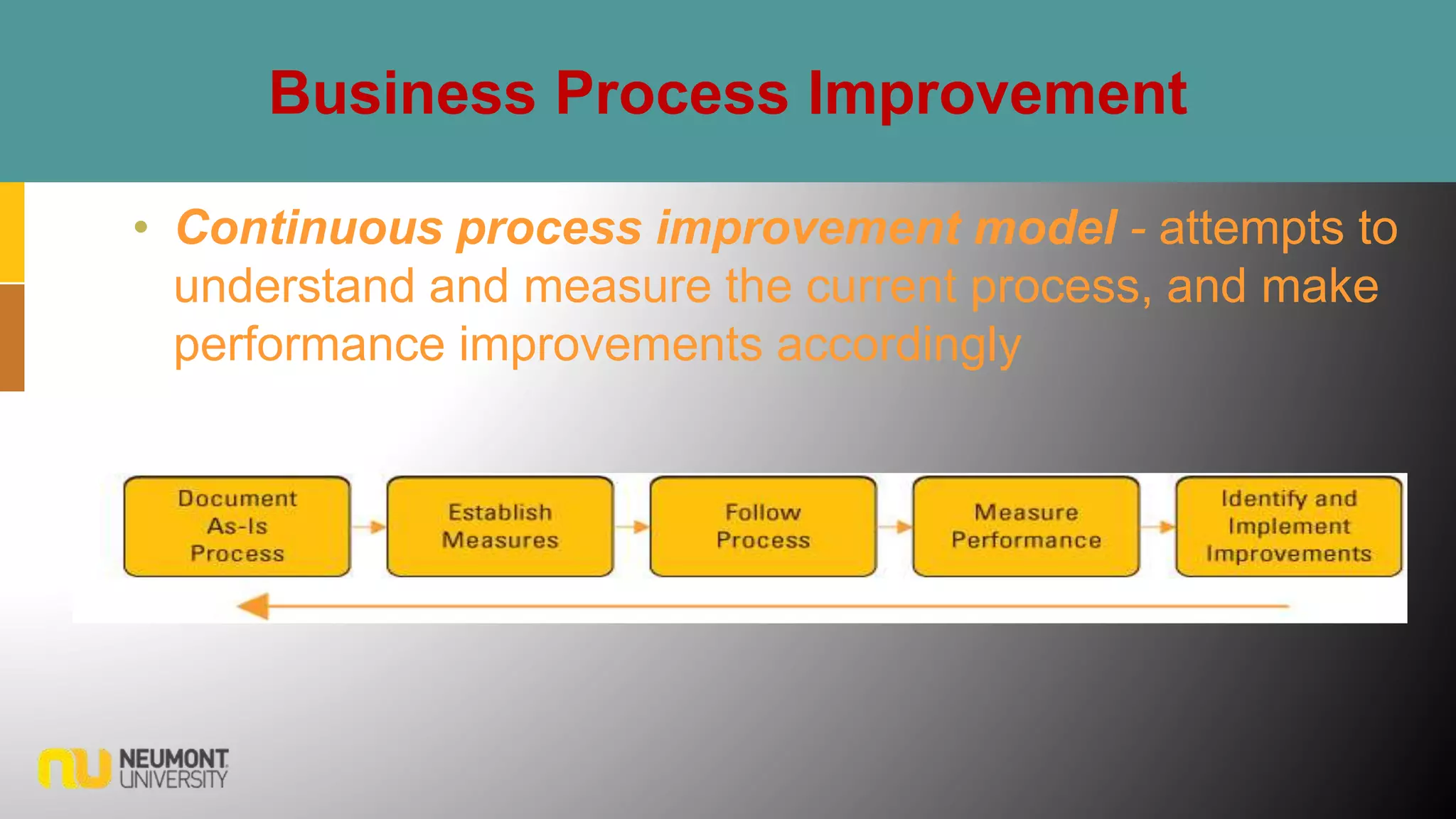
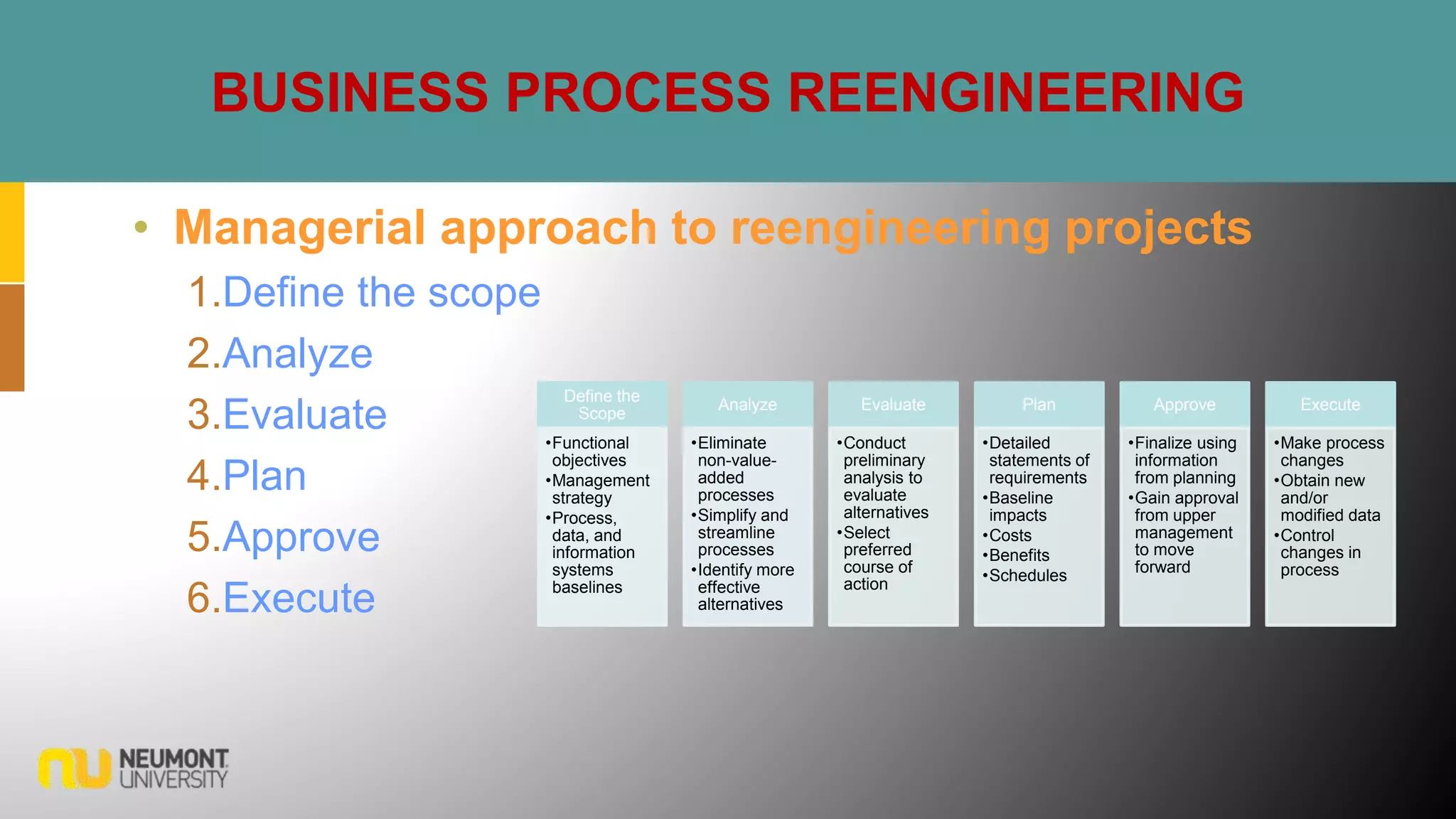
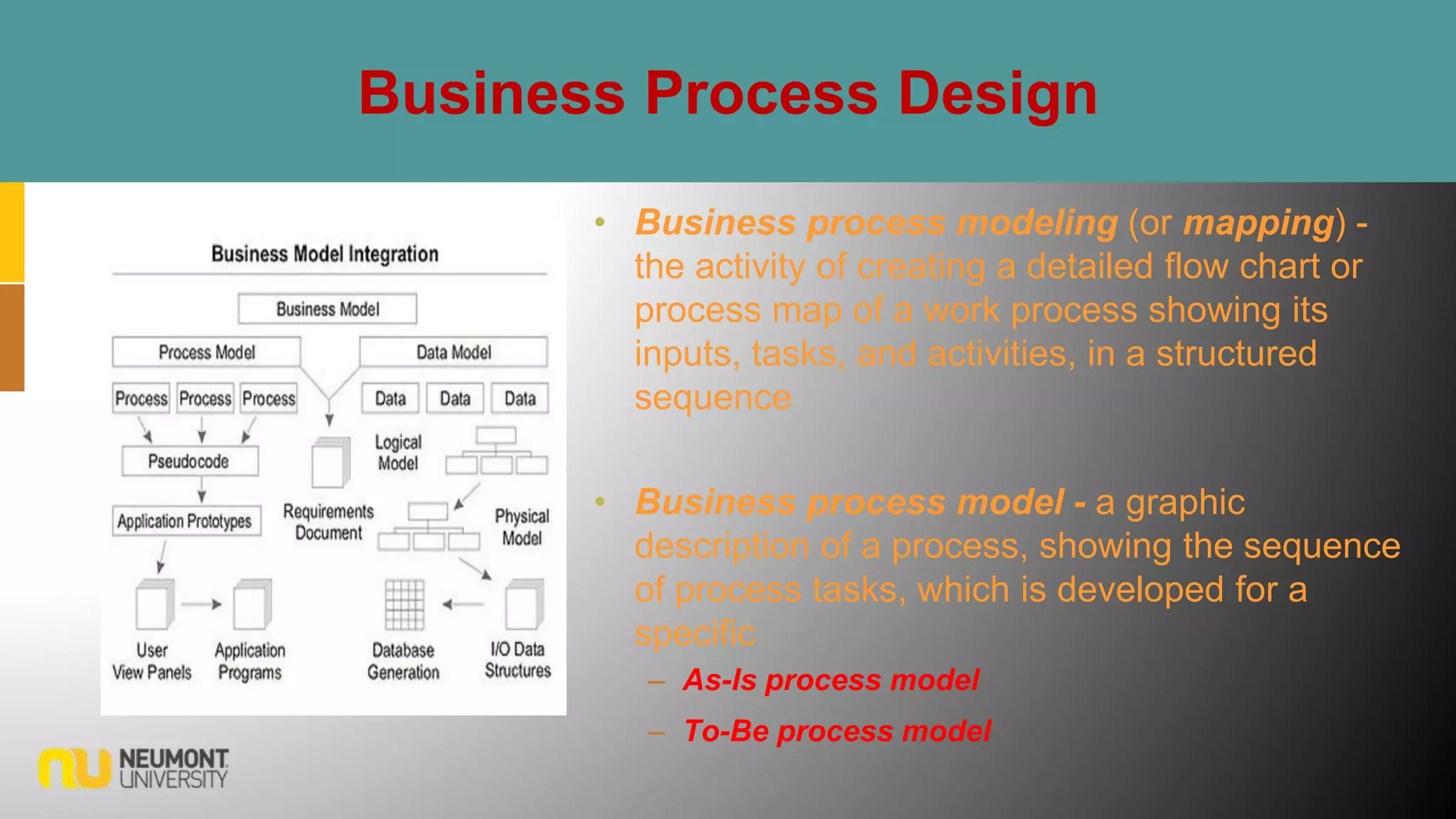
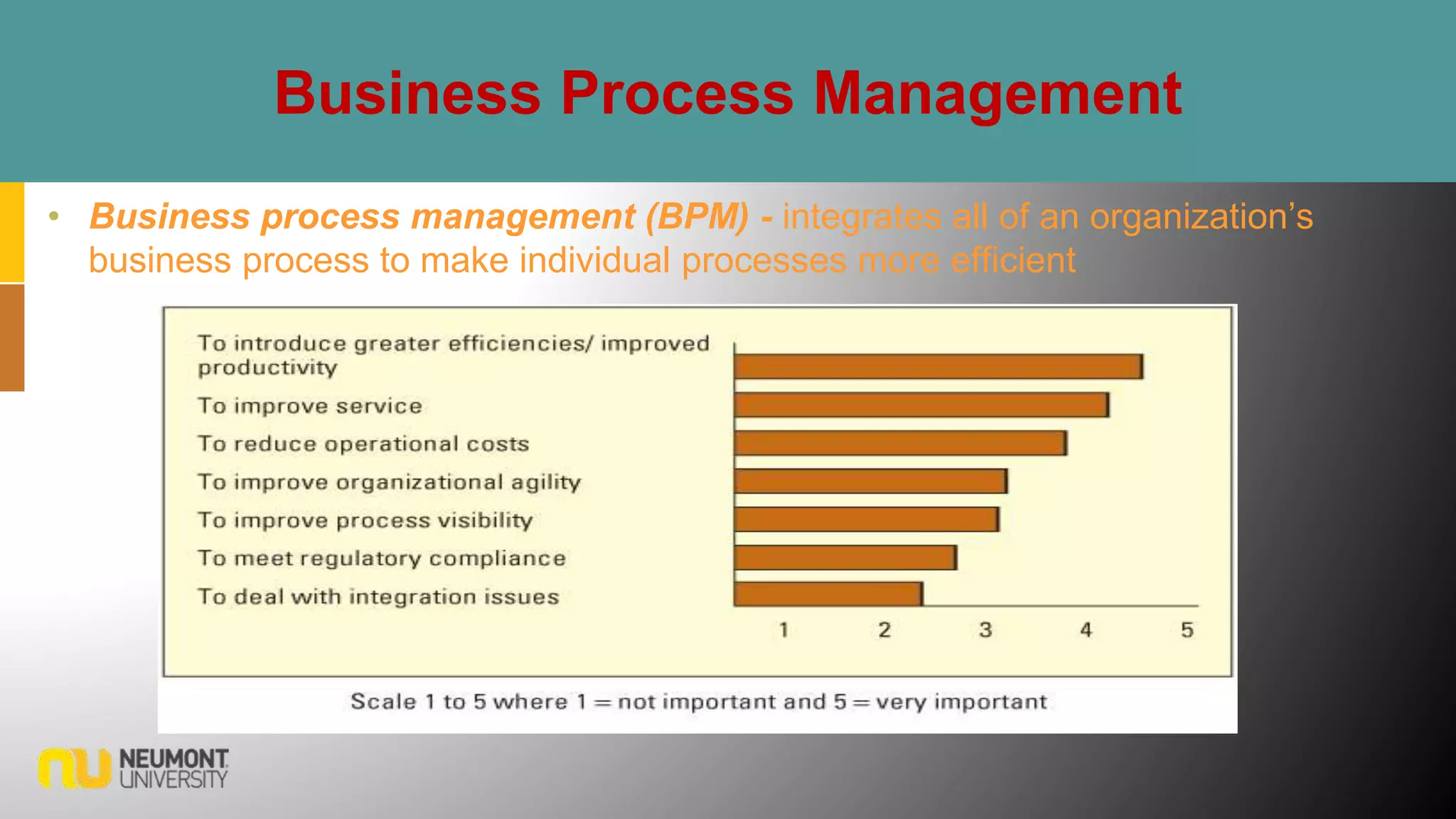
This document defines key terms related to business processes. It explains that a business process is a standardized set of activities that accomplish a specific task, such as processing an order. Business processes transform inputs into outputs for internal or external users. The document also discusses business process improvement, which involves measuring what matters to customers, monitoring key processes, and assigning accountability. It notes that business process modeling creates detailed flow charts of processes. Overall, the document provides an overview of business processes, improvement, and management.