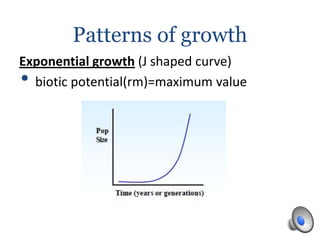
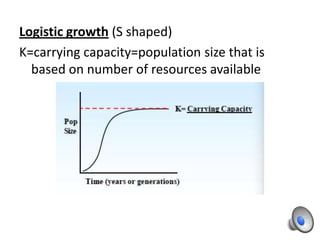
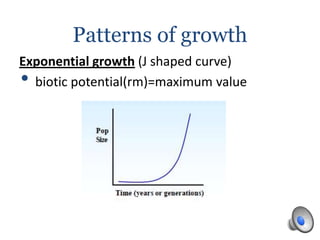
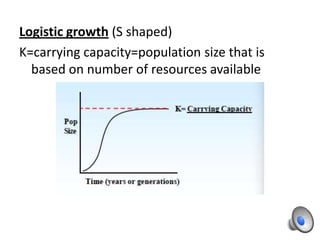
Population growth is determined by biotic potential, which promotes positive growth through intrinsic factors like litter size and gestation, and environmental resistance, which limits growth through extrinsic factors such as weather and food supply. Populations can experience exponential or logistic growth patterns depending on available resources. Limiting factors that influence population size can be density-dependent, like competition and disease, or density-independent, such as weather events. Over time, natural selection causes populations to adapt as limiting factors place stress on populations and favor the survival of the best adapted organisms.