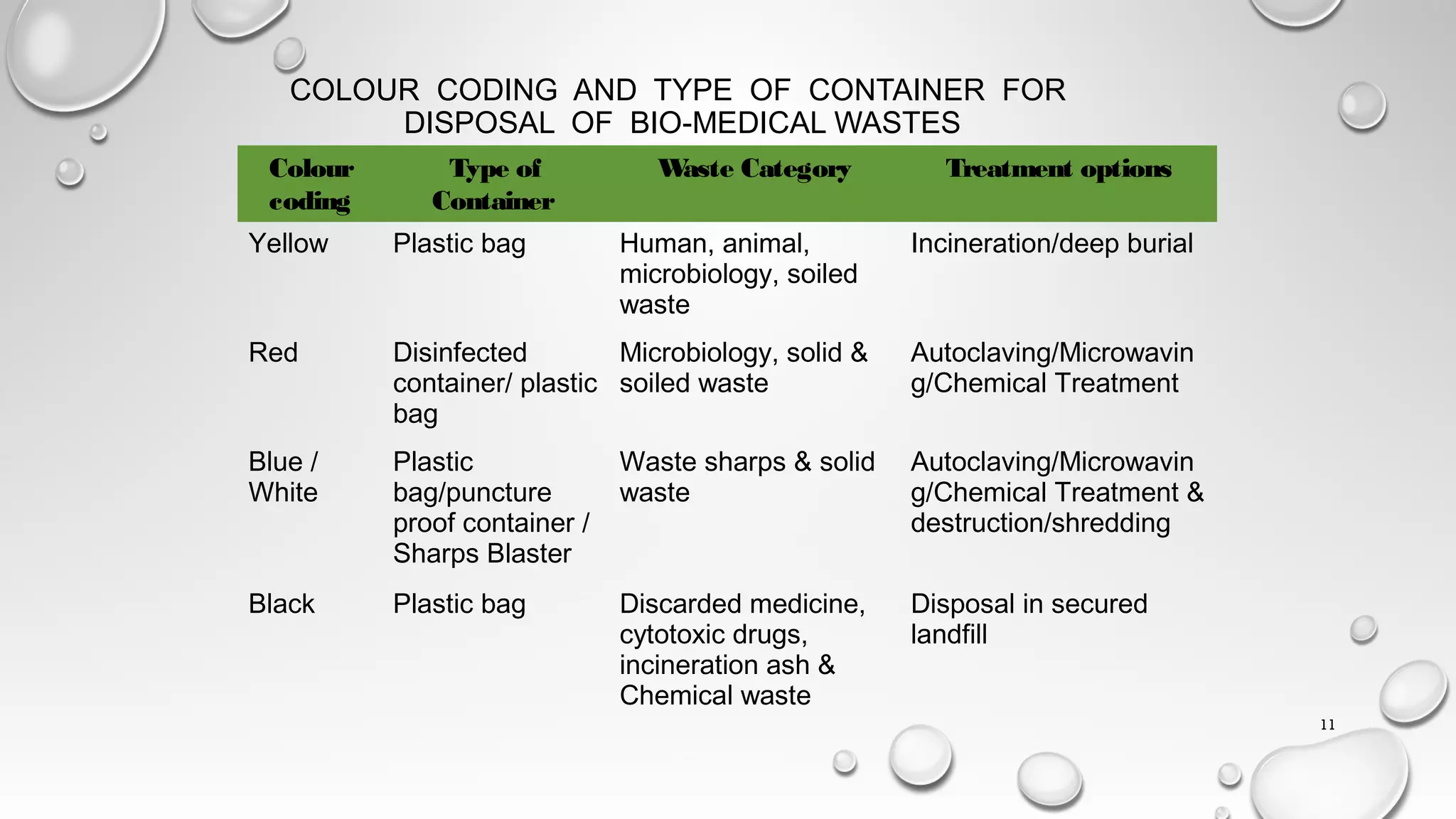
This document discusses biomedical waste management systems. It defines biomedical waste and categorizes it into 10 categories based on type. The types of waste include human tissue, sharps, medications, and more. Improper management of biomedical waste poses health and environmental risks. The key methods for treating biomedical waste mentioned are incineration, autoclaving, hydroclaving, chemical disinfection, and deep burial. India's Biomedical Waste Management Rules outline treatment and disposal standards, including color-coding of waste containers. The rules were updated in 2016 to apply to all healthcare facilities uniformly.