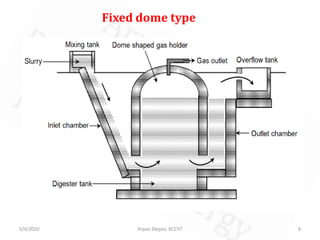
This document discusses various aspects of bioenergy. It begins by defining biogas as a mixture of gases produced from organic waste through anaerobic digestion by bacteria. There are two main types of biogas plants - fixed dome and floating gas holder. The document then discusses the processes of anaerobic digestion, gasification, and liquefaction as three main methods to extract energy from biomass. It provides details on biodiesel production from sources like algae, carbohydrates, oils, and agricultural wastes. The advantages and disadvantages of different bioenergy methods like biogas, gasification, and biodiesel are also summarized.