Embed presentation


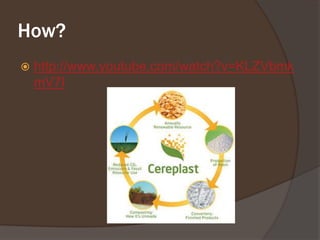






Bioplastics are plastics that are similar in properties to traditional plastics but are derived from renewable biomass sources rather than petroleum, and many are designed to biodegrade. They can be used for both disposable and non-disposable applications like packaging, cups, and phone casings. While bioplastics have benefits like reducing fossil fuel usage and being safer for medical use, they also have drawbacks like higher costs and potential issues with quality, composting, and recycling. As oil prices rise and bioplastic usage increases, they represent an opportunity for crop-producing countries but need to ensure consistency and address issues like methane emissions from composting.








