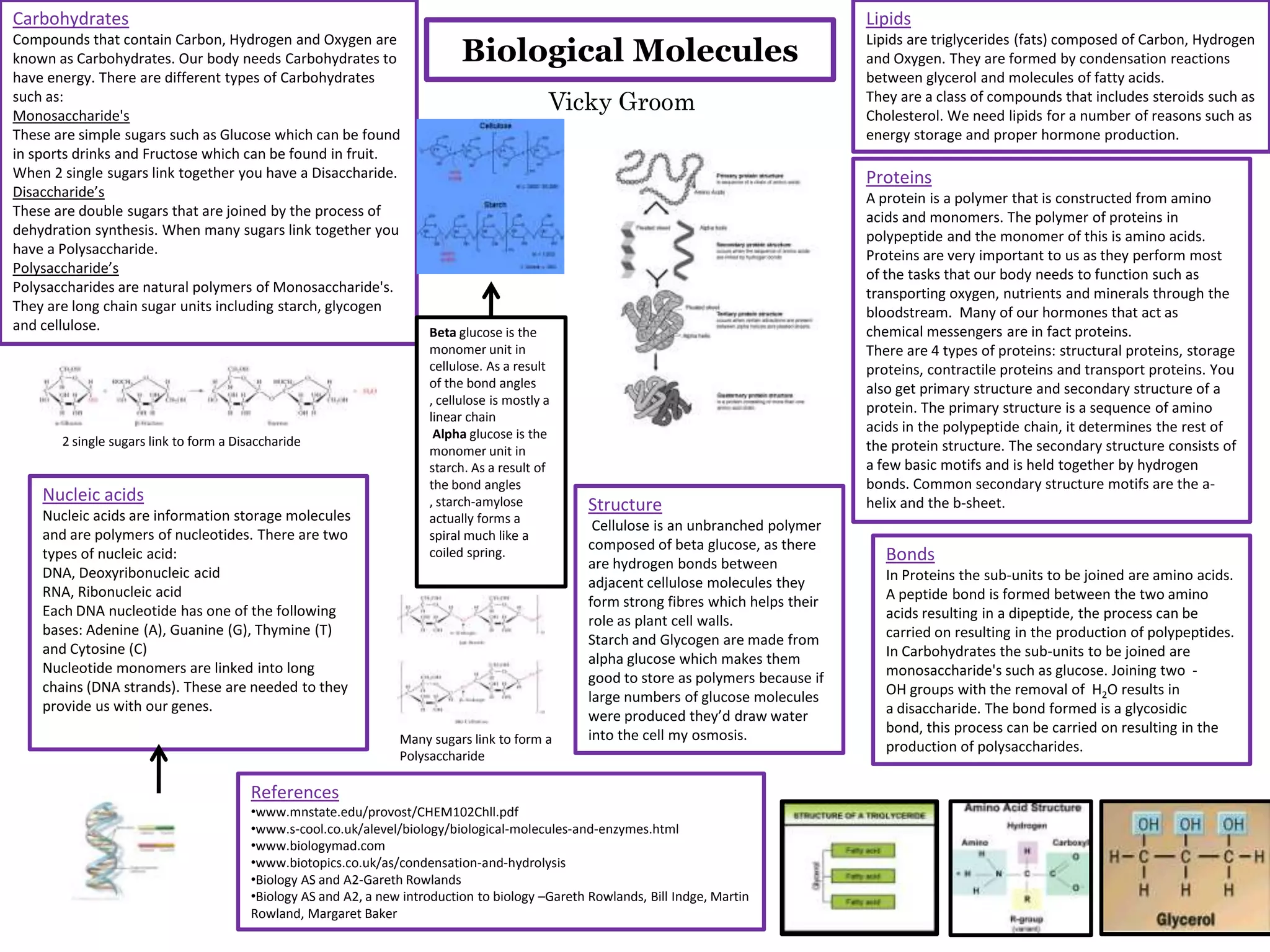
Carbohydrates are compounds made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. They provide our bodies with energy and come in three types: monosaccharides like glucose and fructose, disaccharides formed when two monosaccharides join, and polysaccharides consisting of many joined sugar units like starch, glycogen, and cellulose. Lipids are triglycerides composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen that provide energy storage and hormone production. Proteins are polymers of amino acids that perform critical functions like oxygen transport and hormone messaging. Nucleic acids are information-storing polymers including DNA with bases of adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine, and RNA.