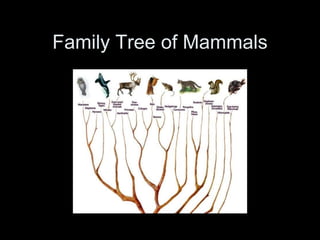
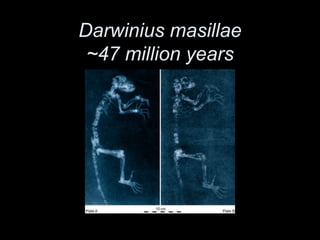
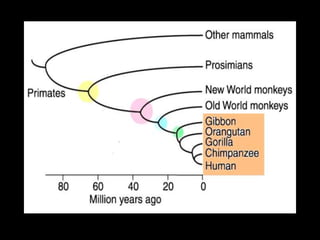
Primates emerged around 58 million years ago and can be divided into several families including prosimians, New World monkeys, Old World monkeys, and hominoids. Primates are distinguished from other mammals by adaptations for tree living like stereoscopic vision, grasping hands, and large brains. The hominoids are the group that includes both apes and humans, who are tailless with large, complex brains and who are good suspensory climbers. Chimpanzees are our closest living relatives, with whom we share over 98% of our DNA.