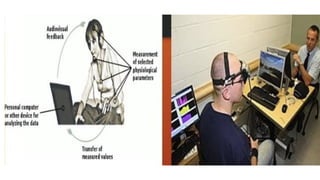
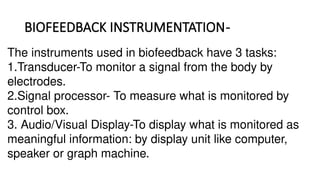
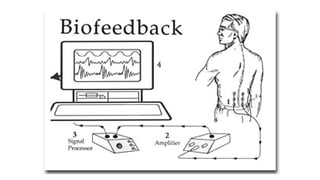
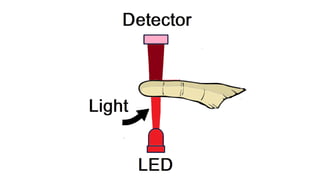
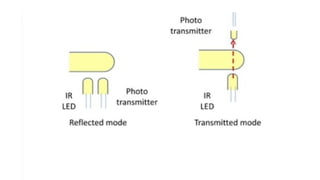
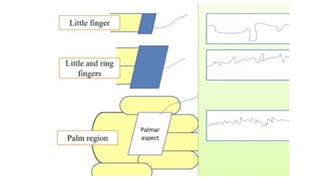
The document discusses biofeedback as a therapeutic technique that uses electronic devices to measure and provide feedback on physiological functions, thereby helping individuals gain control over bodily processes such as muscle activity and stress levels. It outlines the instrumentation used in biofeedback, including transducers, signal processors, and displays, along with various applications such as treating migraines, urinary incontinence, and spasticity. Additionally, it highlights the general principles, limitations, and importance of accurate, relevant, and rapid feedback in enhancing motor learning.