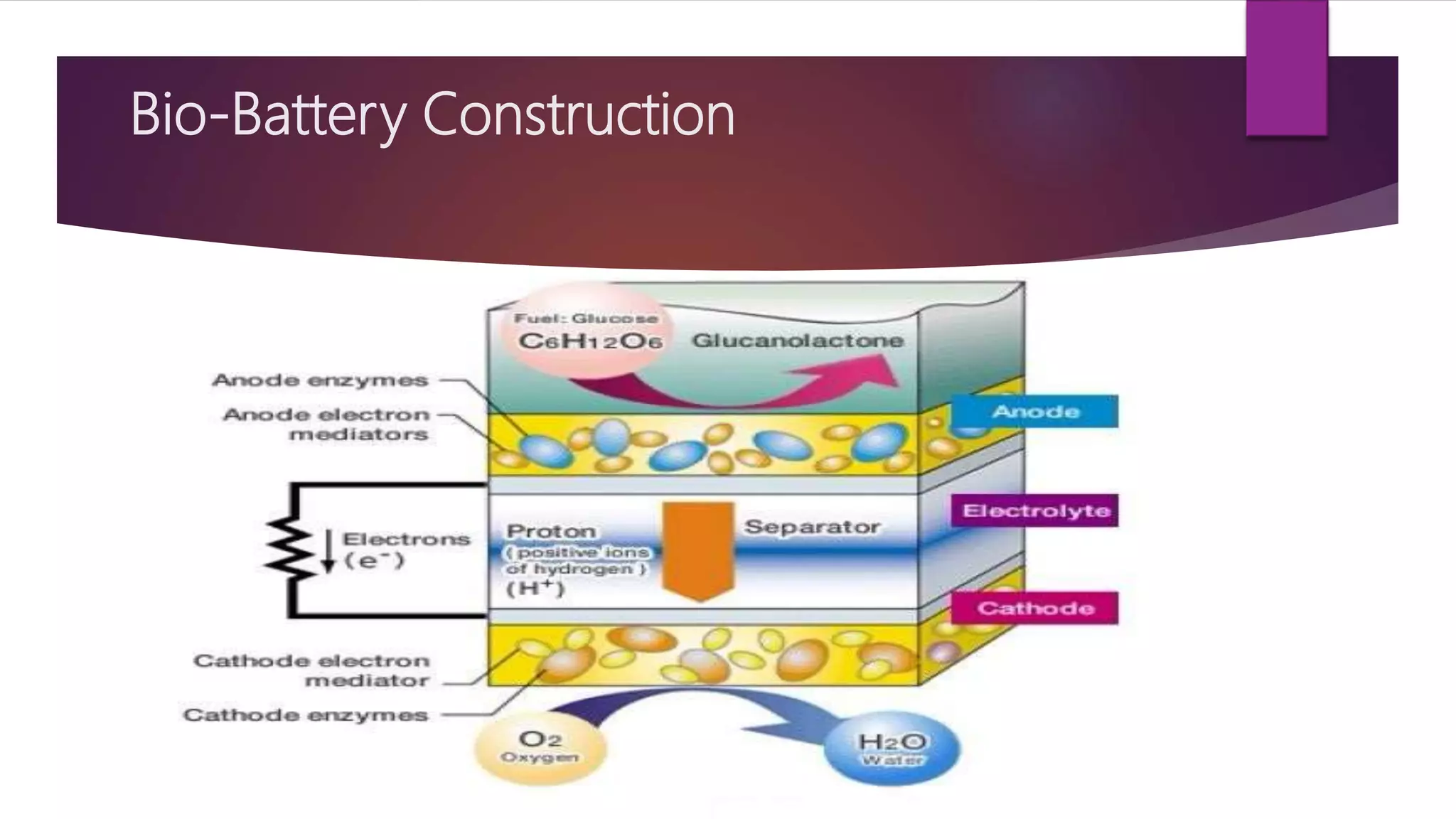
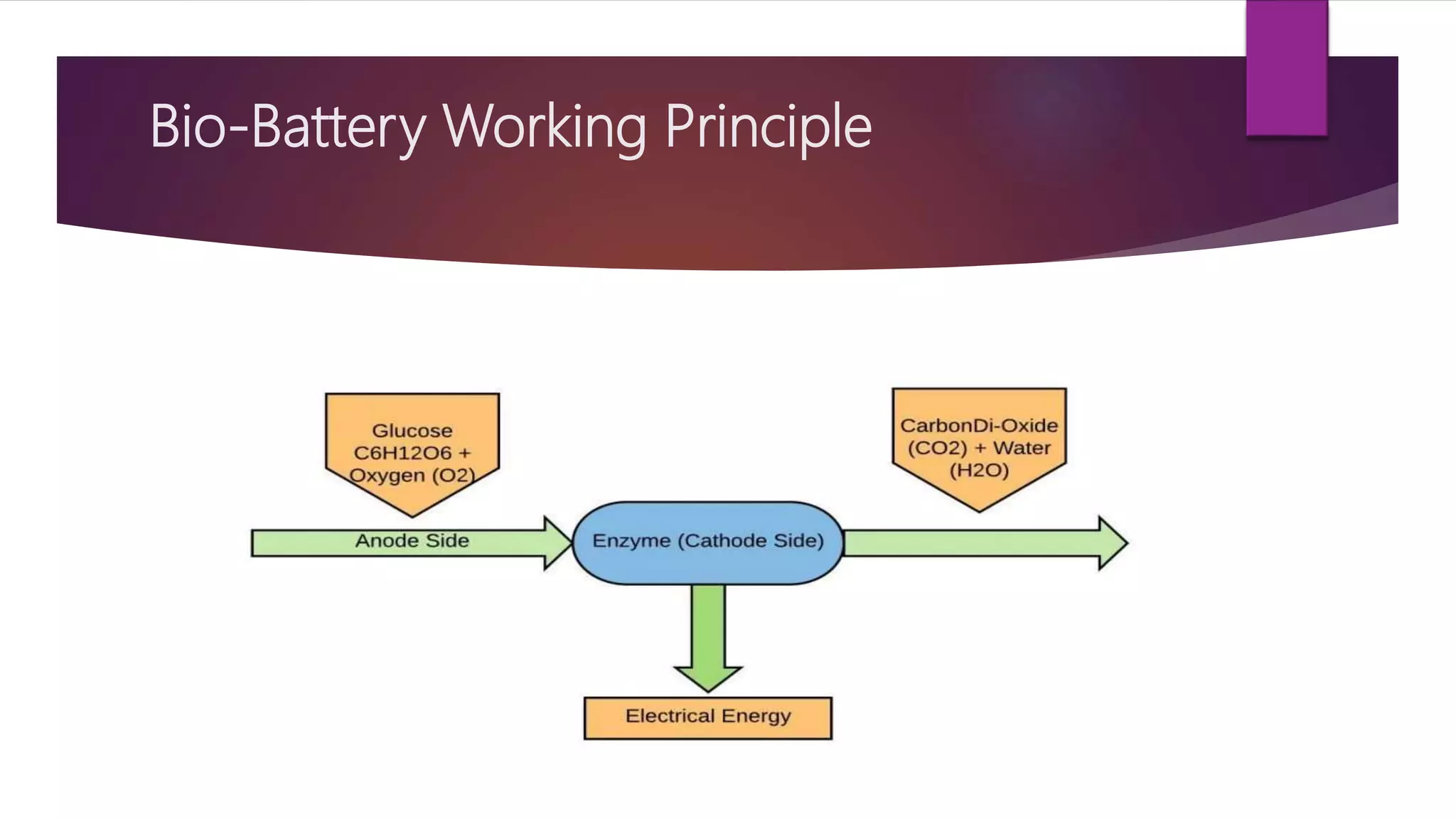
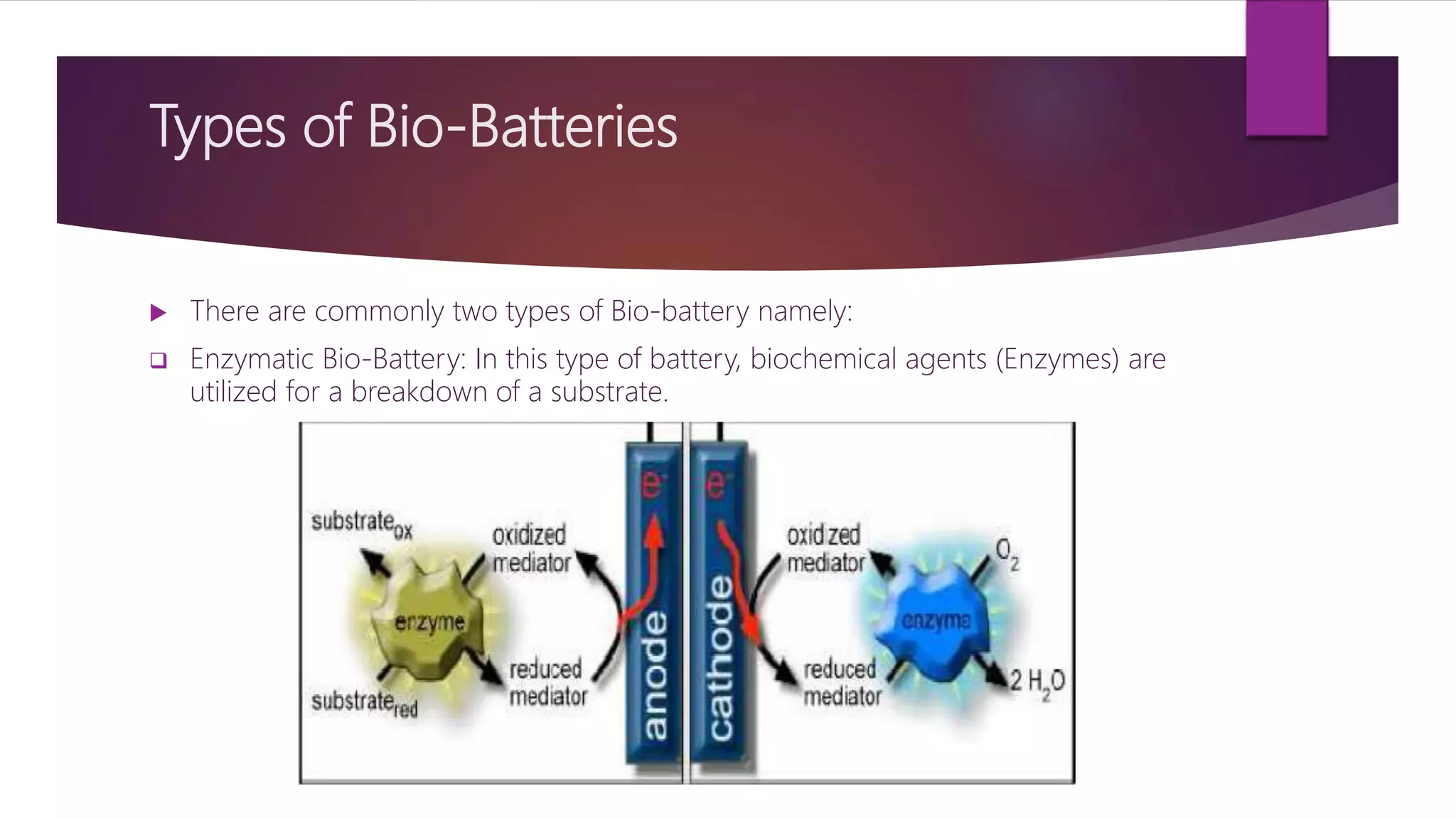
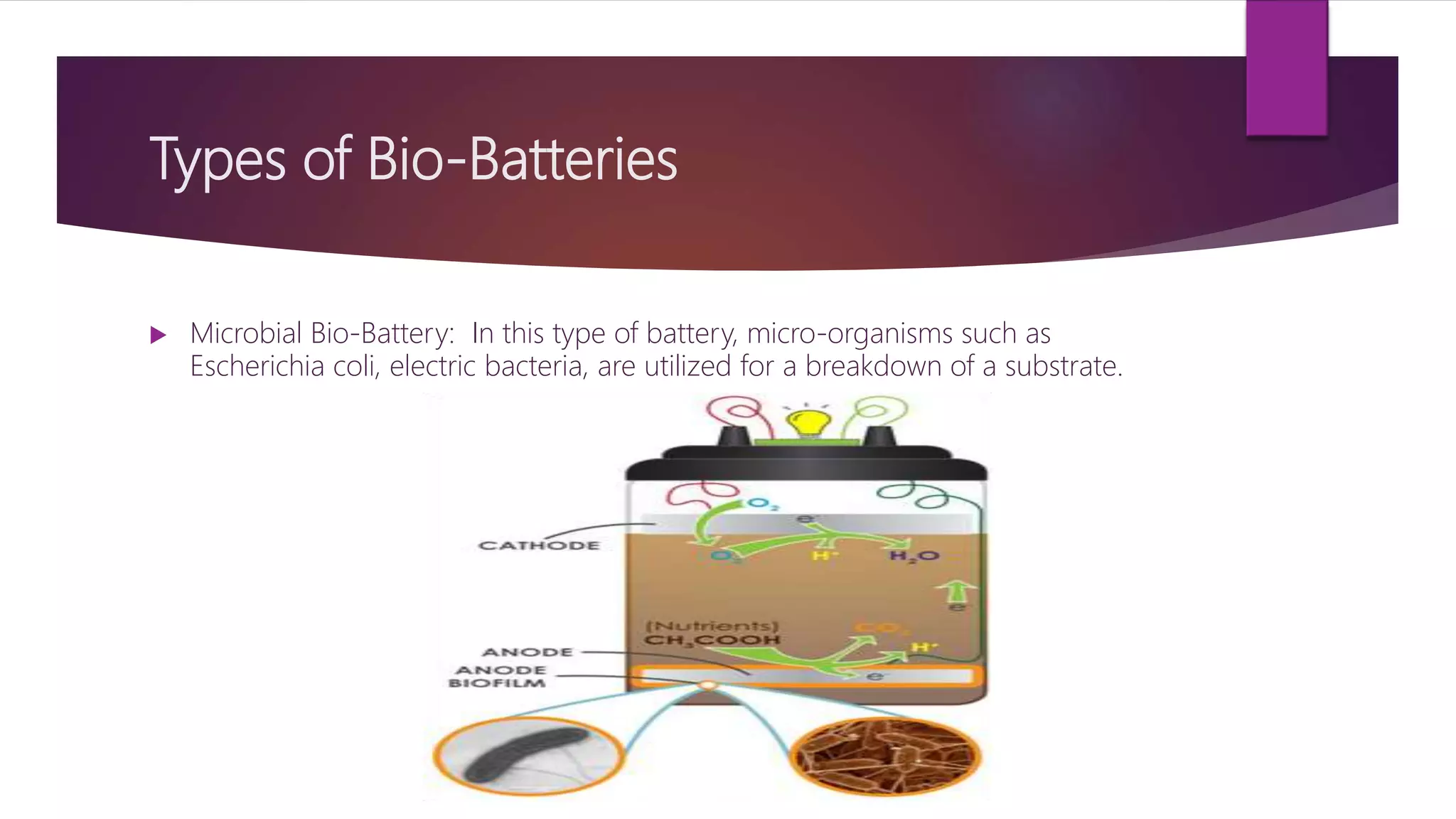
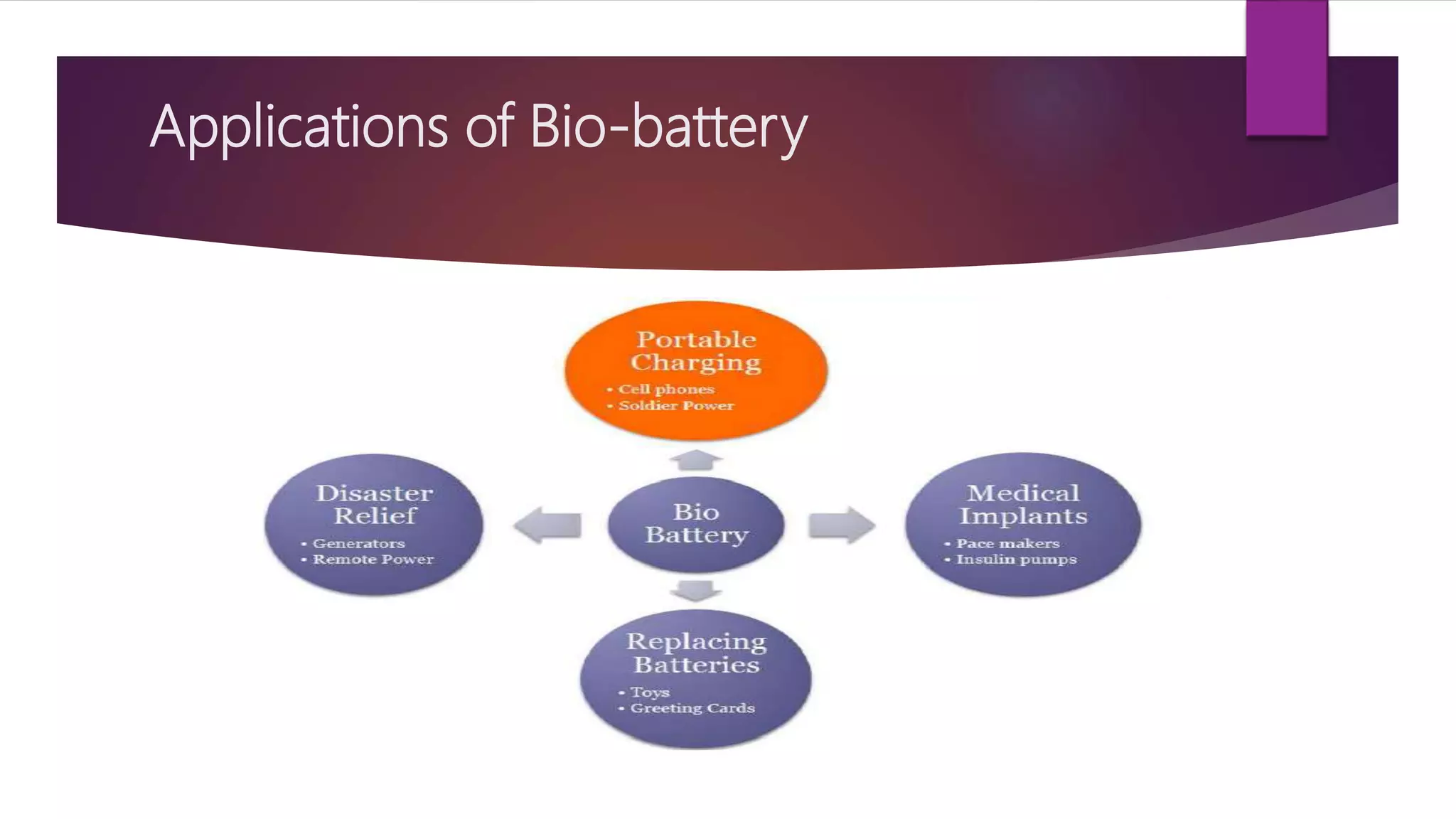
This document provides an overview of bio-batteries, including their working principle, types, advantages, disadvantages, and applications. Bio-batteries generate electrical energy through chemical reactions involving organic compounds like glucose, and include enzymes or microorganisms to break down substrates. There are two main types - enzymatic bio-batteries that use enzymes, and microbial bio-batteries that use microbes. Bio-batteries have advantages like being renewable, non-polluting, and safe, but store less energy than lithium batteries and cannot be used for long-term storage. Applications include powering medical implants, electronics, toys, and remote sensing devices.