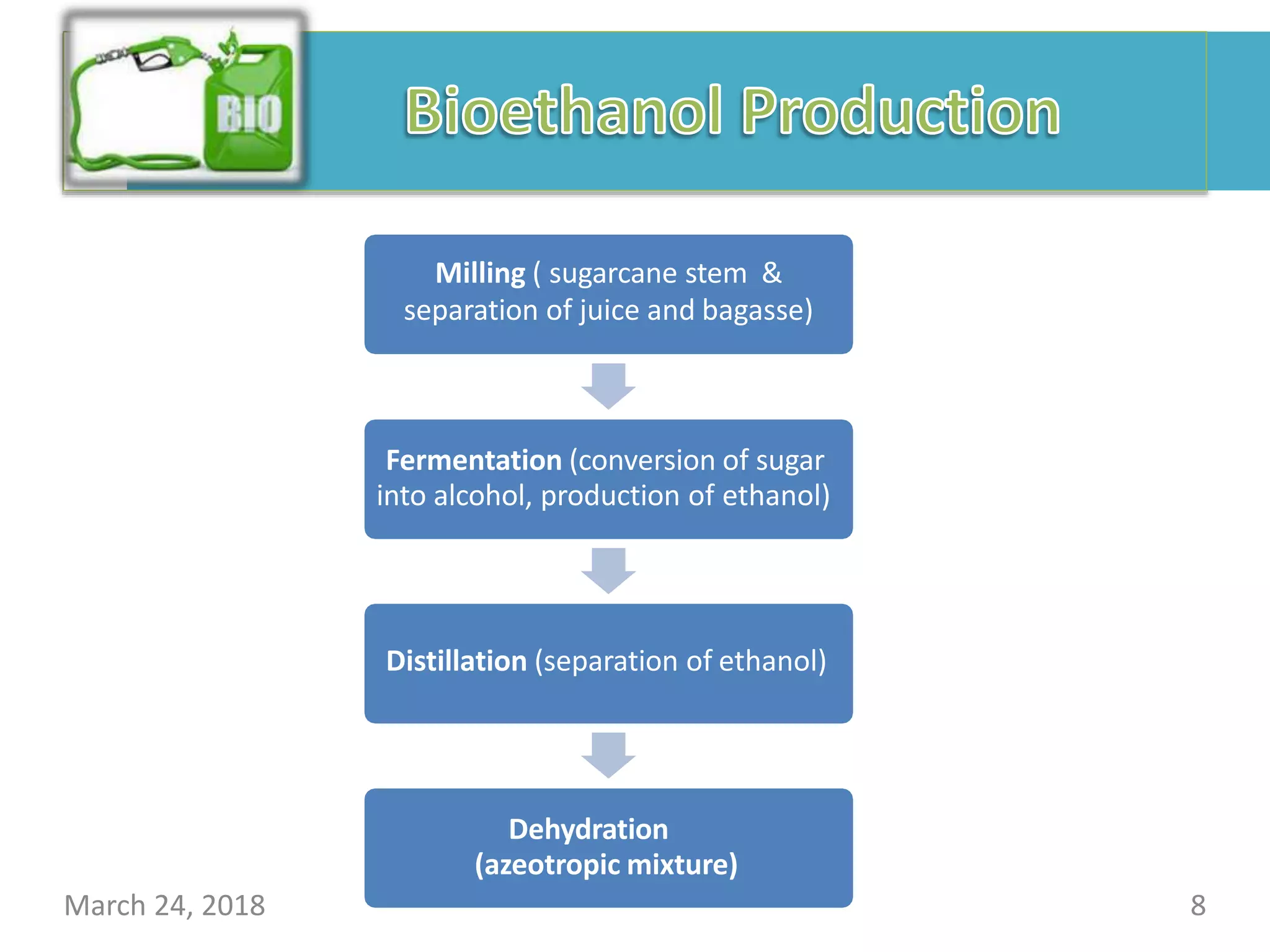
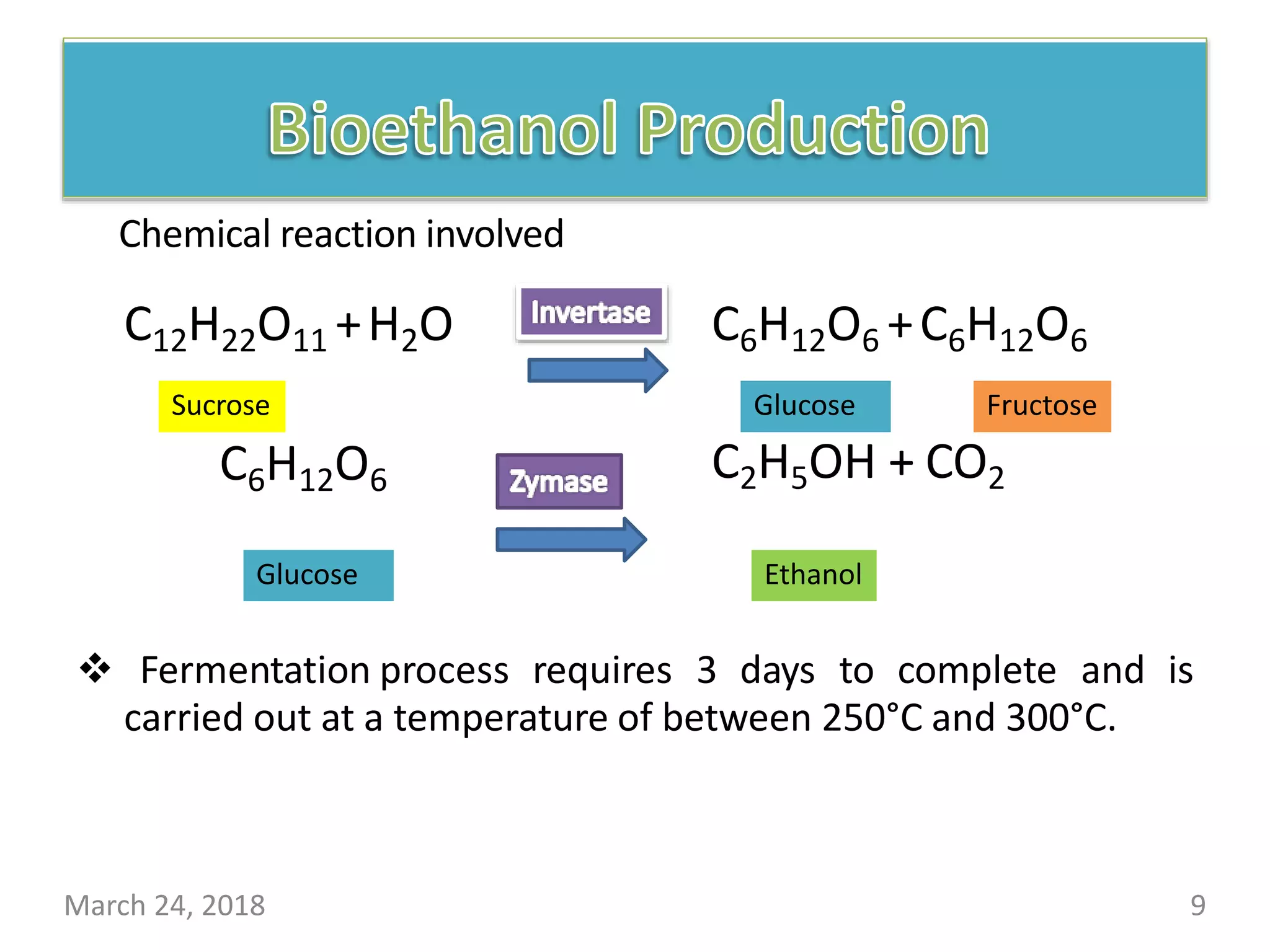
This document presents information about biofuels. It discusses various biofuel feedstocks like corn, sugarcane, and algae. It classifies common biofuels as bioethanol, biodiesel, and biogas. Bioethanol is produced through fermentation of carbohydrate sources and is used as an automotive fuel. Biogas is produced through anaerobic digestion of organic waste and used for cooking and lighting. While biofuels are renewable and reduce pollution, their production also faces challenges related to cost, land use, and food supplies.