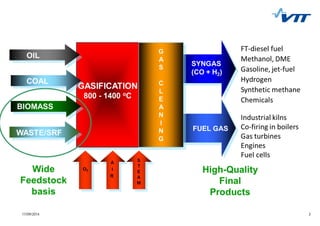
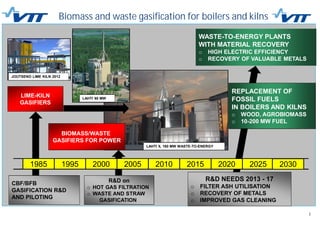
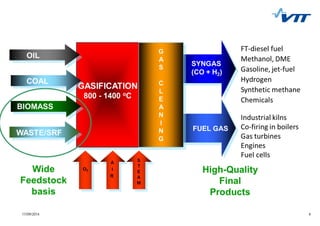
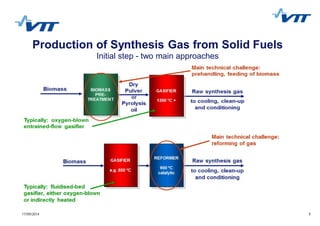
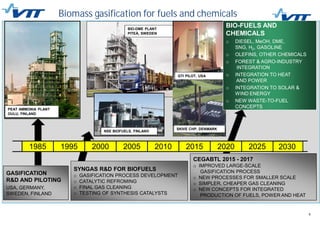
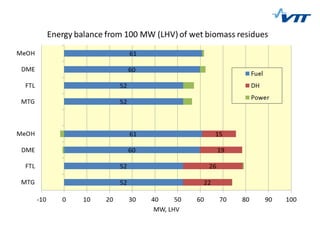
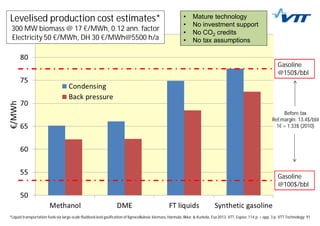
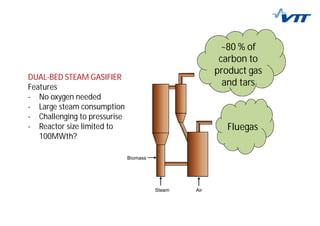
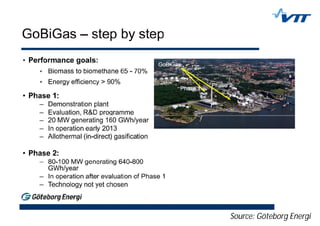
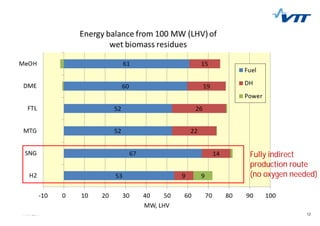
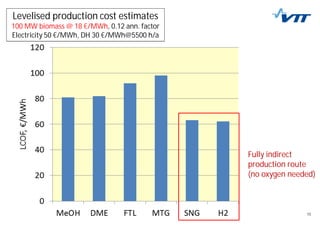
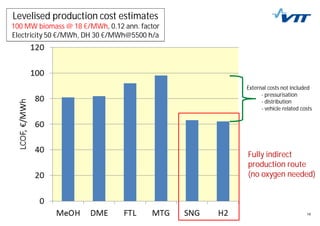
This document summarizes biomass gasification technologies. It discusses various biomass gasification applications including waste-to-energy plants that recover materials, replacing fossil fuels in boilers and kilns, and producing synthesis gas for fuels and chemicals. Technologies are at different stages of development from commercial power plants to R&D on gas cleaning and new concepts. Large scale gasification for liquid fuels is technically demonstrated but high capital costs require large plants with high utilization to be economically competitive compared to petroleum-derived fuels.