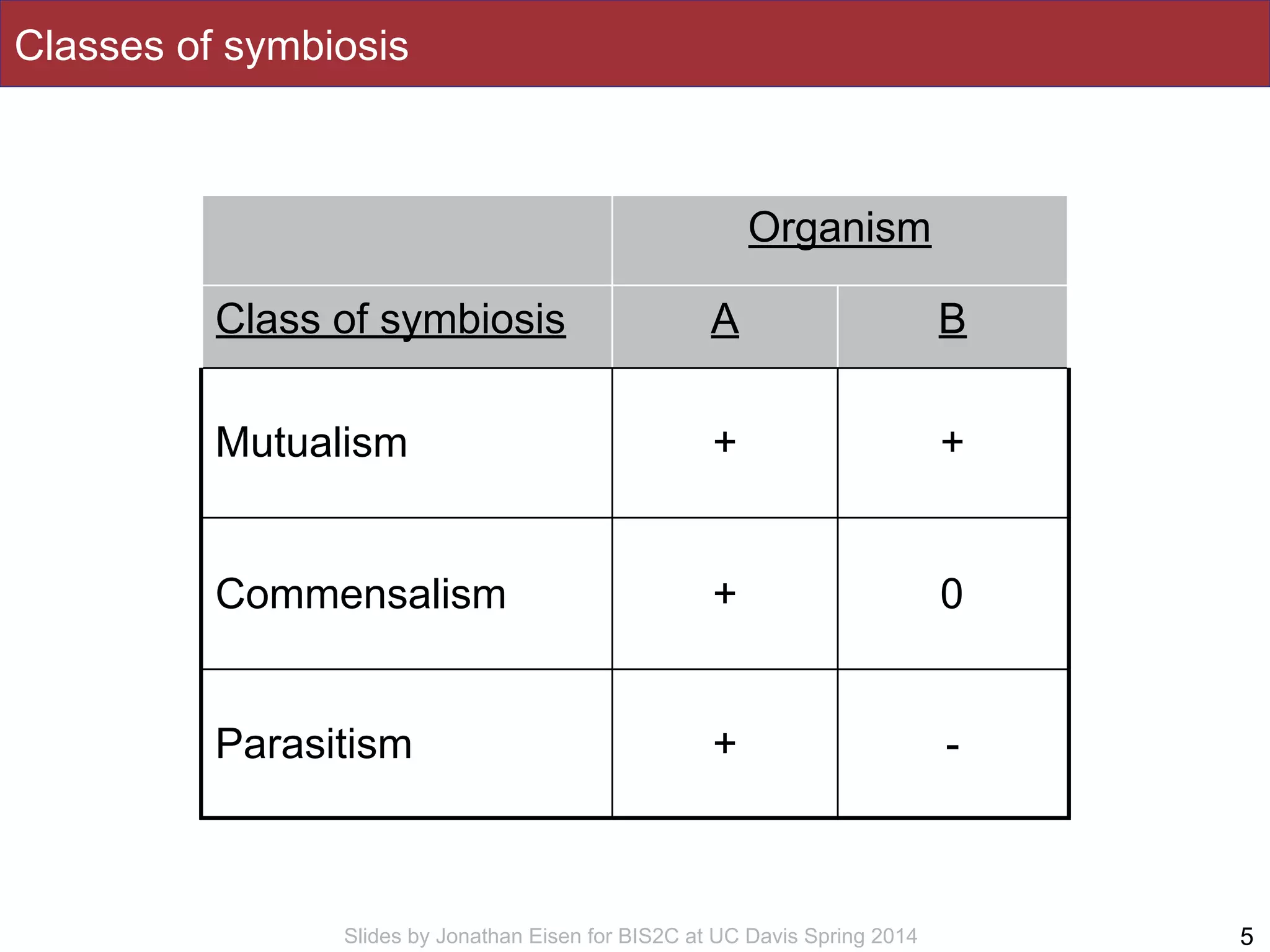
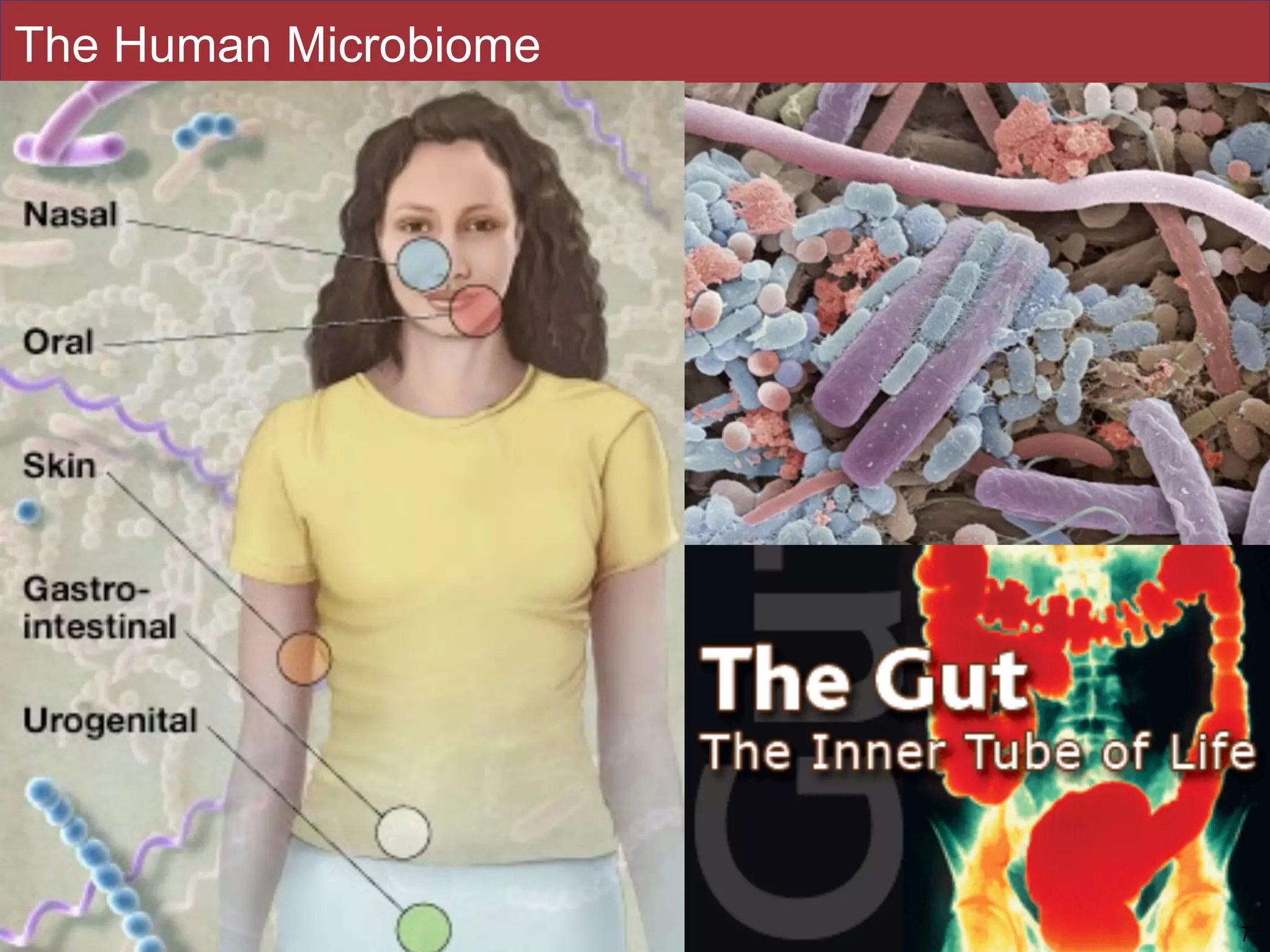
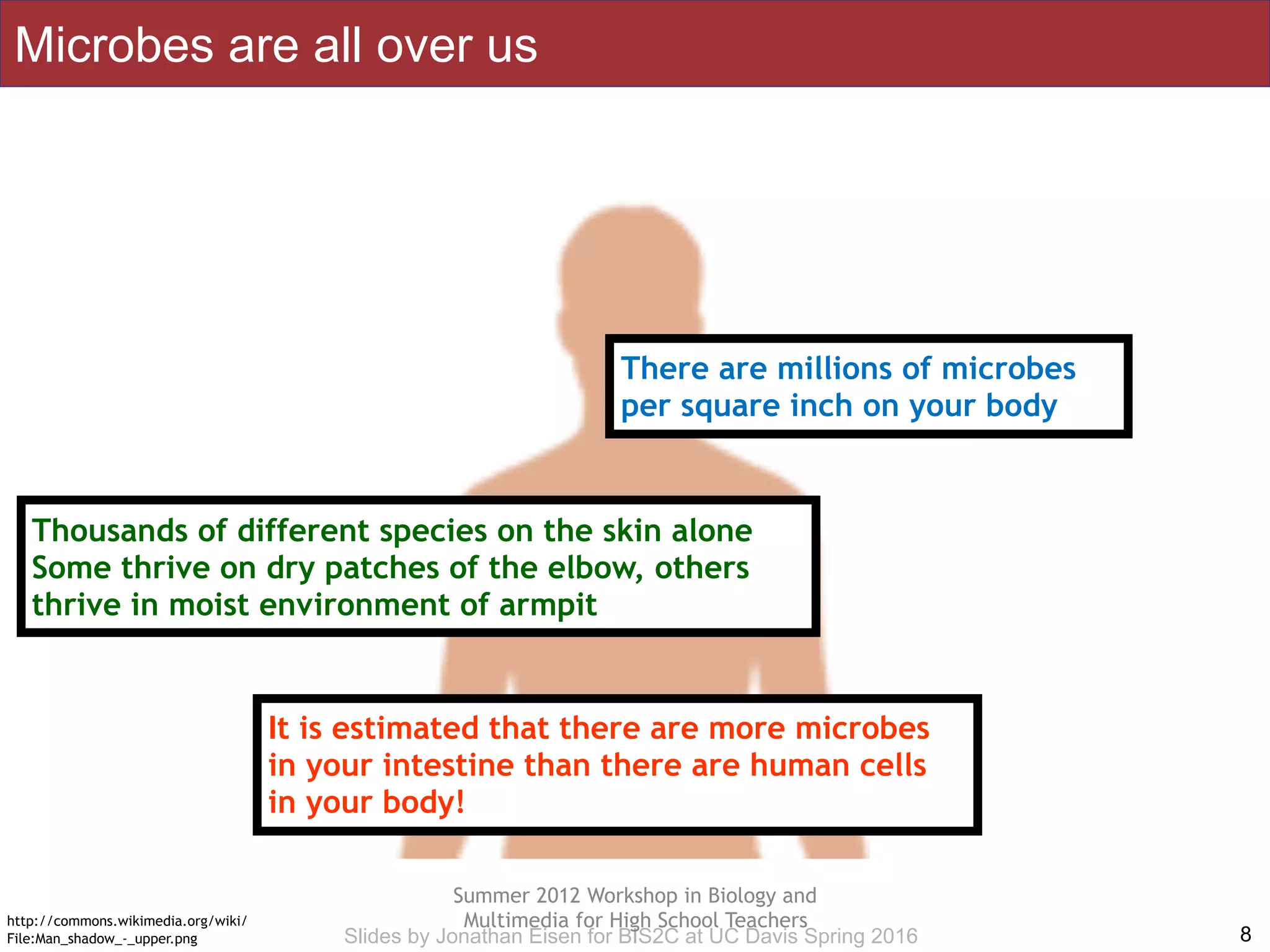
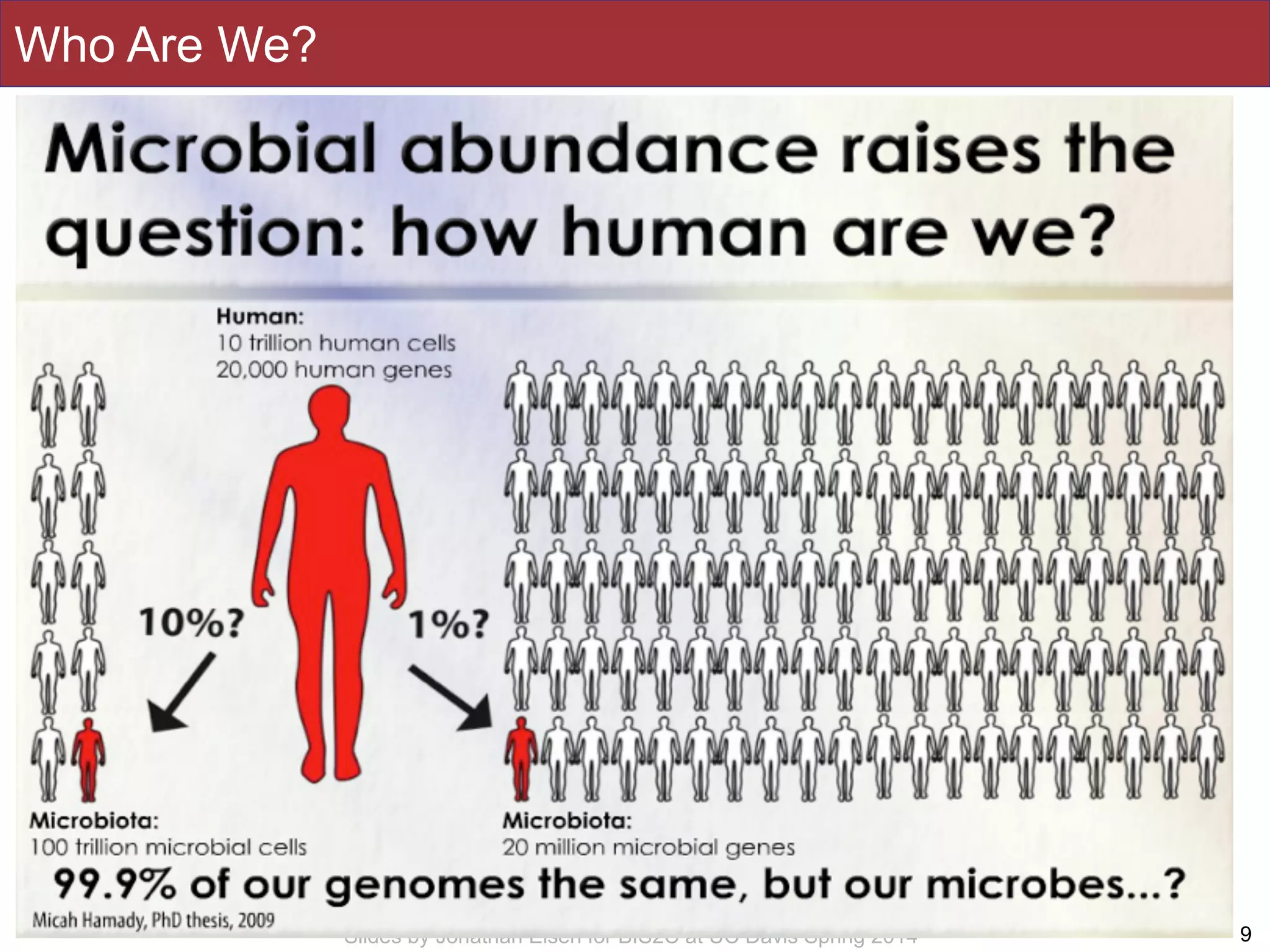
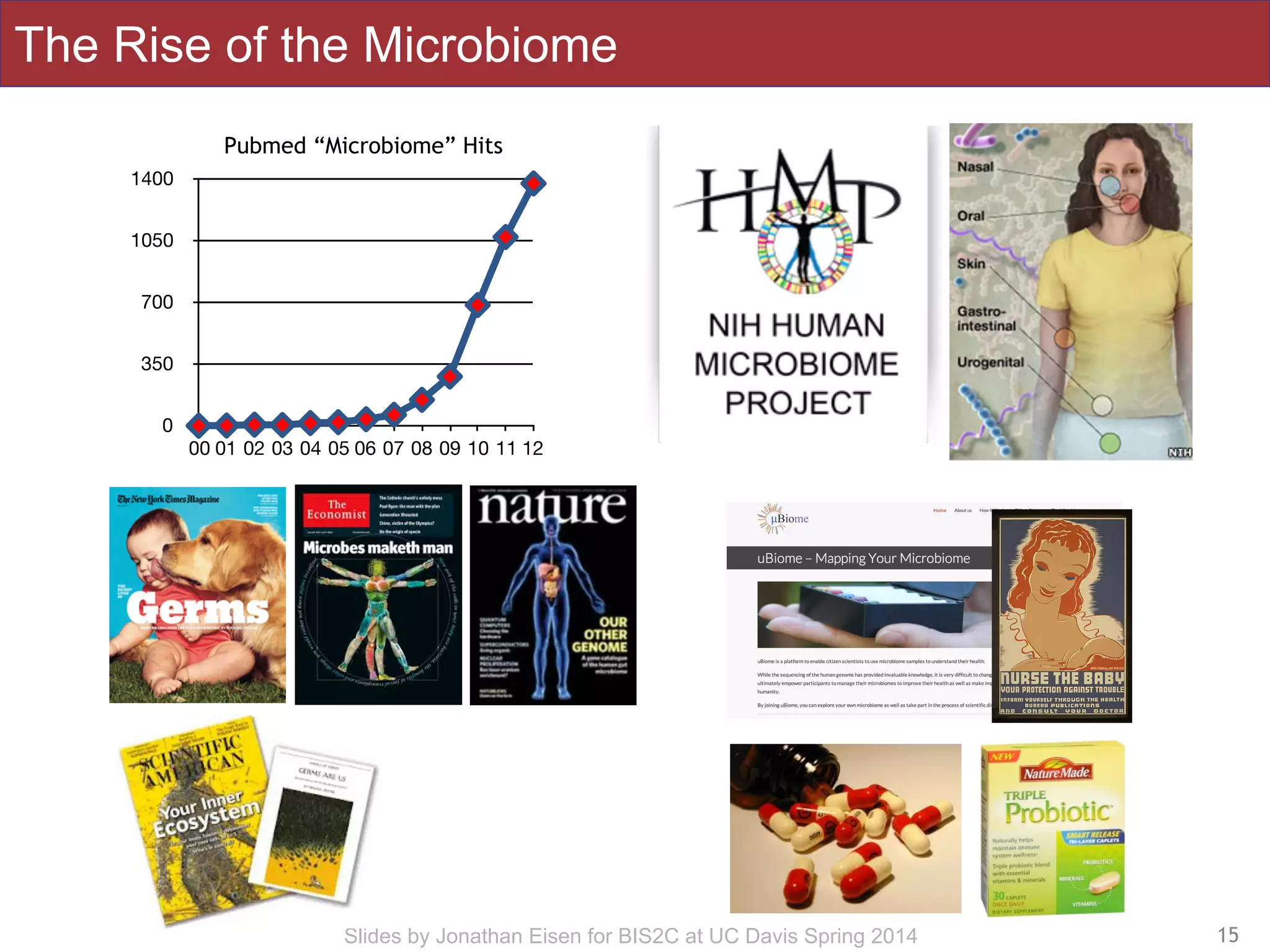
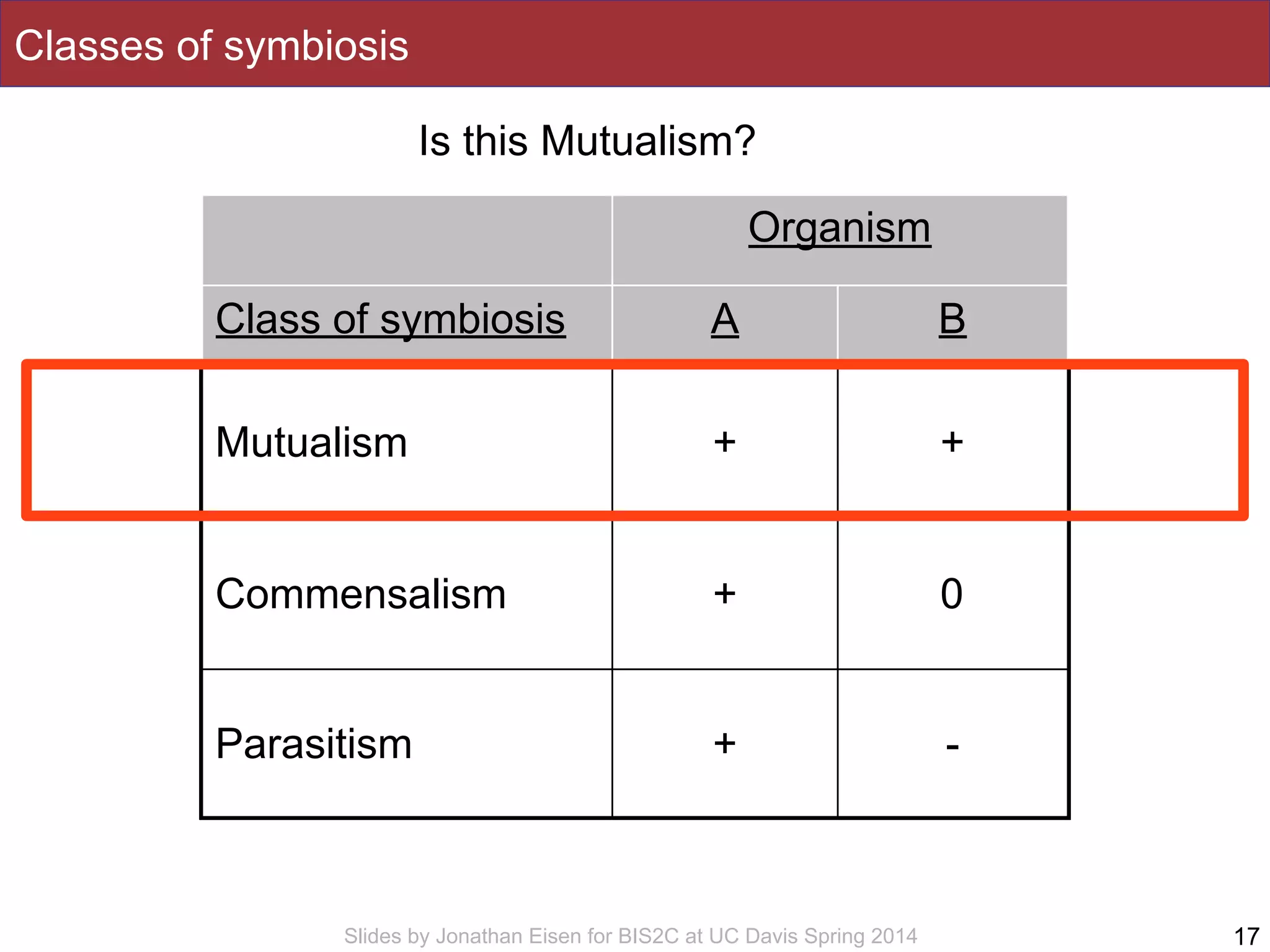
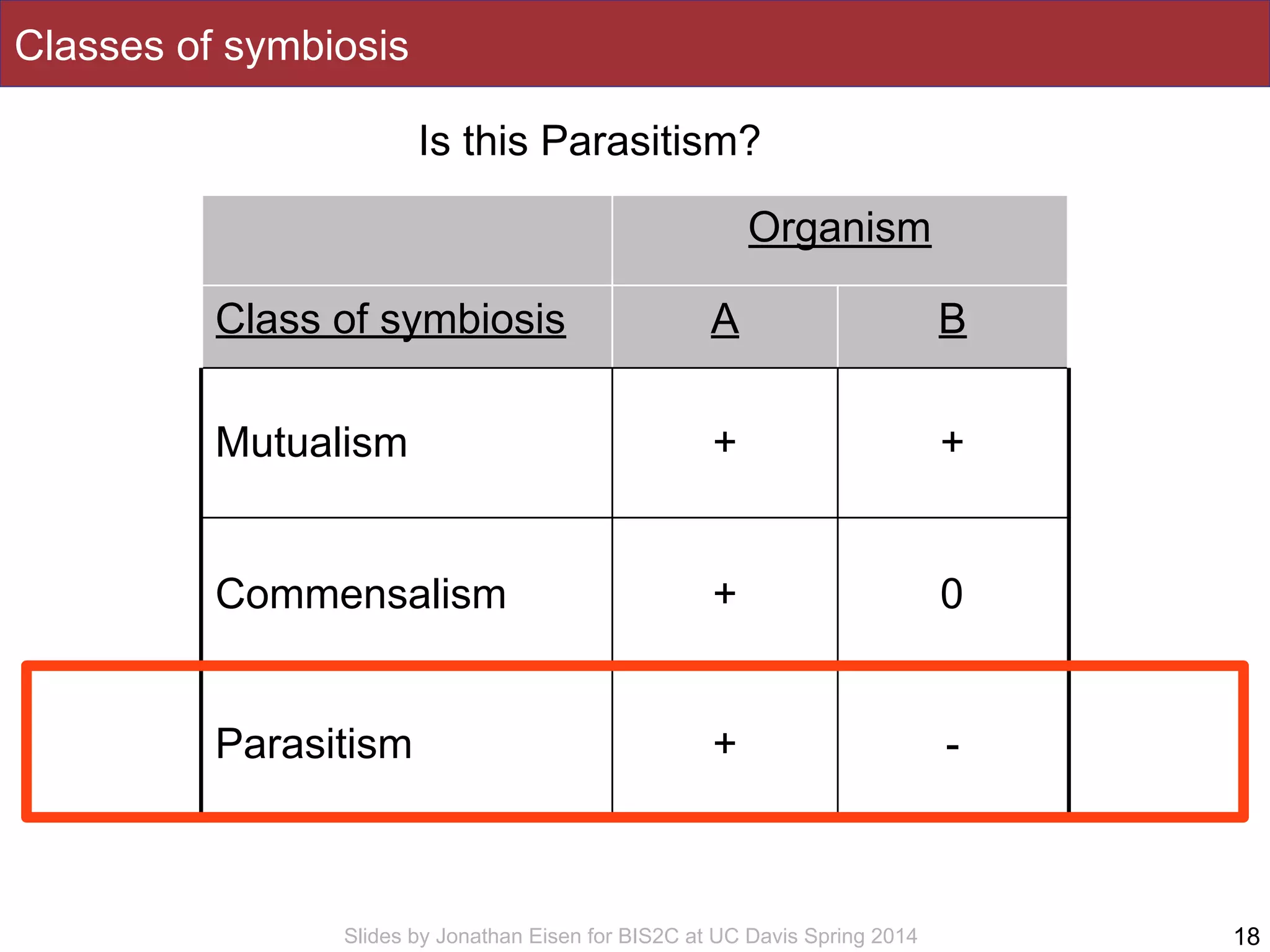
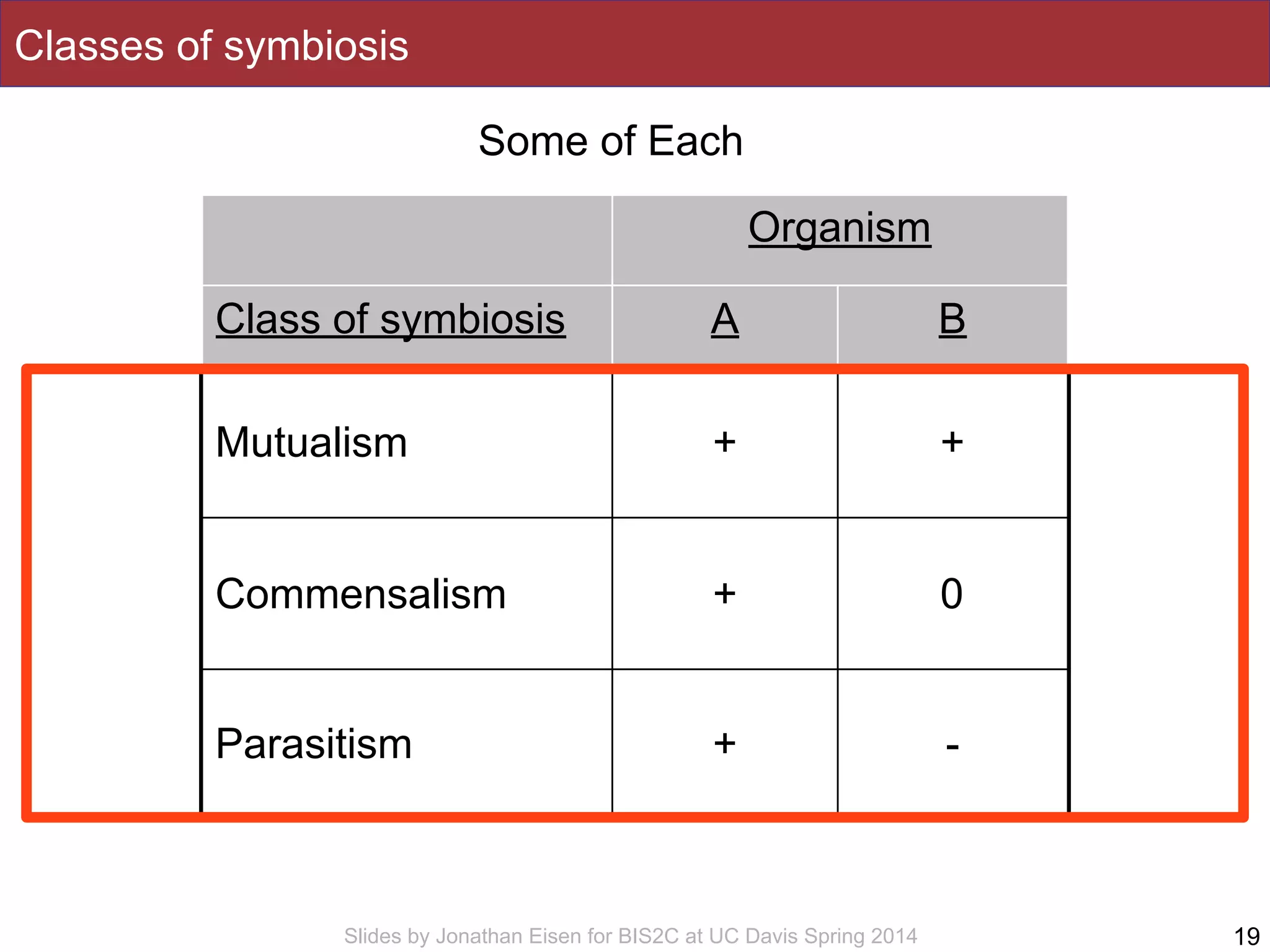
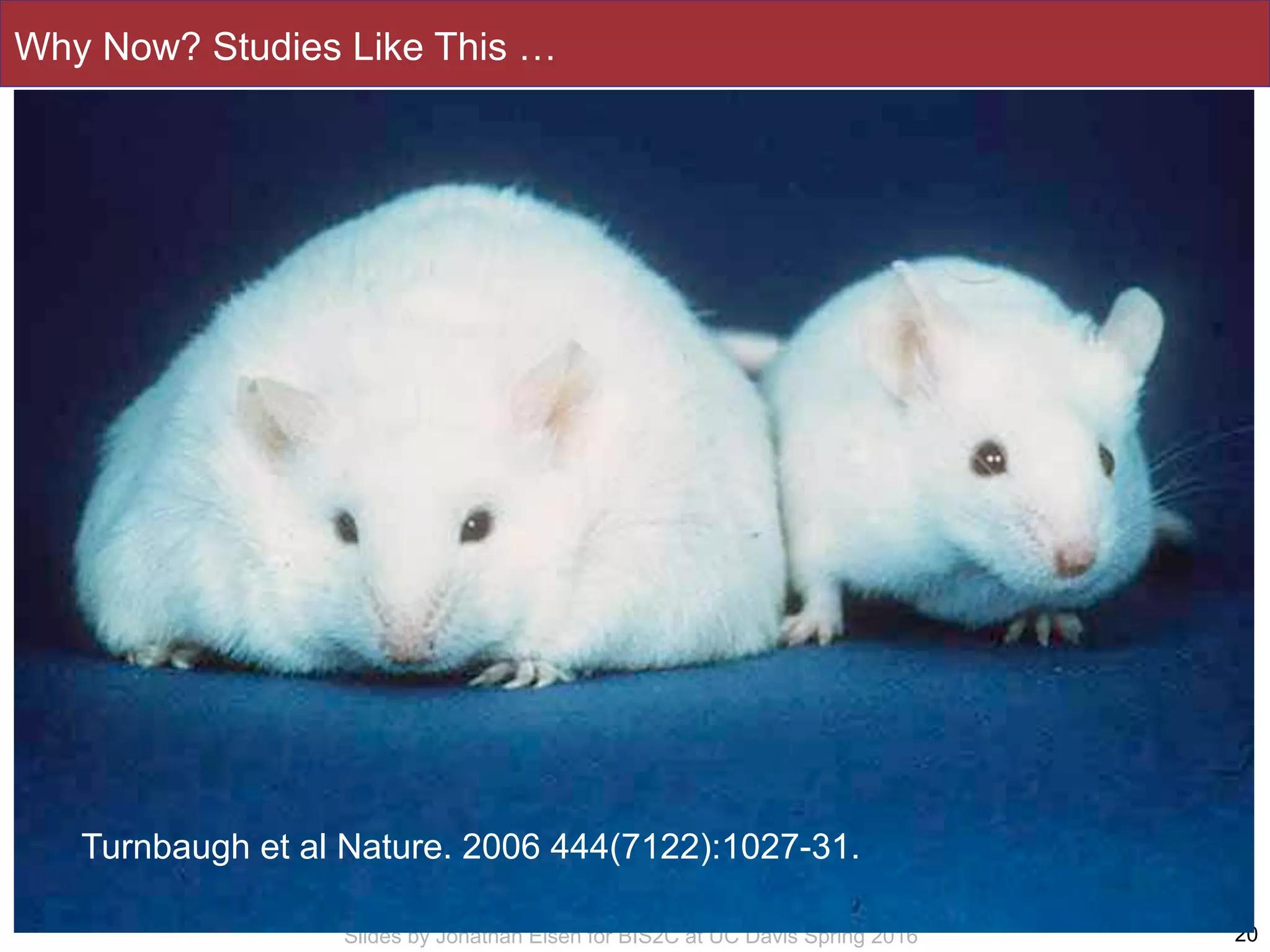
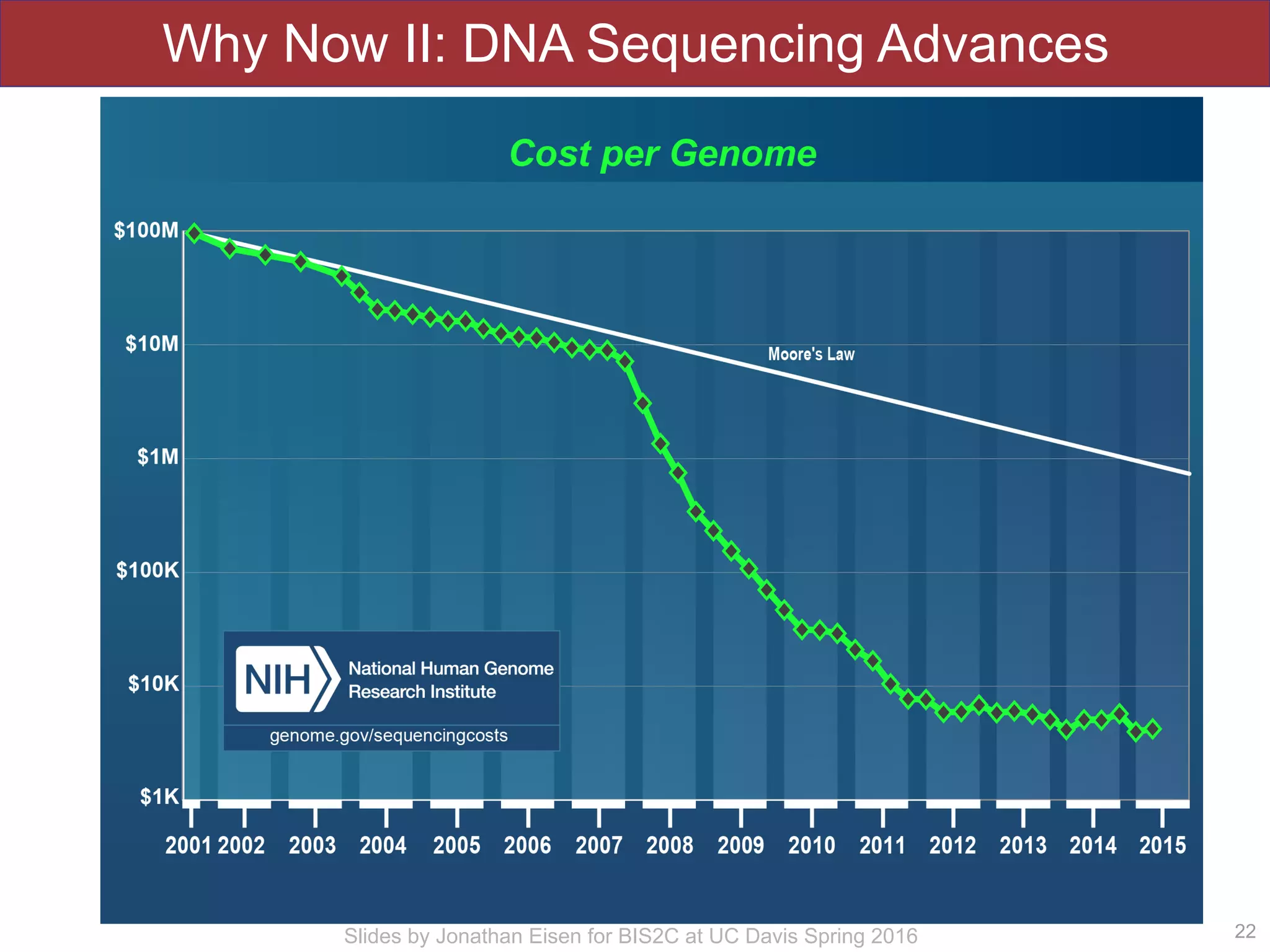
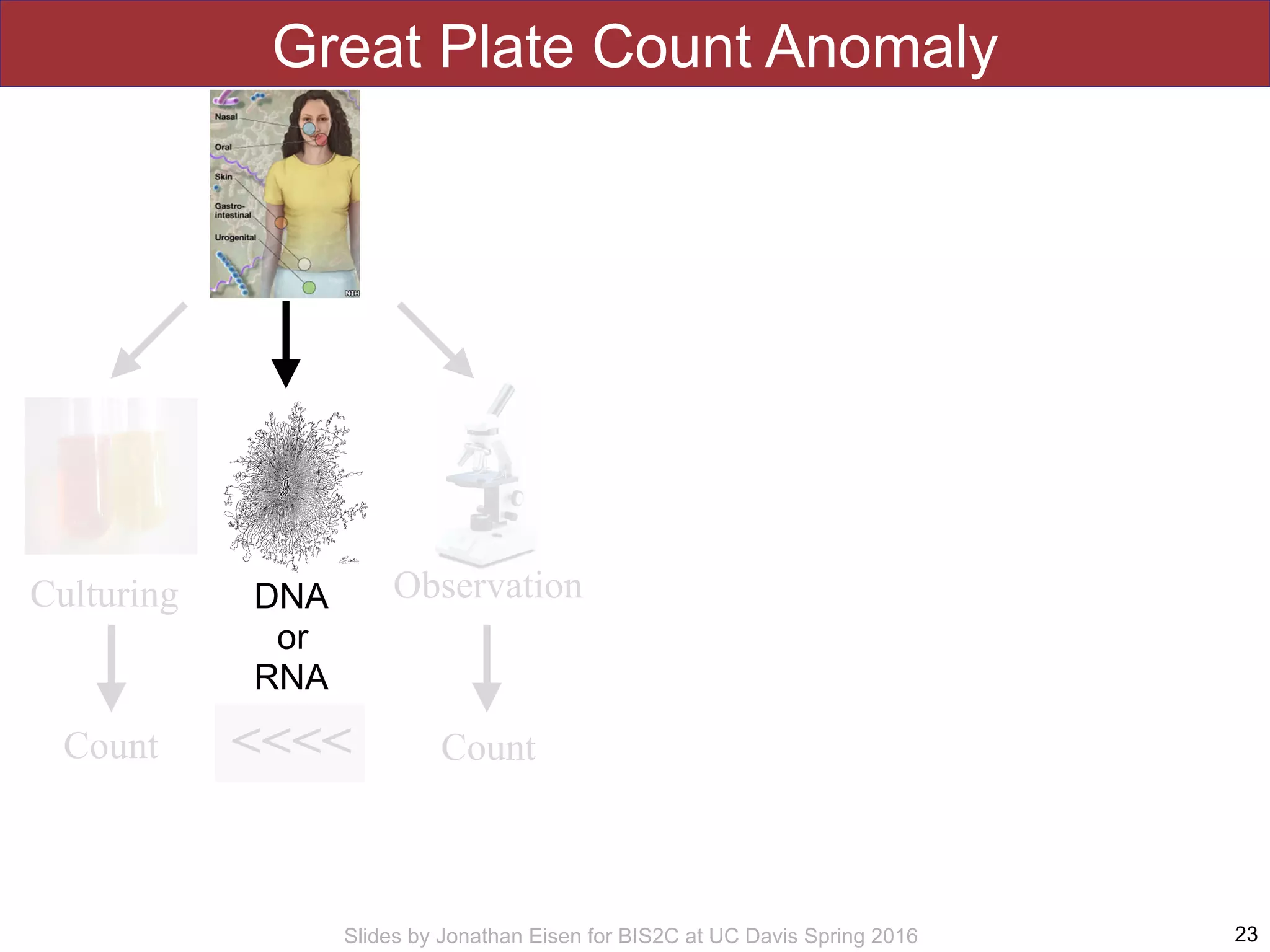
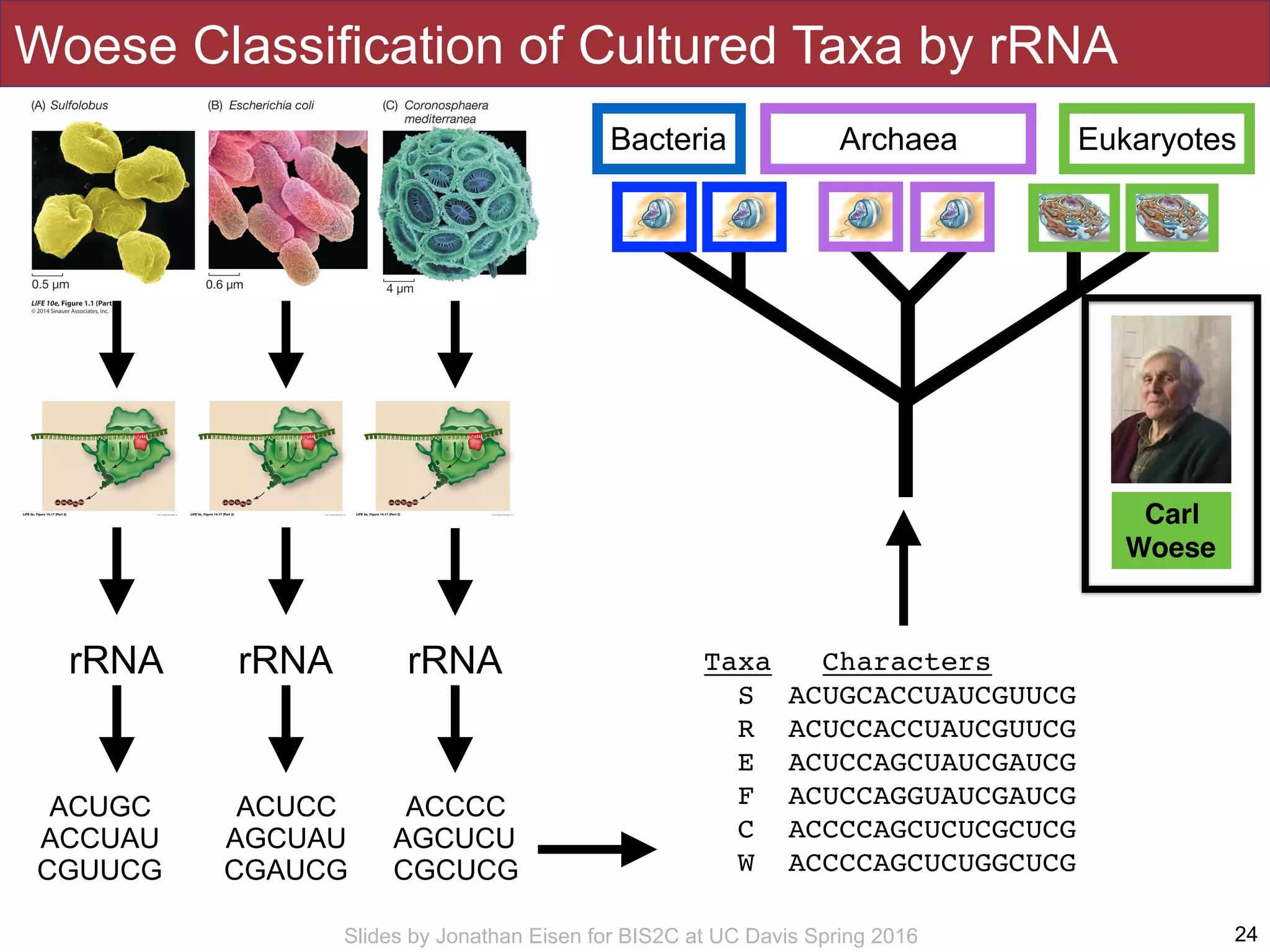
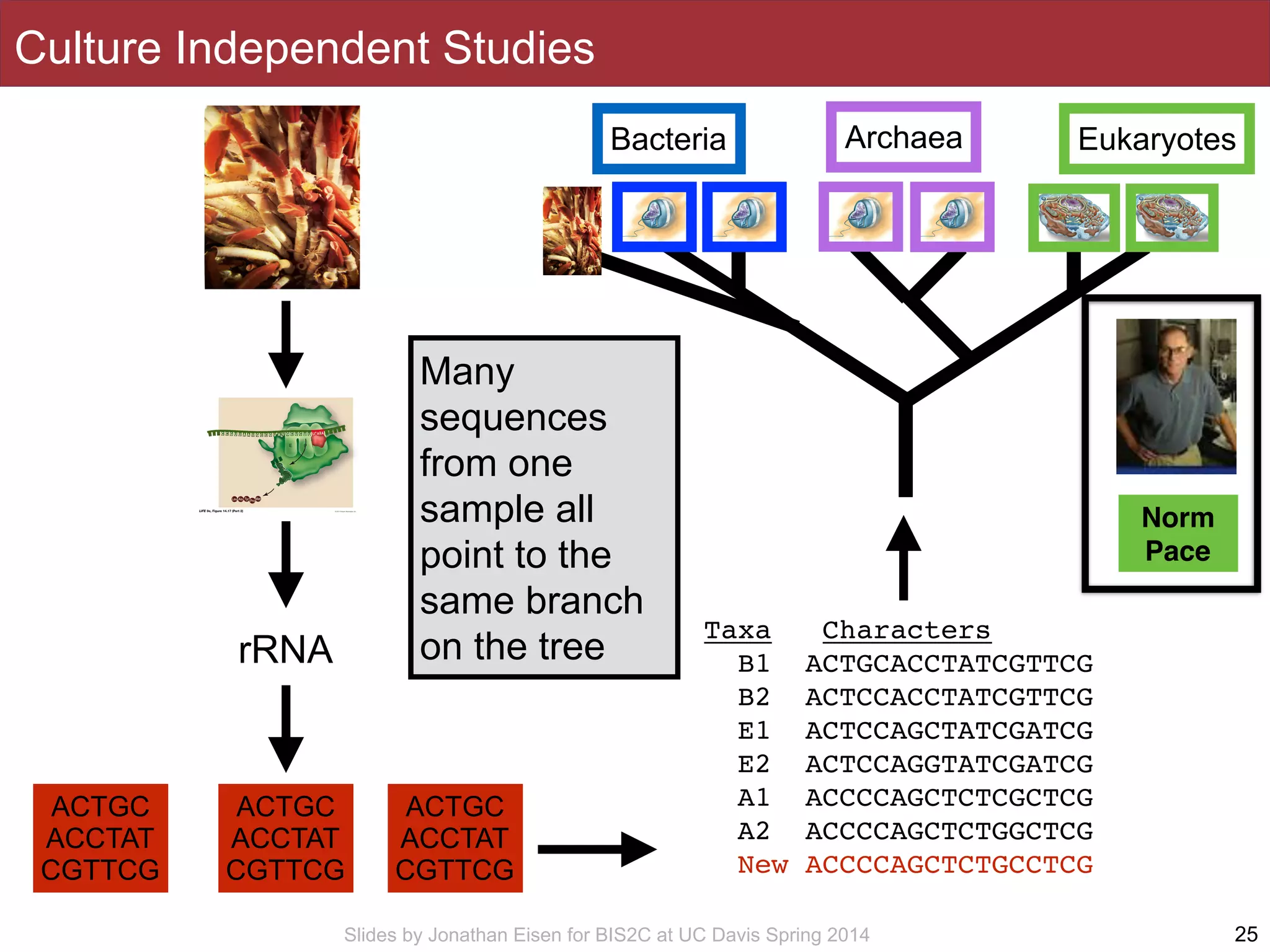
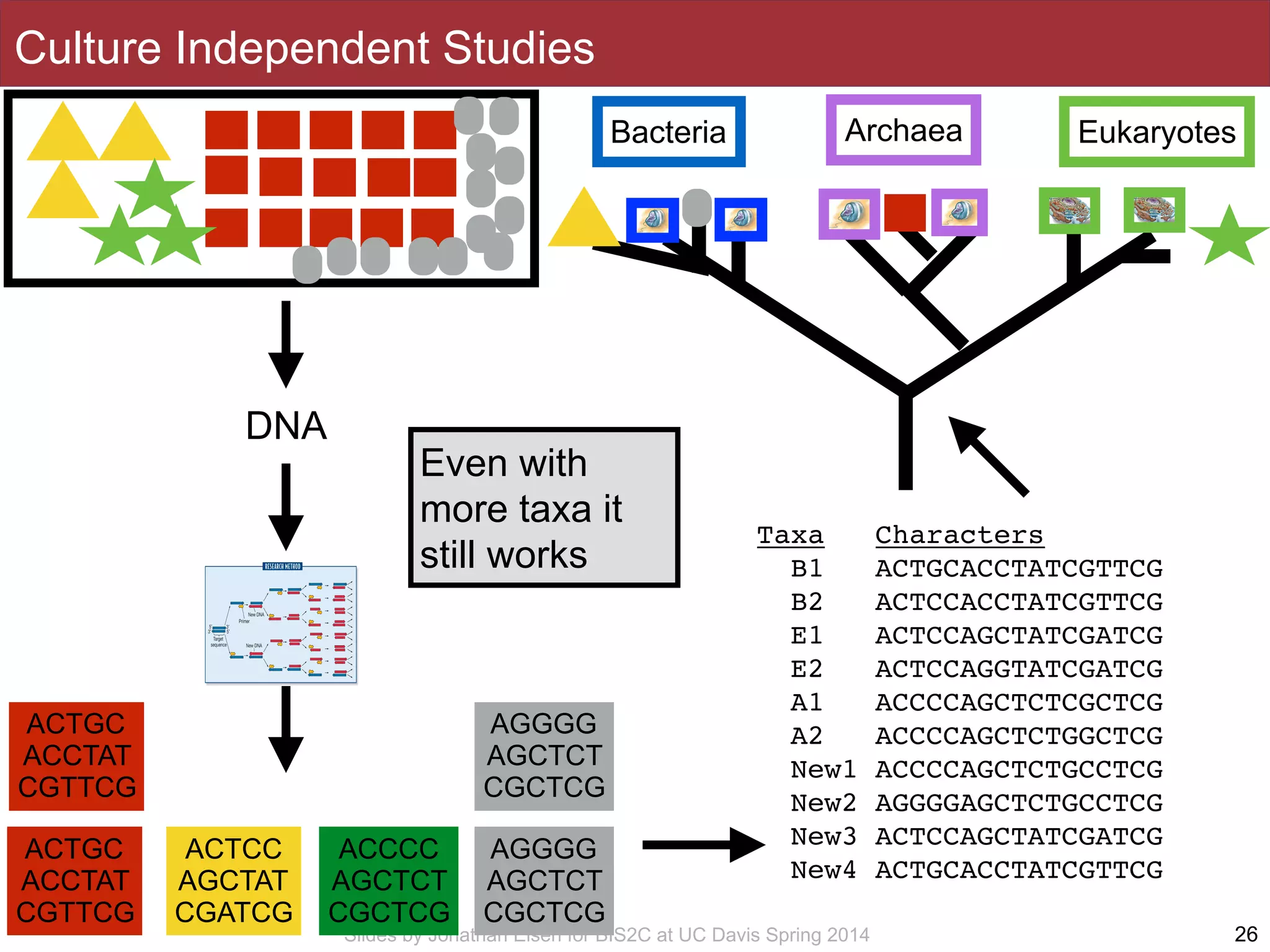
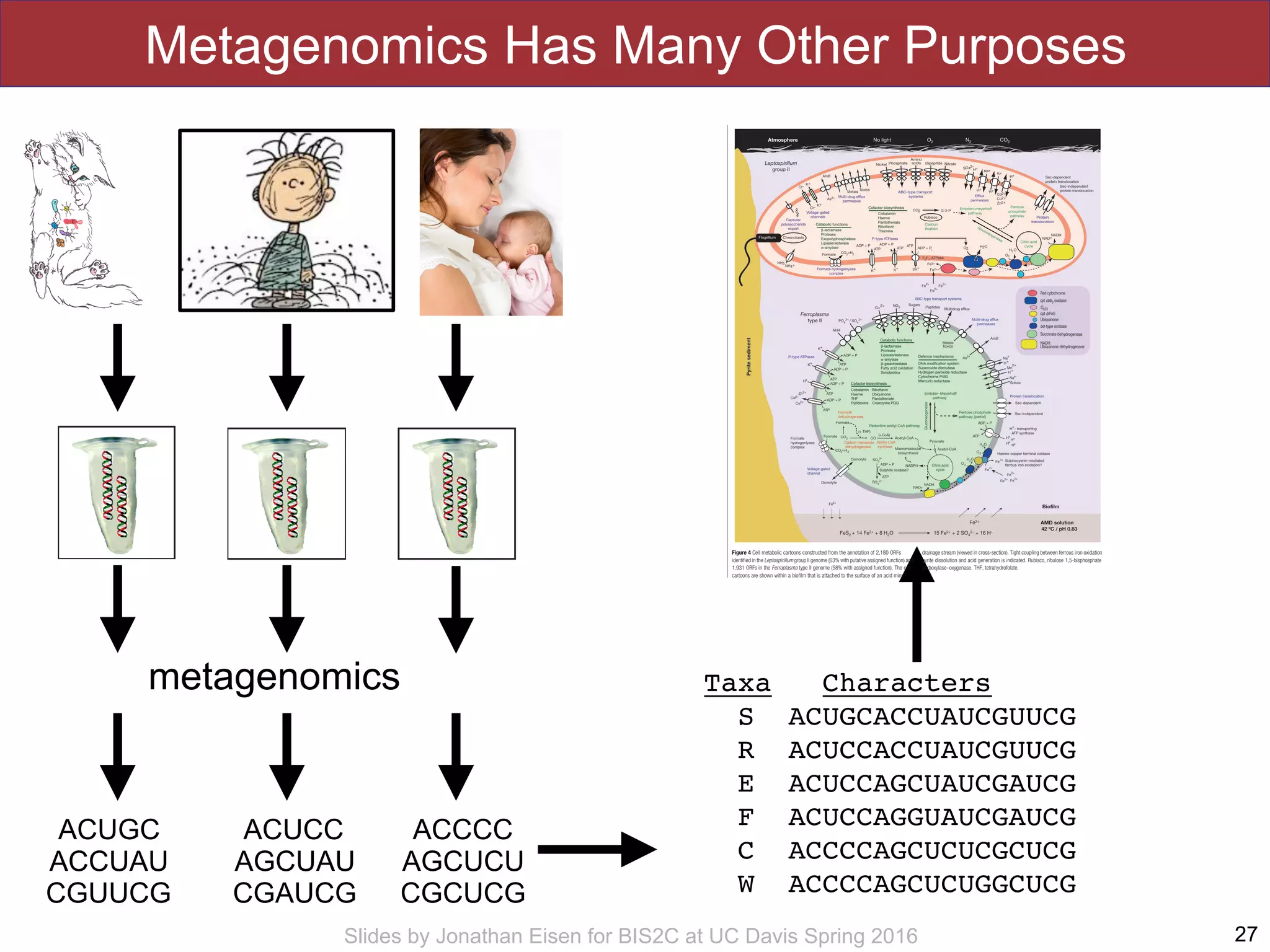
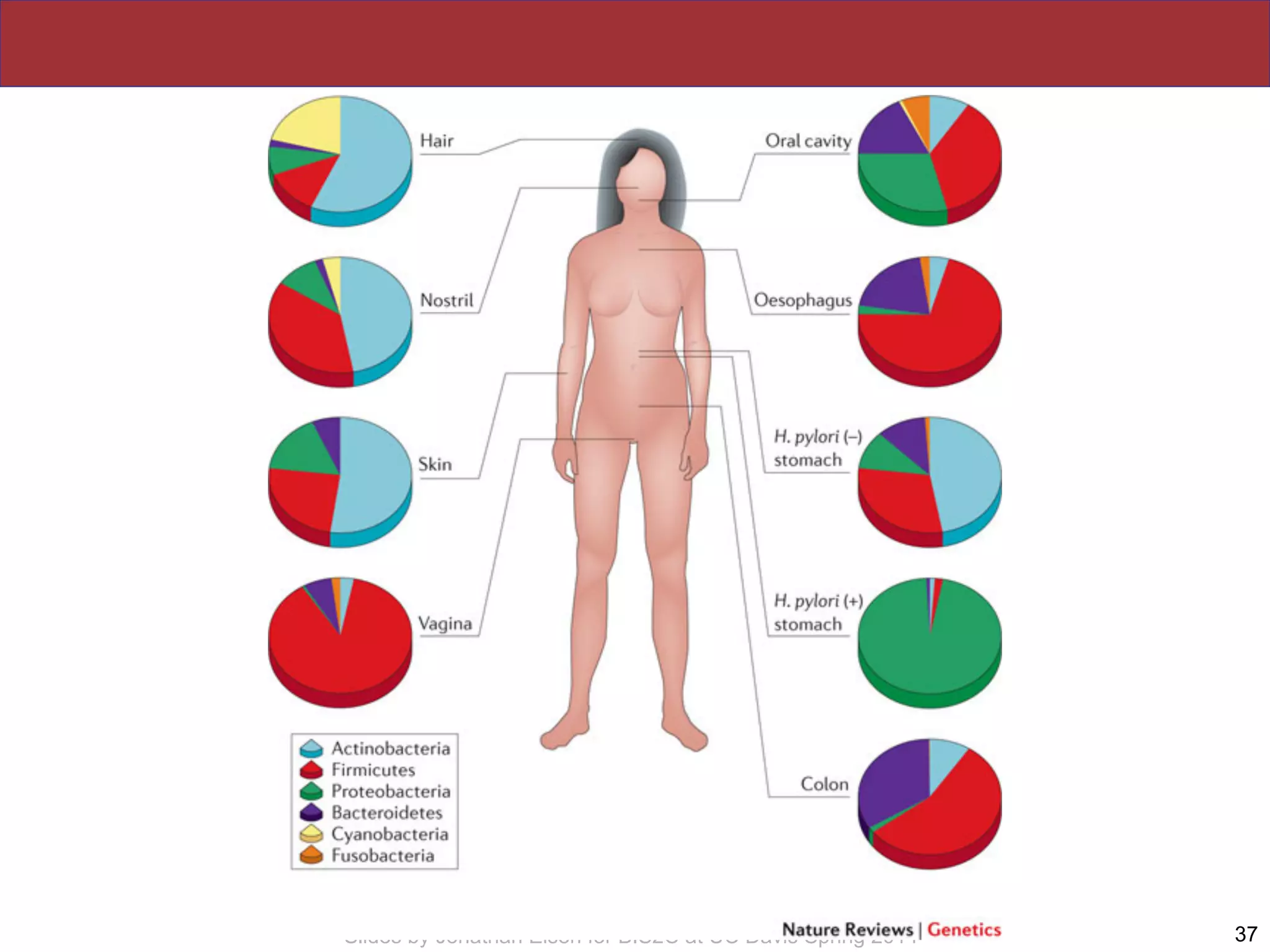
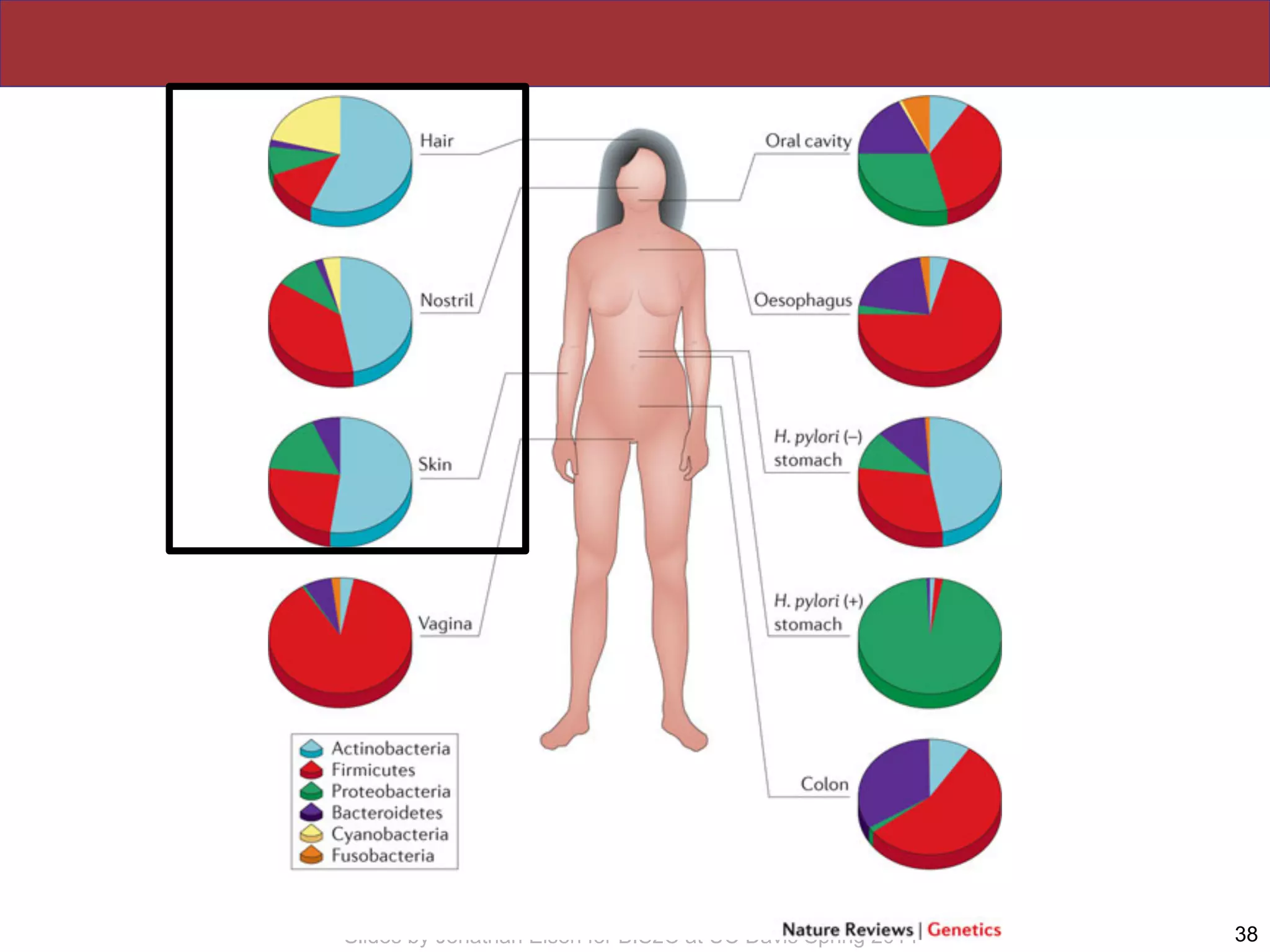
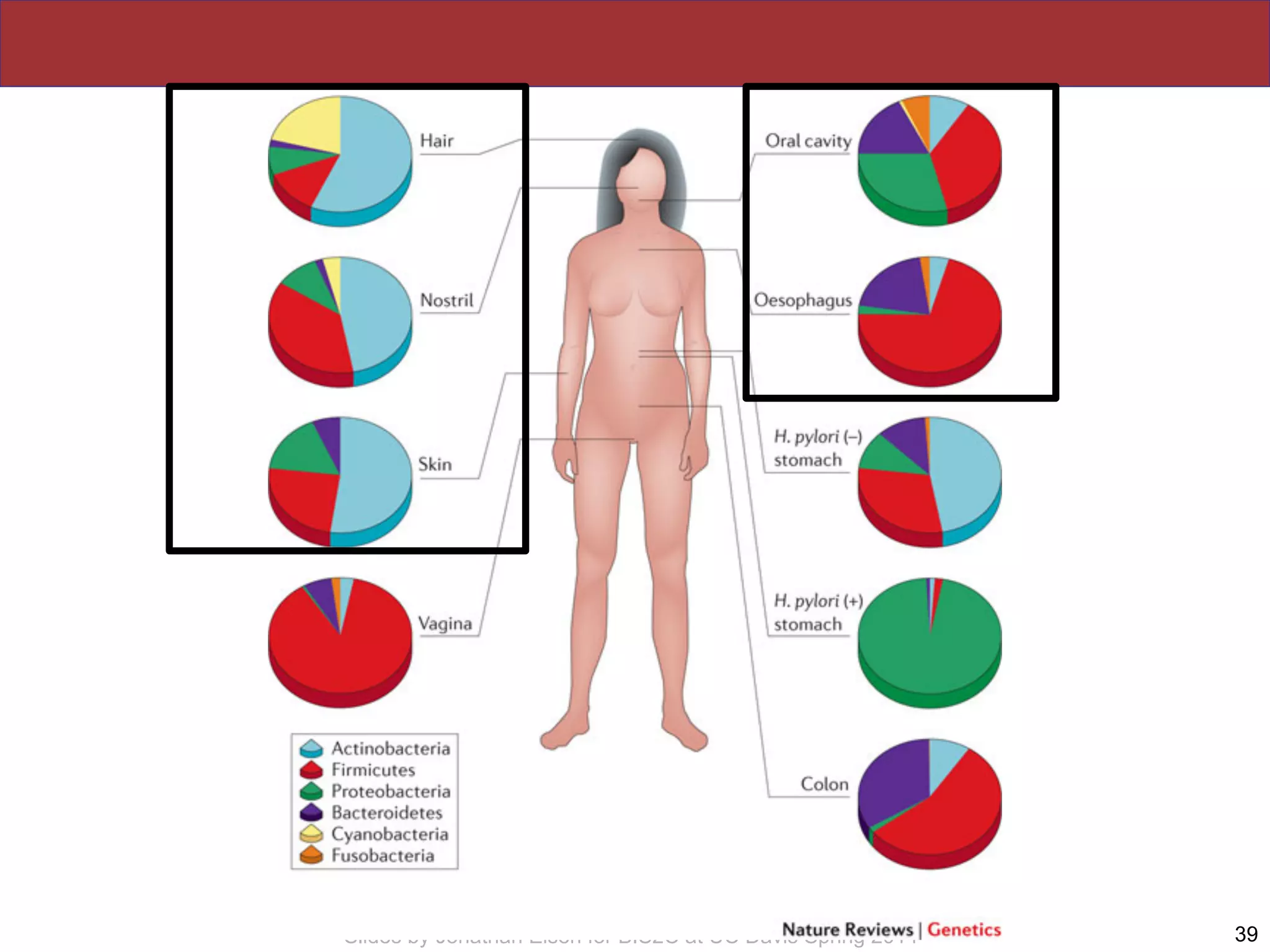
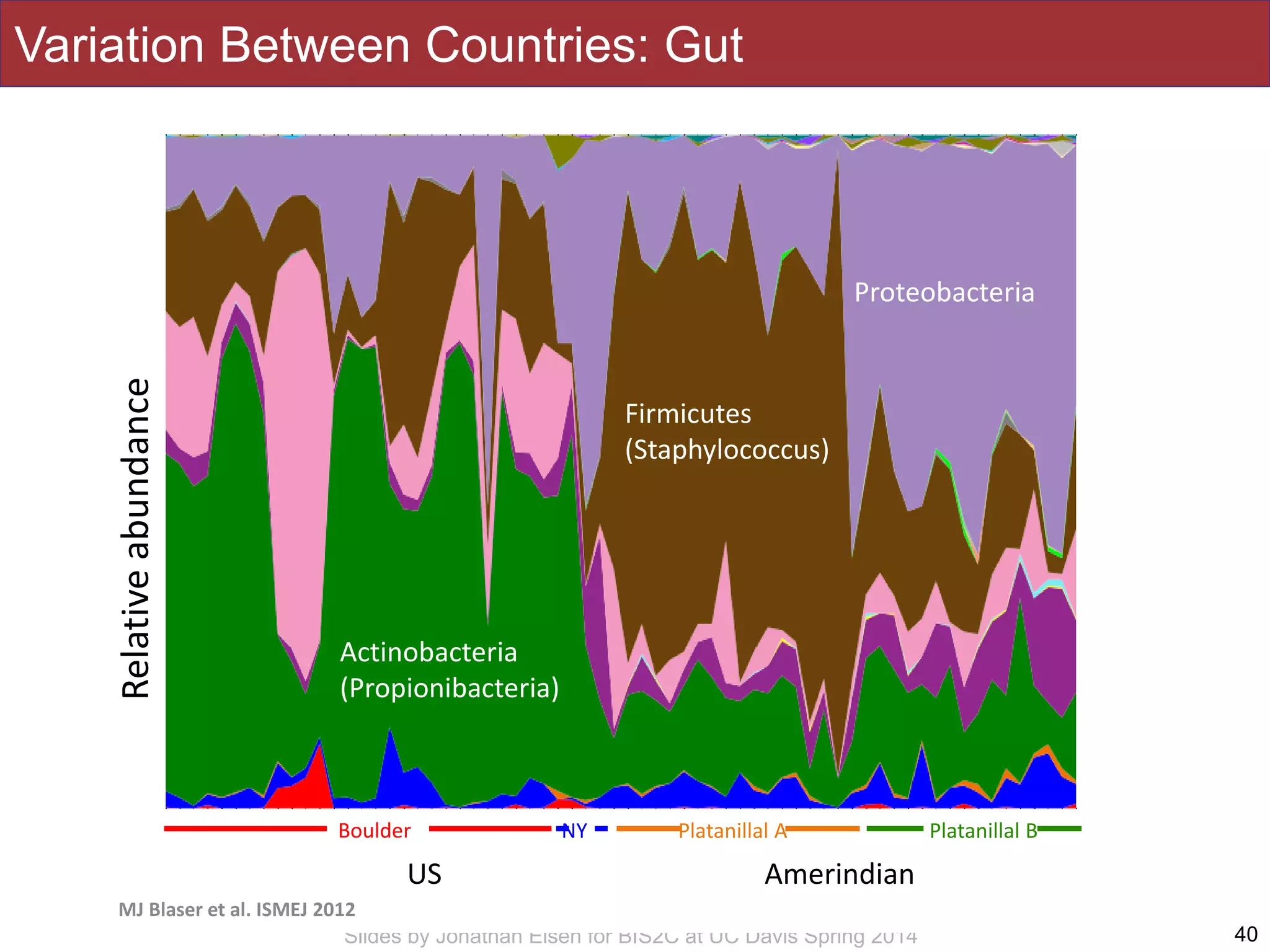
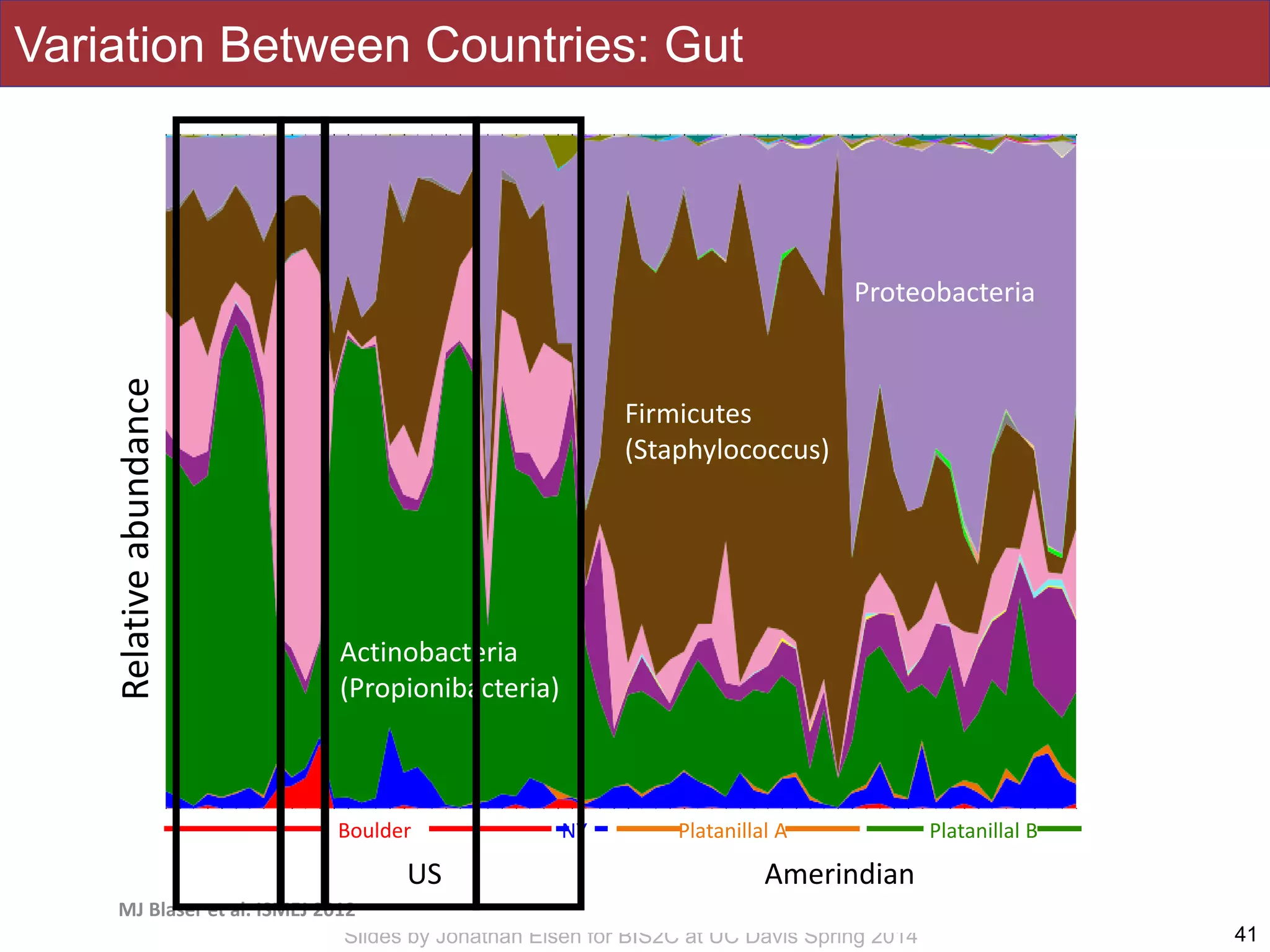
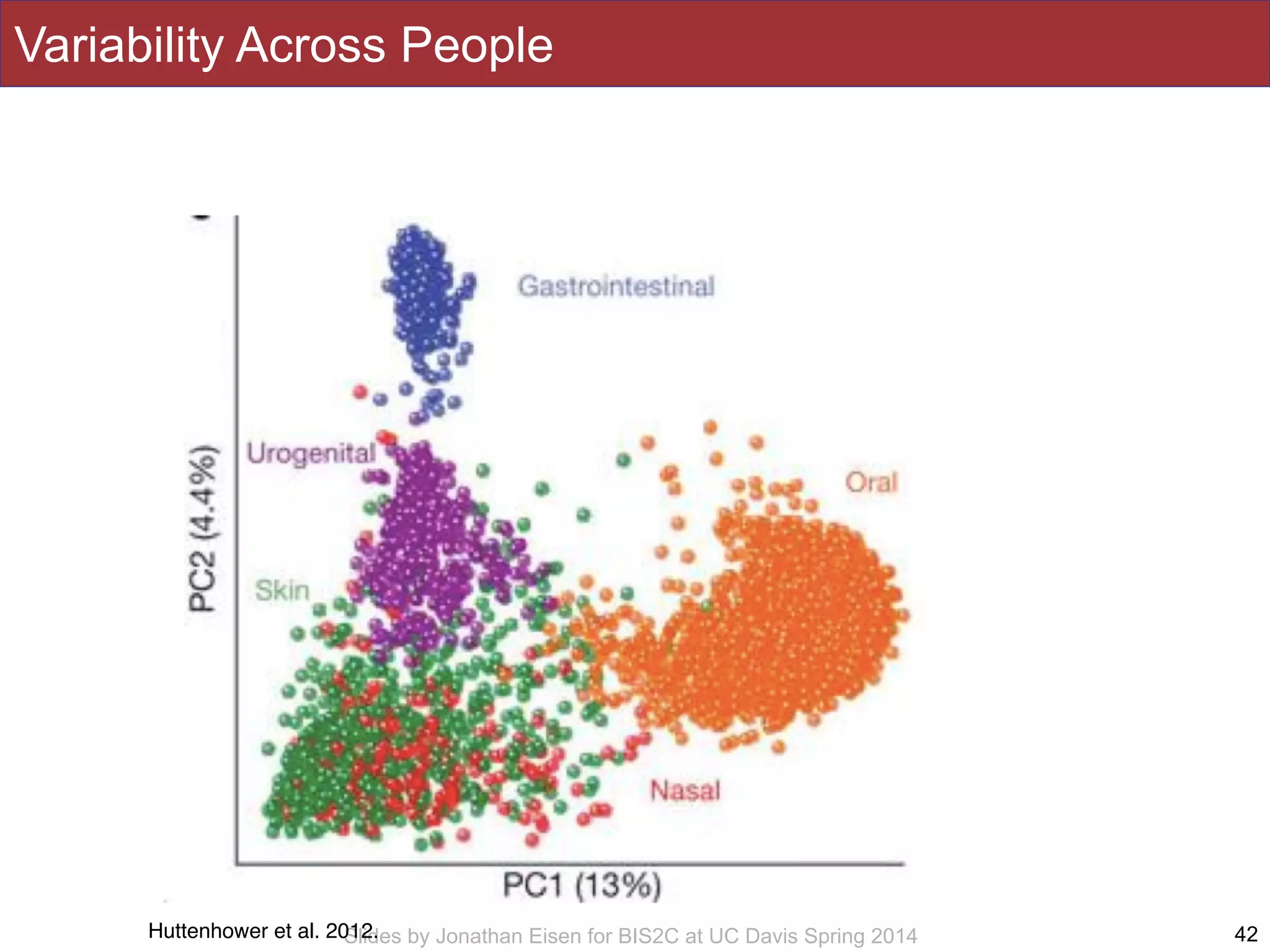
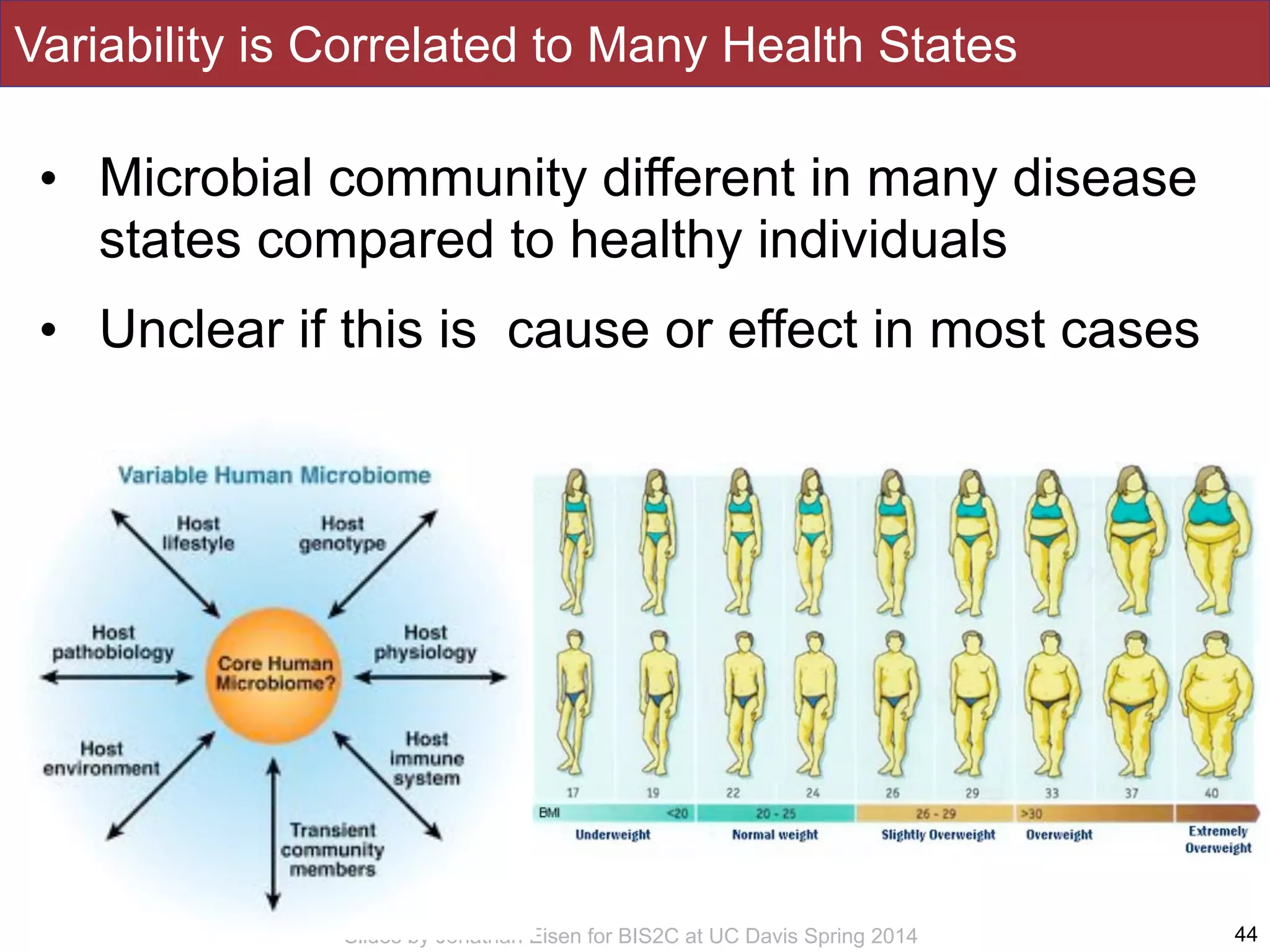
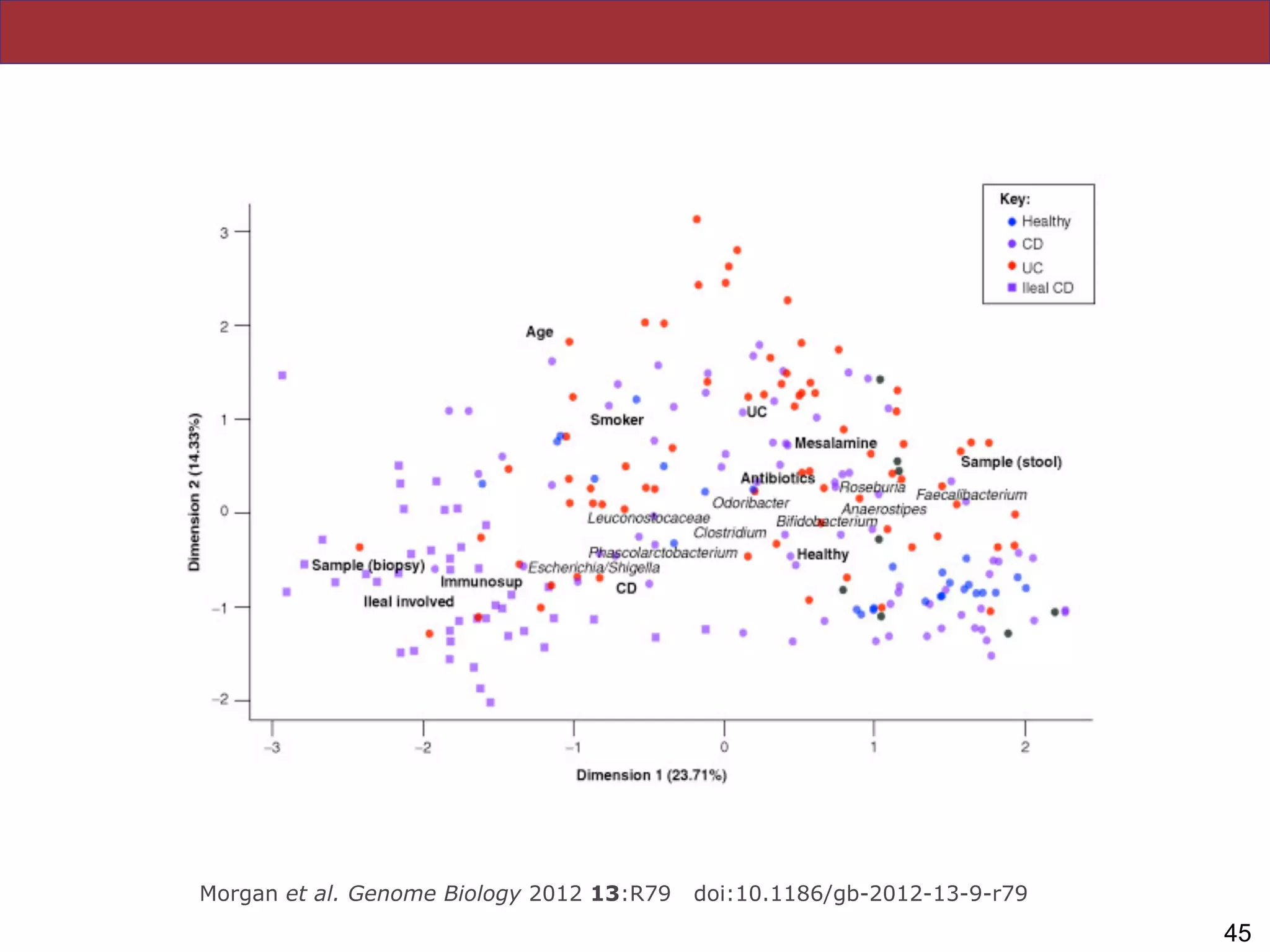
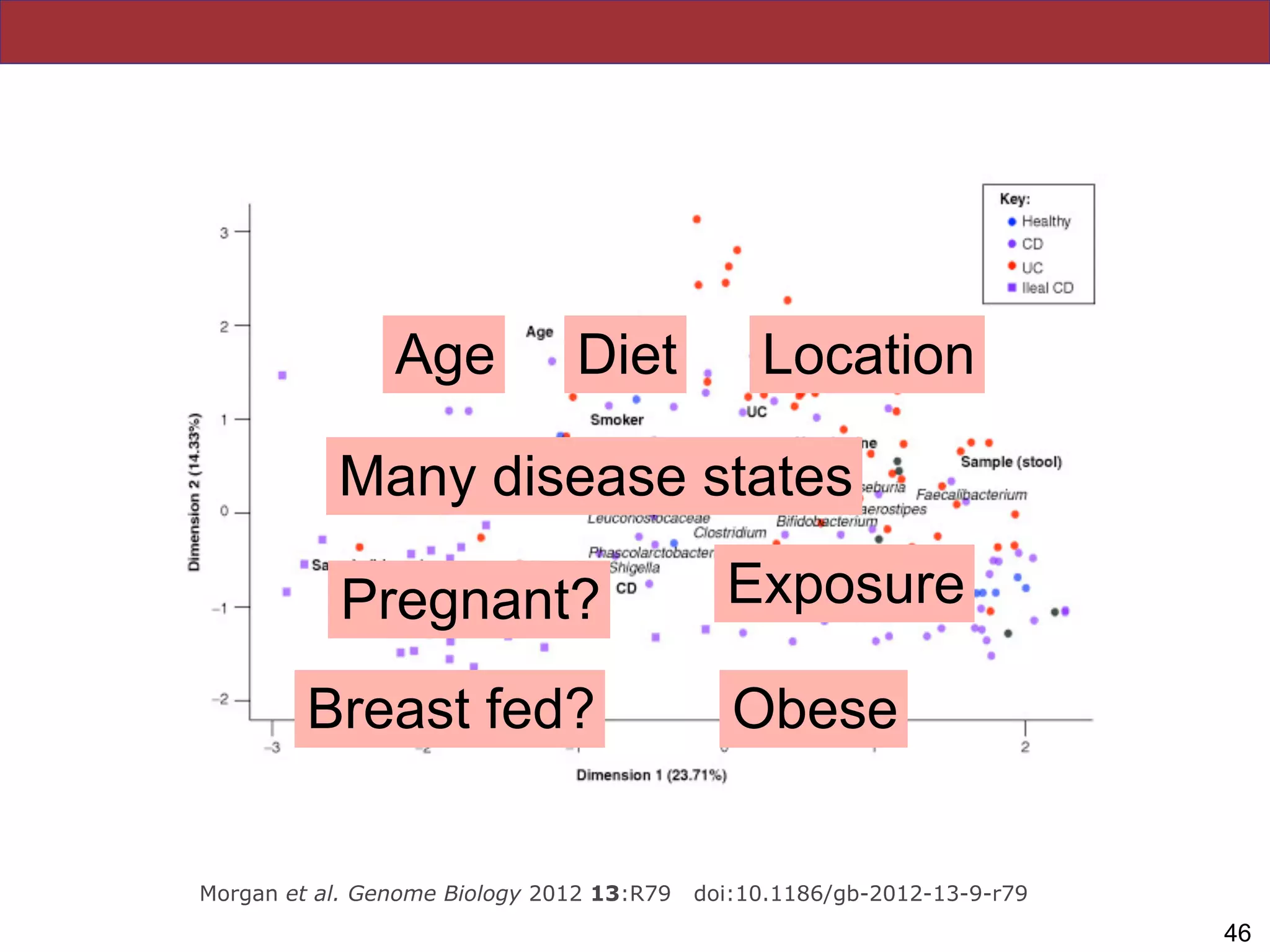
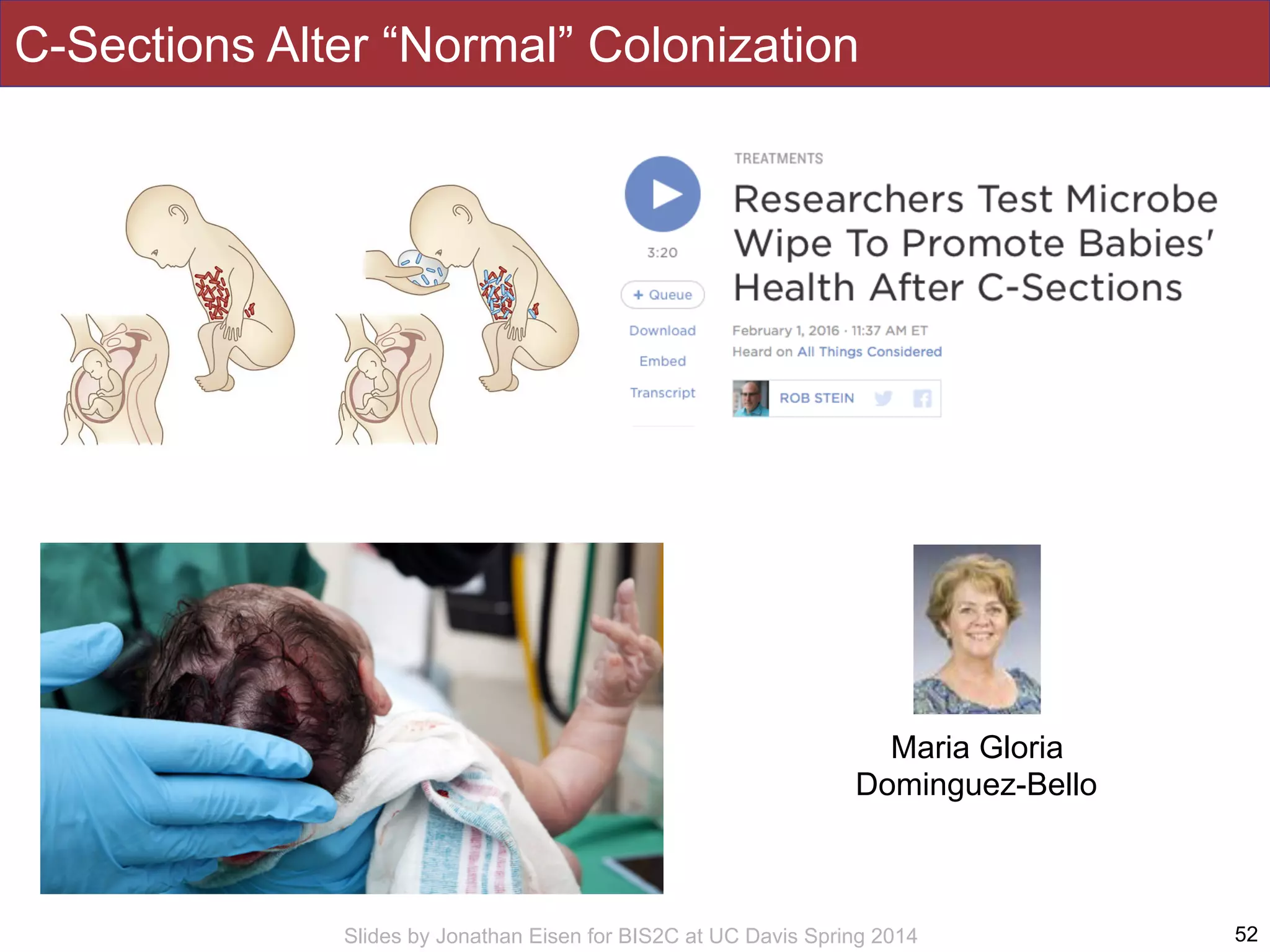
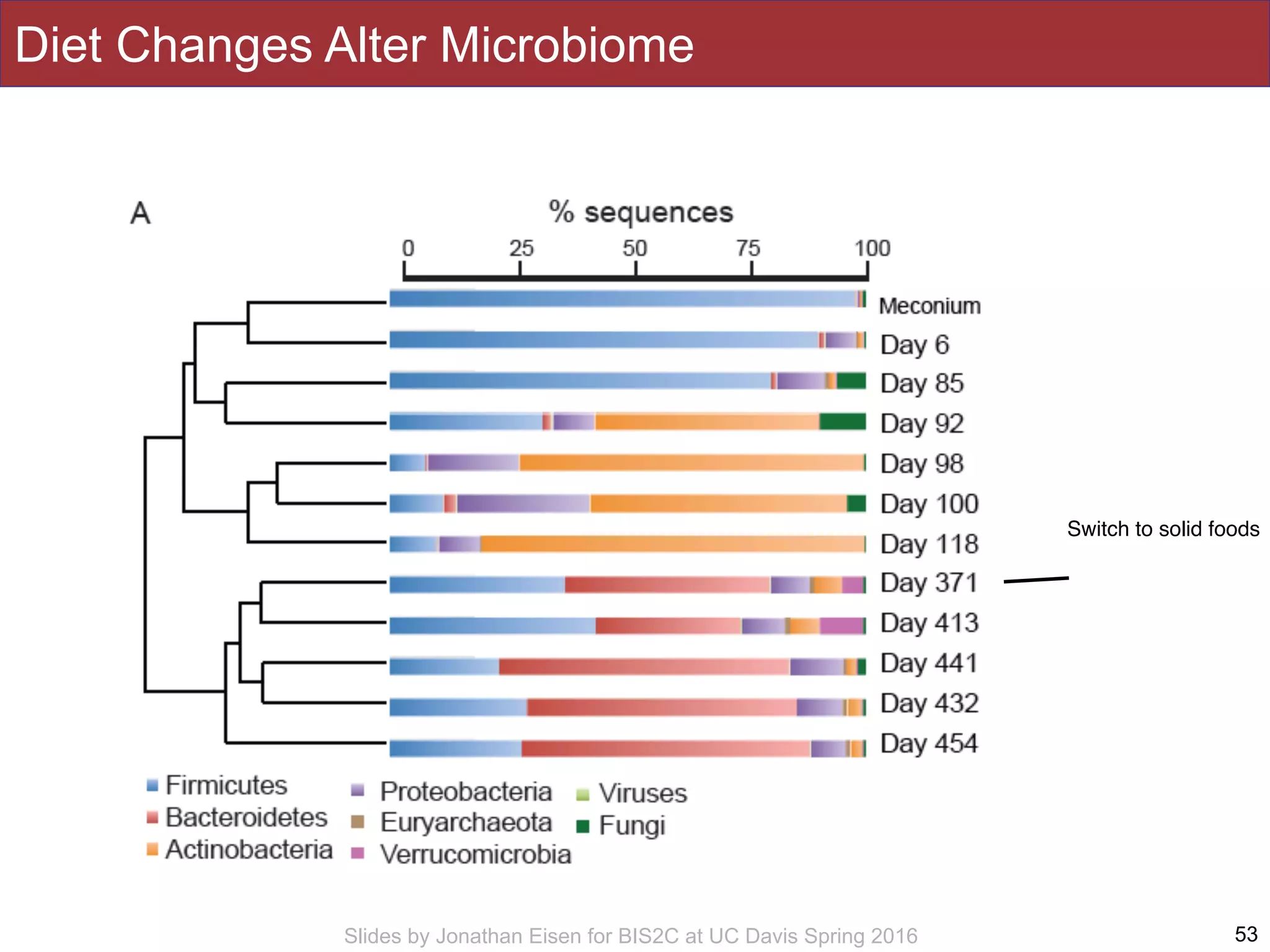
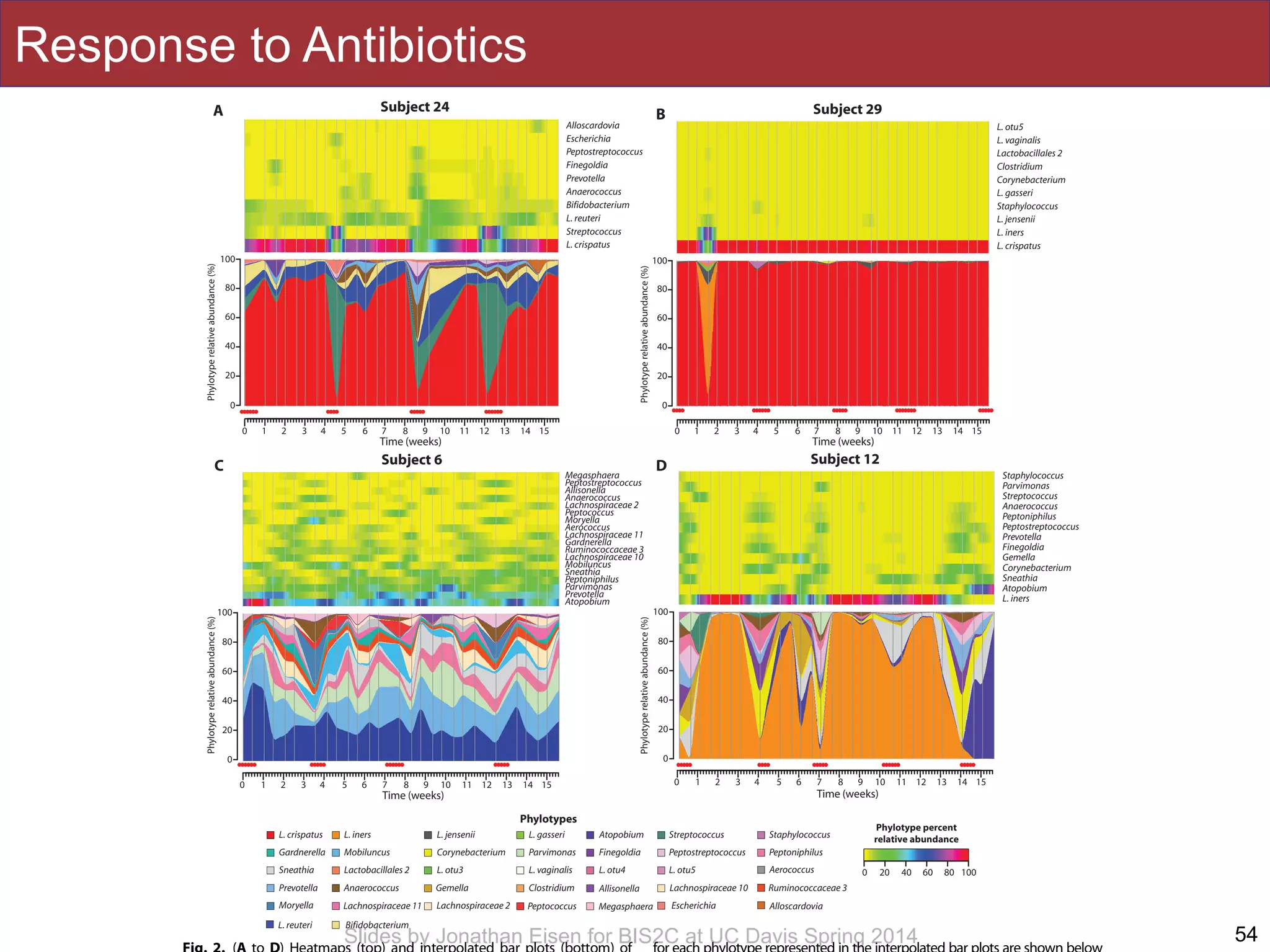
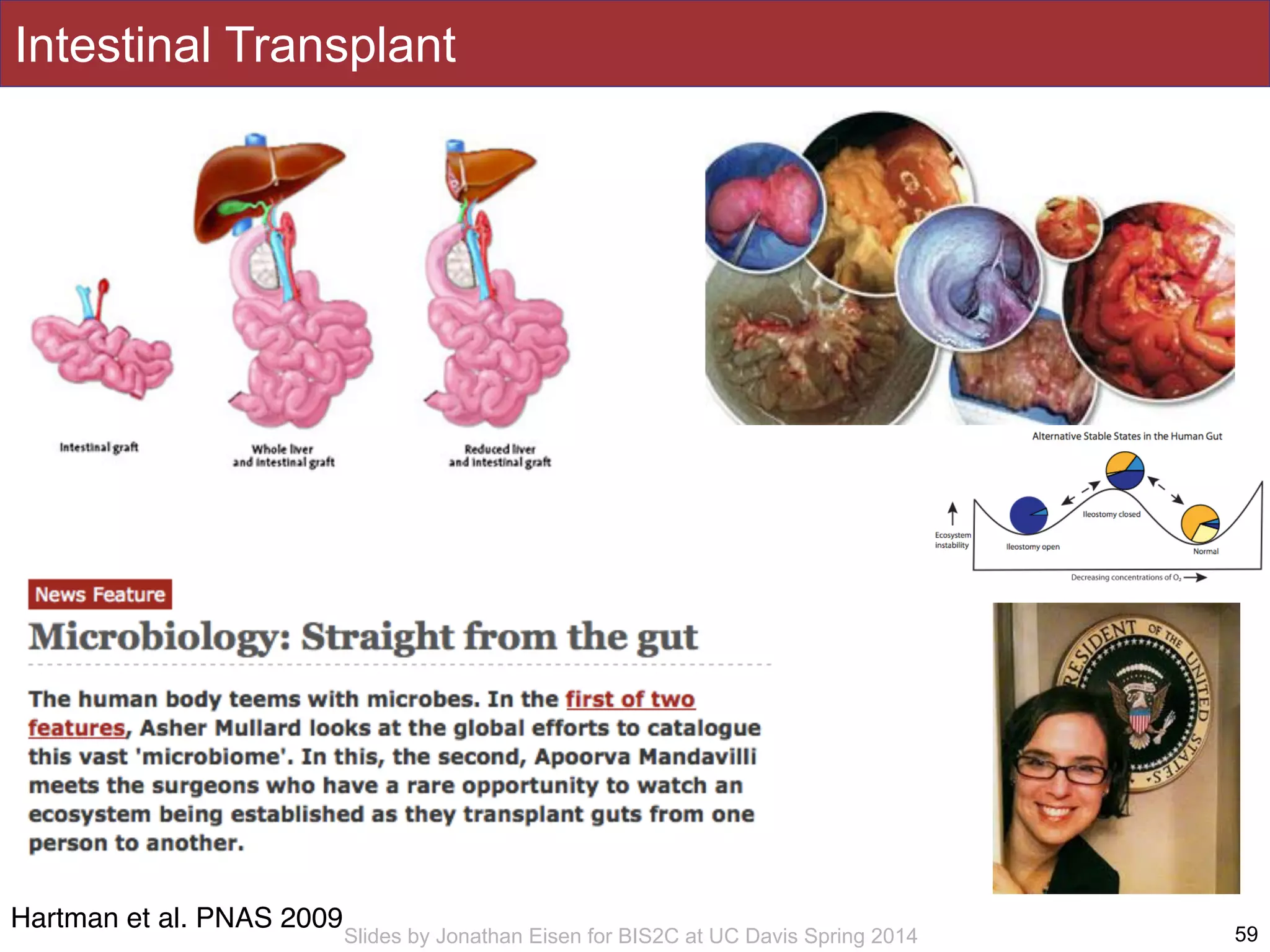
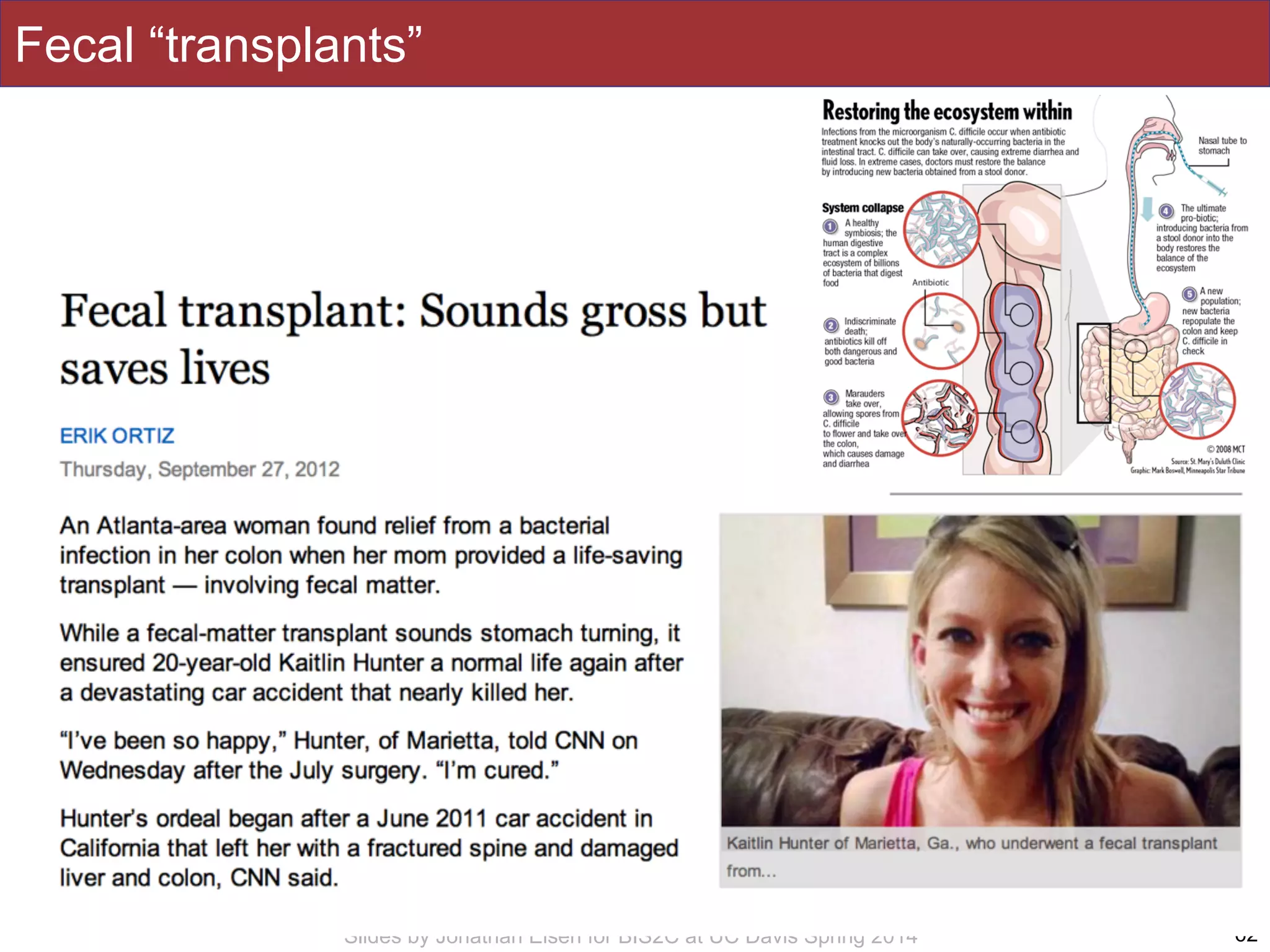
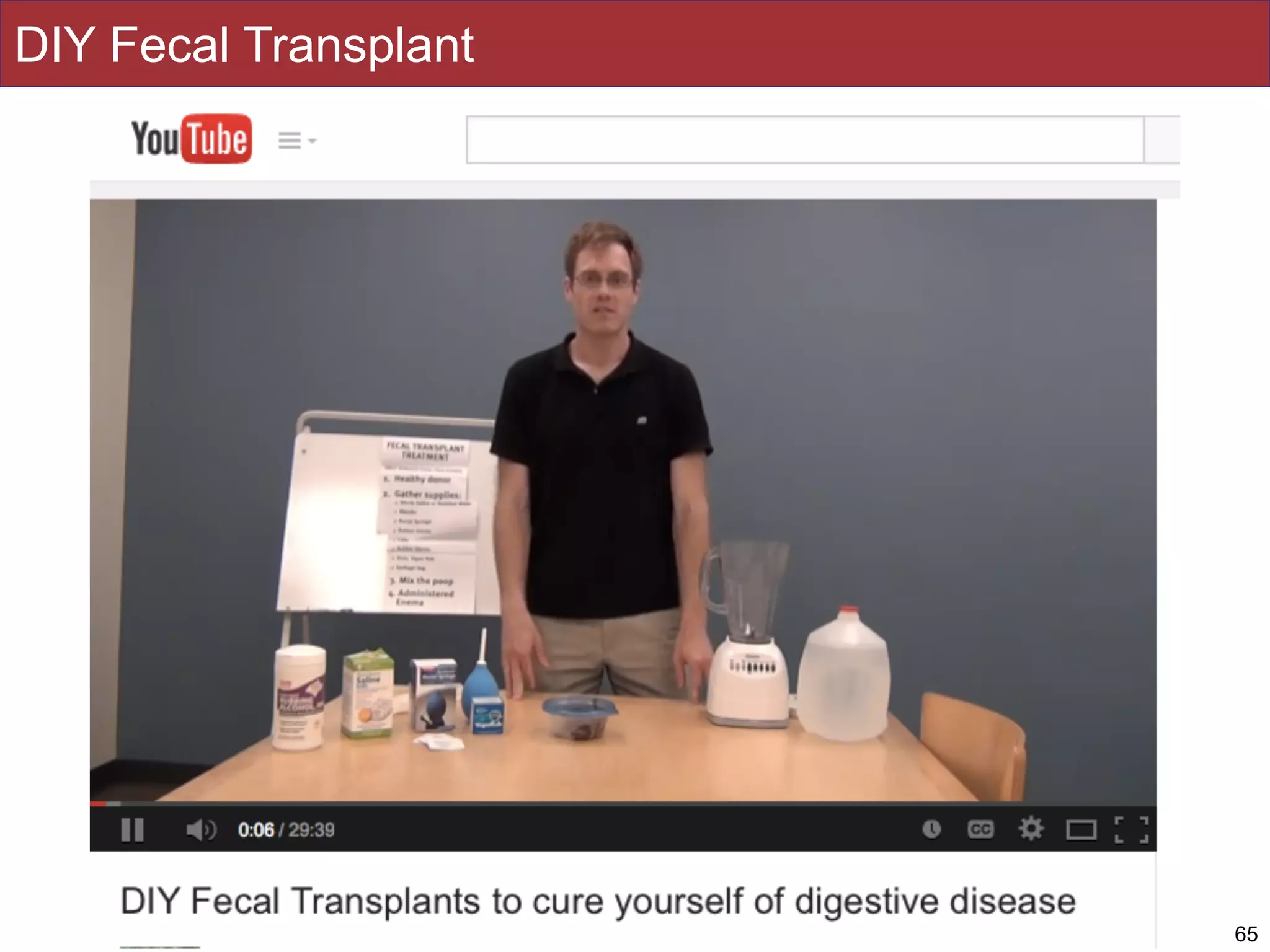
The document summarizes a lecture on the human microbiome. It discusses how humans are colonized by vast numbers of microbes, forming complex microbial ecosystems. There is enormous variation in microbiome composition both within and between individuals, and this variation is associated with health states and phenotypes. Research has identified some possible causes of microbiome variation and suggests it may be possible to alter or restore microbiome composition.