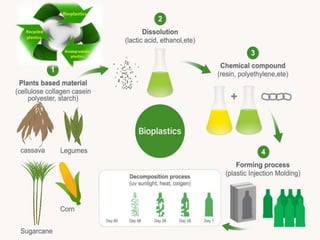
Bioplastics, made from renewable resources like sugarcane and corn, offer a more environmentally friendly alternative to traditional plastics, boasting quicker decomposition rates and reduced carbon footprints. However, they come with challenges such as higher costs, limited composting infrastructure, and potential adverse effects from genetically modified crops. Their applications span various industries, including automotive, electronics, and packaging, highlighting their versatility and growing importance in sustainability efforts.