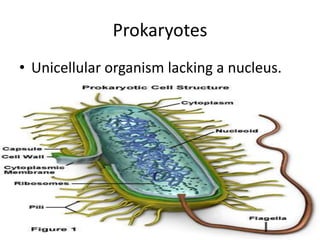
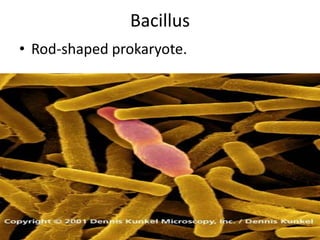
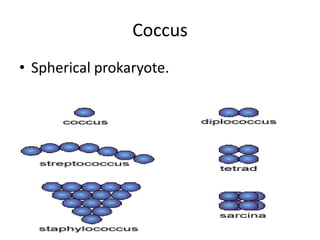
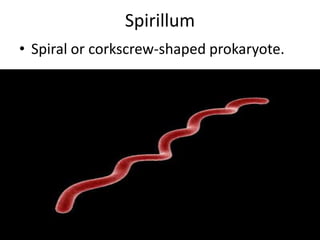
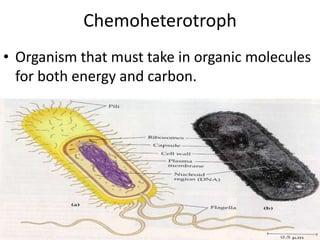
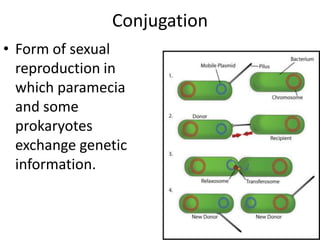
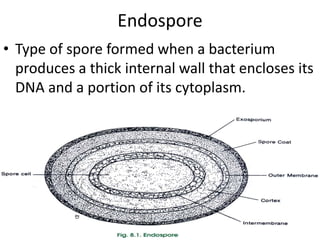
This document defines and describes different types of bacteria and their characteristics. It discusses bacteria that are prokaryotes, different shapes including bacillus and coccus, and how they obtain energy and carbon including photoautotrophs, chemoautotrophs, and chemoheterotrophs. It also covers various forms of reproduction in bacteria like binary fission, conjugation, and endospores. Key processes like nitrogen fixation are also defined.