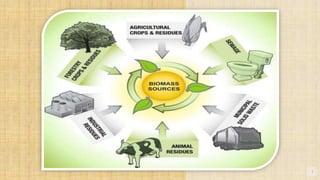
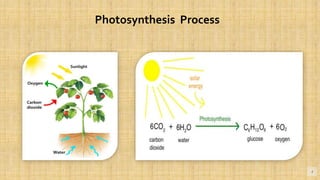
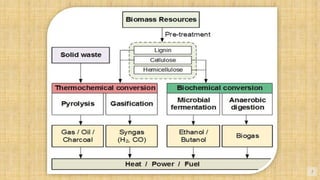
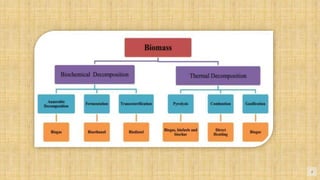
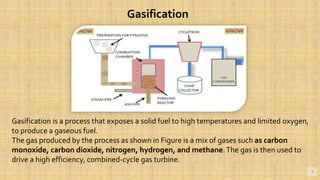
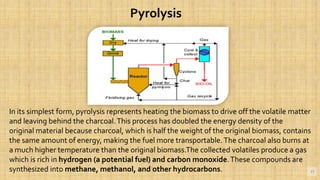
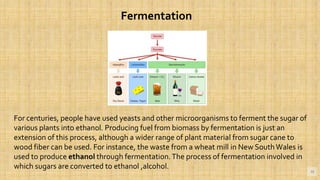
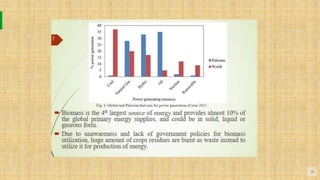
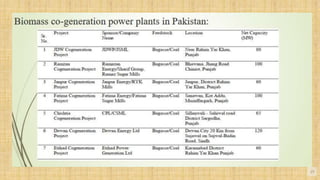
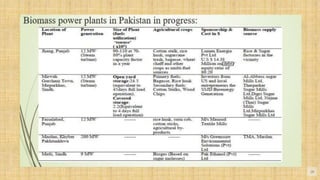
Biomass is organic matter from plants and animals that can be used as a renewable source of energy. It includes materials like wood, manure, and plant waste. Biomass contains stored solar energy and is considered renewable because plants and organic matter can regrow or be replenished. There are several methods to extract energy from biomass, including direct combustion, gasification, anaerobic digestion, pyrolysis, and fermentation. Each method has advantages such as being renewable and producing a usable fuel, though they also have disadvantages like emissions or inefficient energy conversion. Pakistan relies on biomass such as wood for domestic energy needs given its availability.