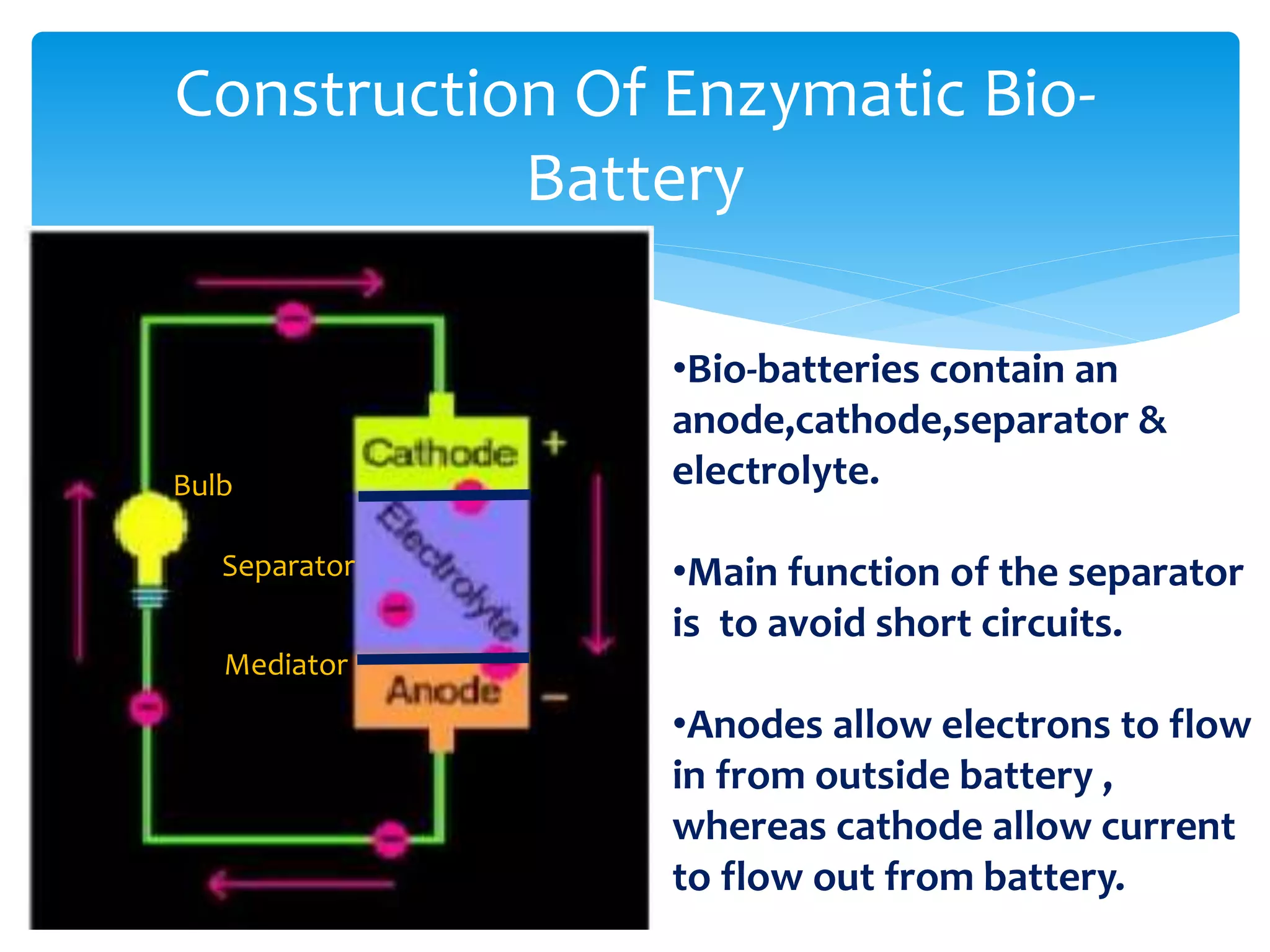
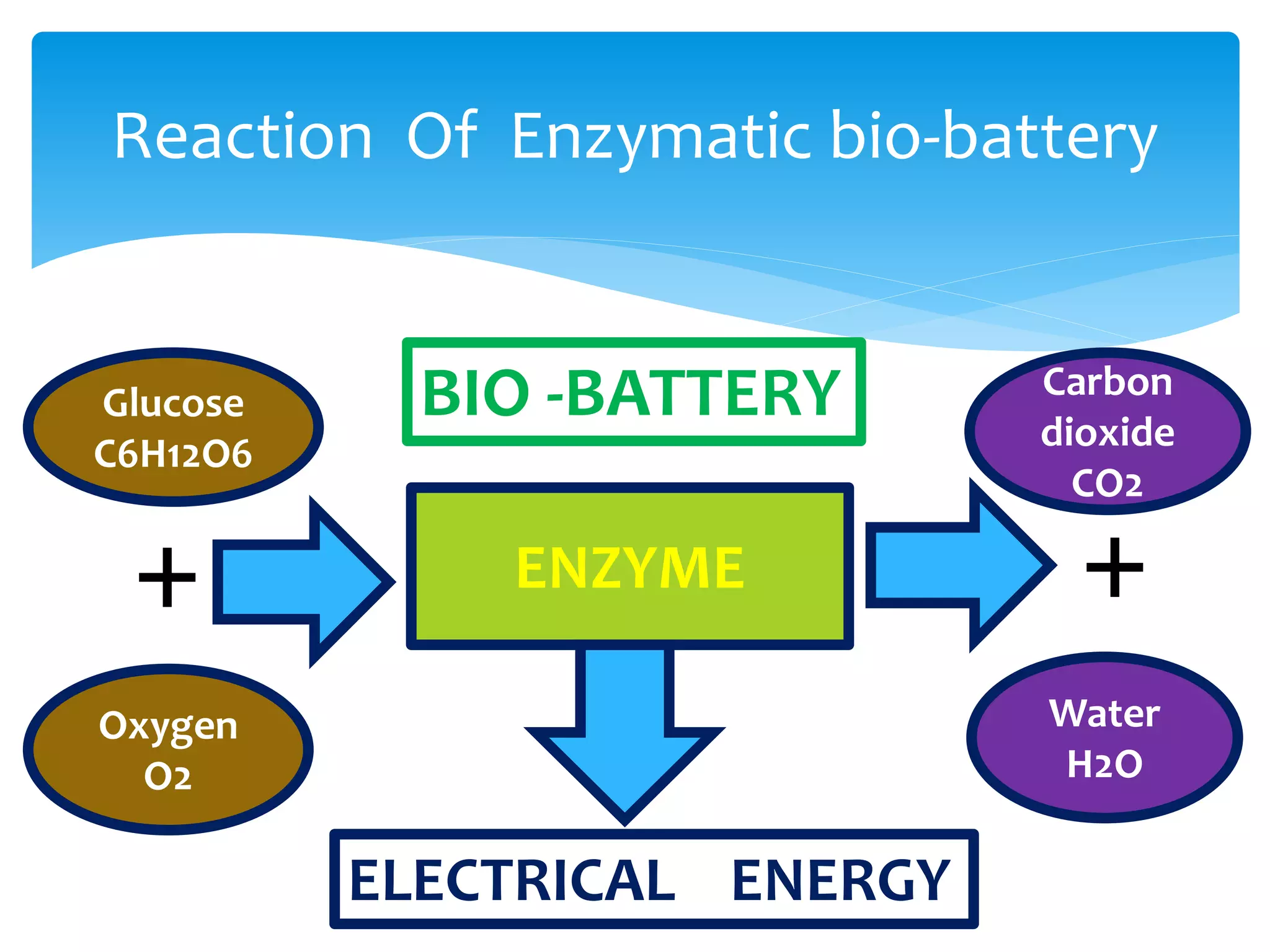
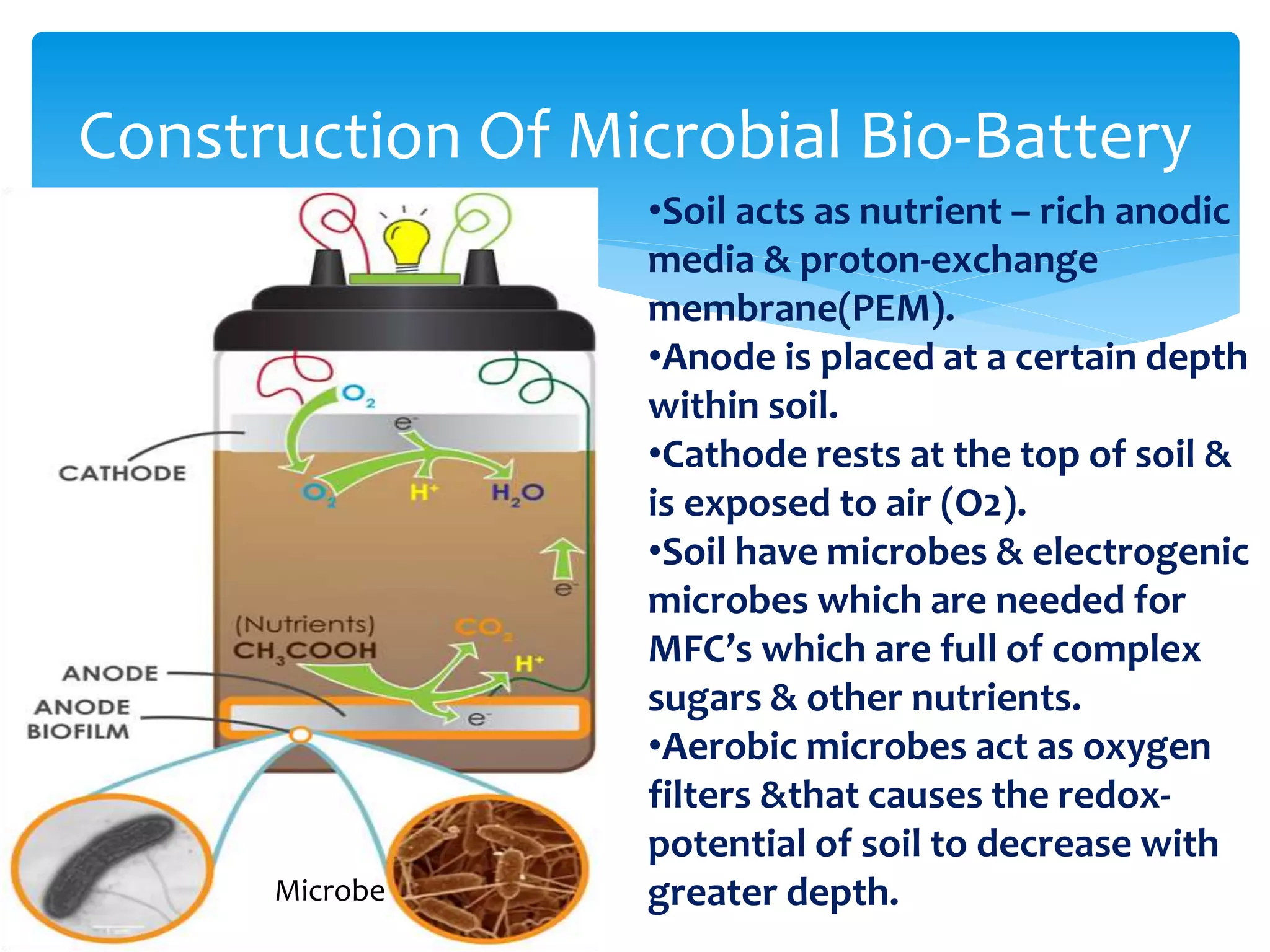
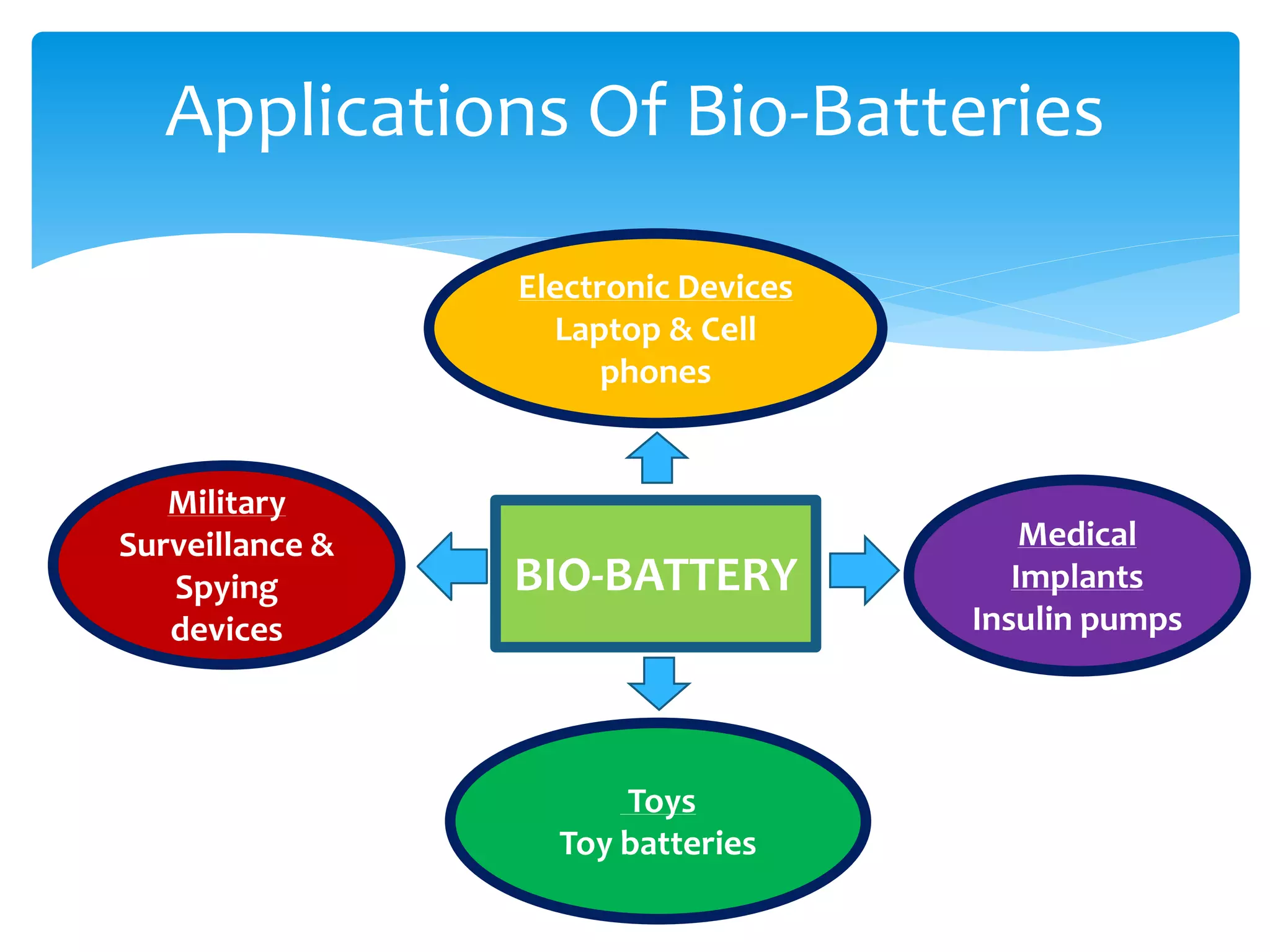
This document discusses bio-batteries, which are eco-friendly batteries that use biological materials like enzymes or microorganisms to generate electricity. It describes the history of bio-batteries, the different types including enzymatic and microbial batteries, how they work, potential applications, and advantages over conventional batteries like being non-toxic and renewable. While bio-batteries show promise as a green energy source, the document notes they currently have lower energy retention compared to other batteries. Overall, the document provides an overview of bio-batteries as an environmentally-friendly battery technology.