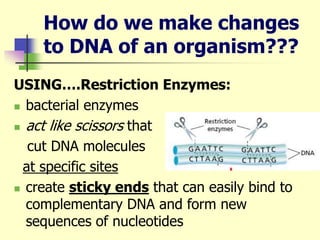
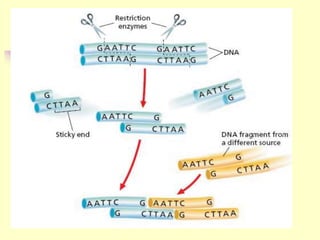
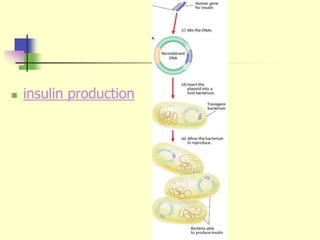
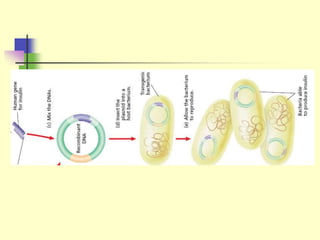
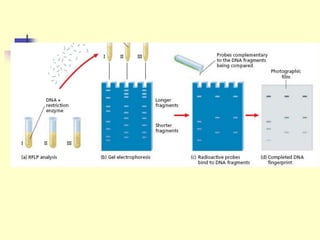
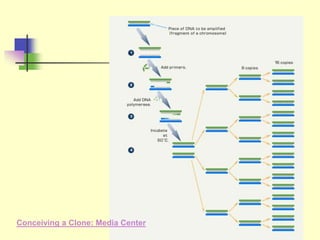
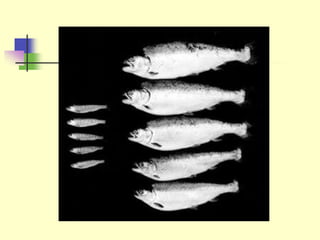
Genetic engineering is the process of manipulating DNA to modify or improve organisms. It uses techniques like restriction enzymes to cut DNA at specific sites, allowing genes from one organism to be spliced into another. For example, plasmids from bacteria can be altered to contain human genes, then inserted back into the bacteria to produce human proteins like insulin at large scale. Genetic engineering has applications in medicine, agriculture, forensics, and research. However, some safety issues need further study, such as impacts of genetically modified crops on human health and the environment.