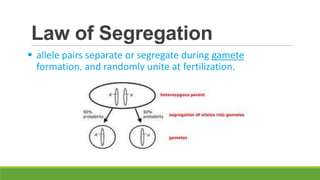
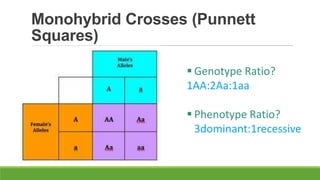
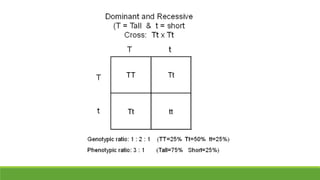
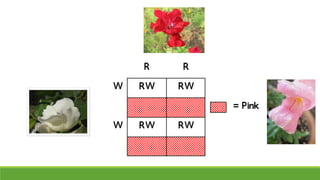
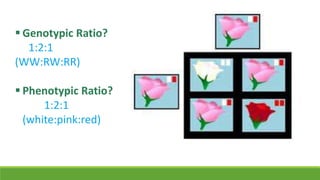
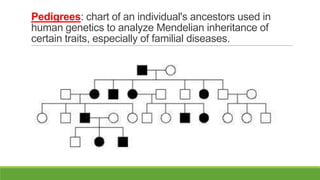
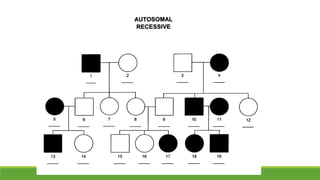
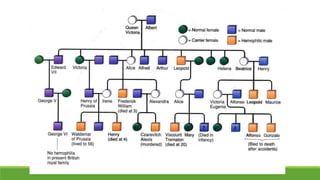
The document summarizes key concepts in genetics including alleles, dominant and recessive traits, monohybrid and dihybrid crosses, incomplete dominance, sex-linked traits, multiple alleles, and pedigrees. It provides examples of Punnett squares to determine possible genotypes and phenotypes of offspring from genetic crosses between parents with different traits. Key terms like phenotype, genotype, homozygous, and heterozygous are defined.