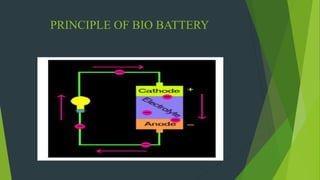
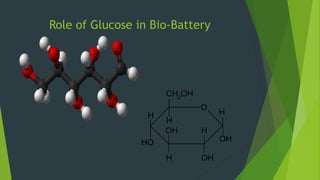
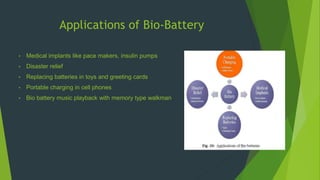
A bio-battery is an energy storage device powered by organic compounds like glucose in human blood. It works by converting glucose into gluconolactone, protons, and electrons. Bio-batteries have advantages like being instantly rechargeable from readily available fuel sources like glucose, but have disadvantages like preserving less energy and not being suitable for long-term storage. Future improvements could make bio-batteries more practical as an eco-friendly form of portable energy production.