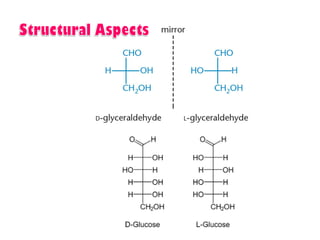
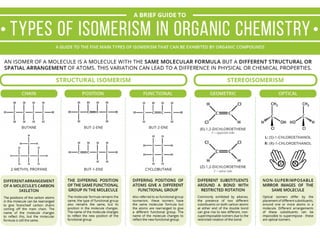
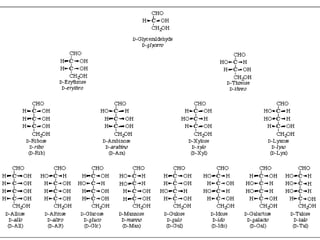
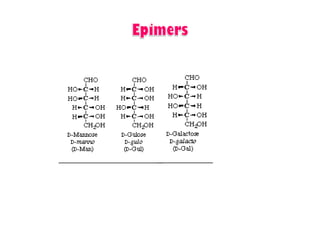
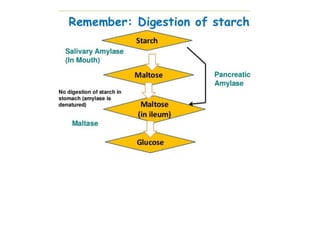
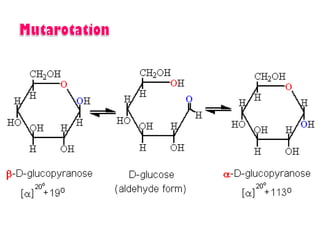
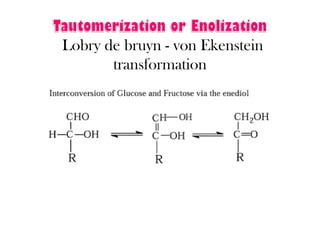
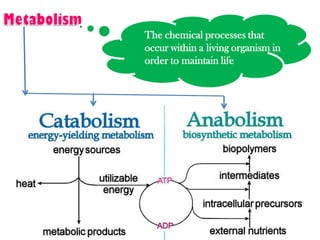
This document discusses carbohydrate metabolism and related pathways in the human body. It covers:
- The roles of carbohydrates in providing energy and fuel for muscles and the central nervous system.
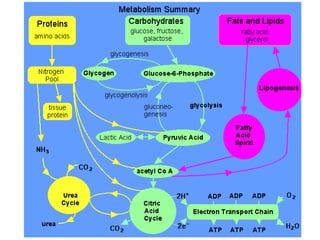
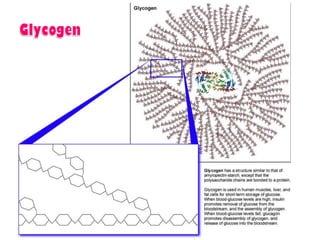
- Glycogen storage locations and amounts in the body. Glycogen stored in muscles is used directly by that muscle during exercise.
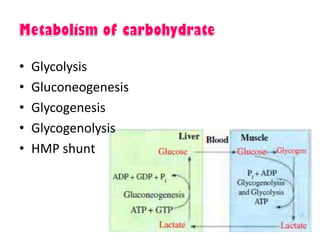
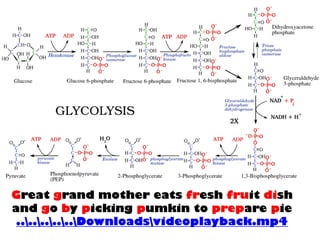
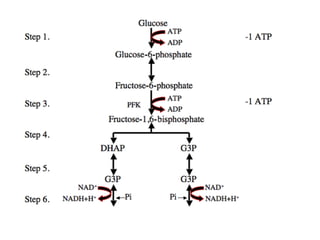
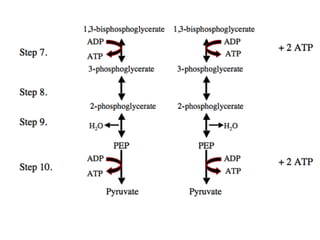
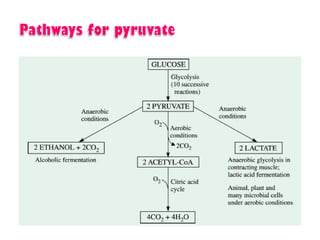
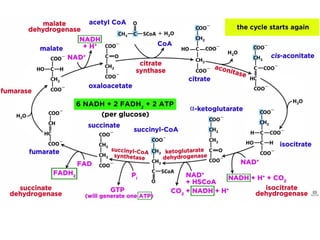
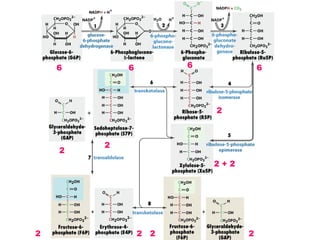
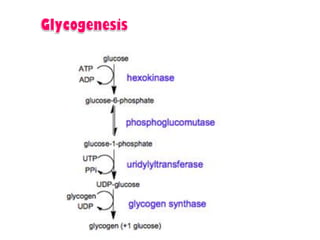
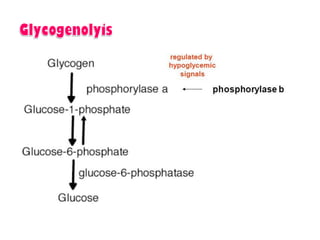
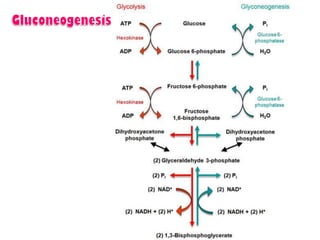
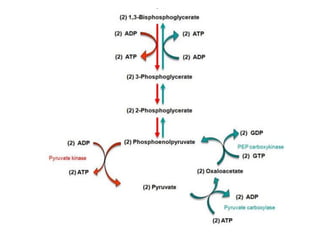
- Key pathways involved in carbohydrate metabolism including glycolysis, gluconeogenesis, glycogenesis, glycogenolysis, the HMP shunt, and the pentose phosphate pathway.
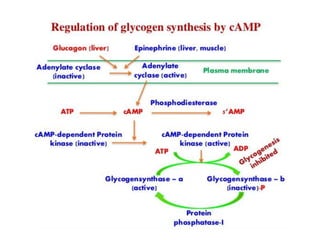
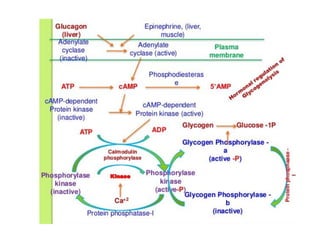
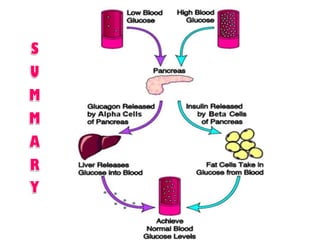
- Coordination of glycogen synthesis and degradation through regulating enzymes to maintain blood glucose levels.