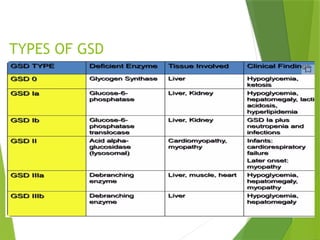
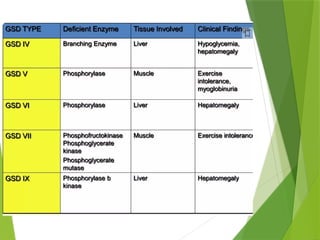
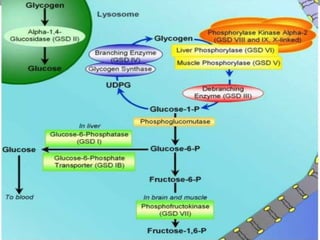
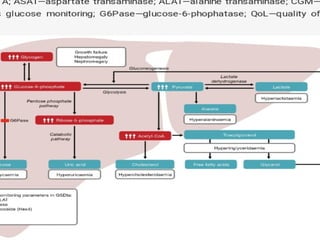
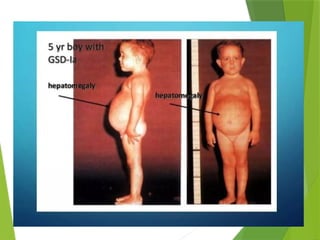
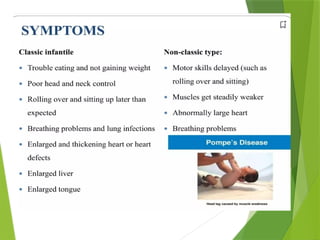
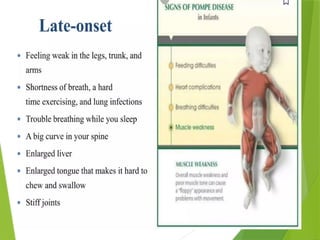
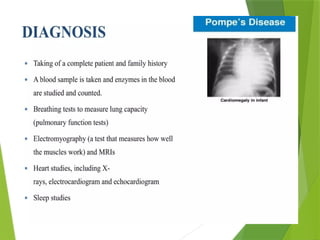
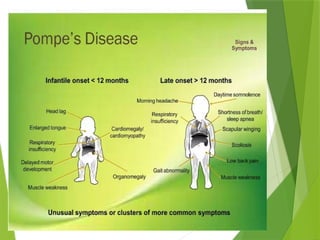
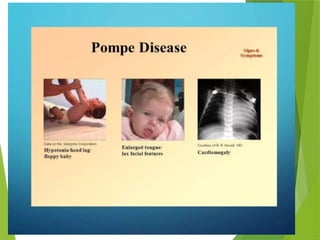
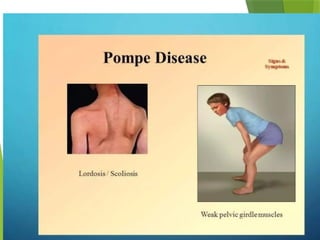
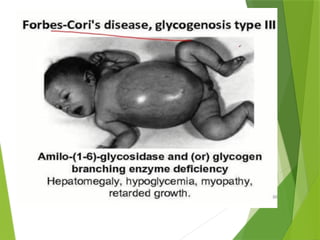
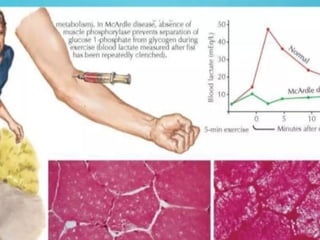
Glycogen storage diseases are metabolic disorders caused by enzyme deficiencies affecting glycogen synthesis and degradation, leading to abnormal glycogen accumulation in various tissues. Different types, such as von Gierke's disease and McArdle's disease, present with specific clinical features, including hypoglycemia, muscle cramps, and organ enlargement, with varying prognoses and treatment options. Management approaches vary based on the type of GSD, involving dietary interventions, enzyme replacement therapies, and surgical options as needed.