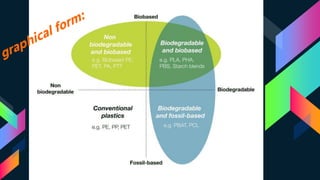
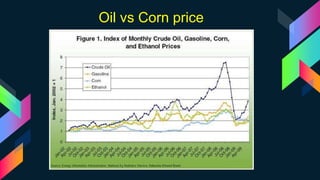
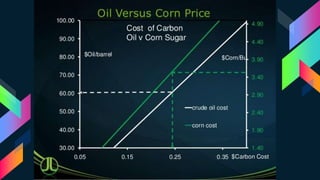
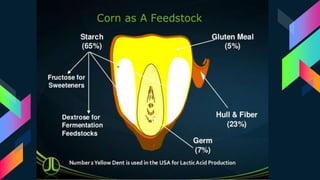
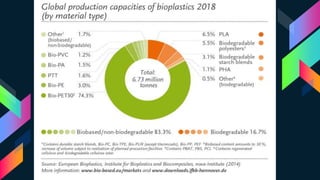
This document discusses bioplastics, which are plastics derived from renewable biomass sources such as vegetable fats and oils, corn starch, or microbiota. It describes the classification of plastics as thermosets or thermoplastics and classifications based on origin as synthetic, bioplastic, biodegradable, or non-biodegradable. Key bioplastic polymers discussed include starch-based, sugar-based, and cellulose-based bioplastics as well as synthetic materials. The document also outlines various microorganisms involved in bioplastic production, drivers for bioplastics, and sustainability considerations.
























![References...
›[1] E. S. Stevens, Green Plastics: An introduction to the
new science of biodegradable plastics, Princeton
University Press, New Jersey, 2002.
›[2] M. Vert, Biomacromolecules 6 (2005) 538-546.
›[3] Q. Yang, M. Hirata, Y. Hsu, D. Lu, Y. Kimura, J. Appl.
Polym. Sci. 131 (2014) 39952.
›[4] B. Saulnier, S. Ponsart, J. Coudane, H. Garreau, M. Vert,
Macromol. Biosci. 4 (2004) 232-237.
›[5]
http://worldaccount.basf.com/wa/plasticsAP~ja_JP/portal/
show/content/products/biodegradable_plastics/ecoflex
›[6] V. Nagarajan, M. Singh, H. Kane, M. Khalili, M. J.
Bramucci, Polym. Environ. 14 (2006) 281-287.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vivekplastics-160331033009/85/Bioplastics-34-320.jpg)
