The document discusses binary trees, including their basic terminology, properties, representations, traversal methods, and common operations. It provides algorithms for inserting nodes, deleting nodes, and merging two binary trees. The key points covered are:
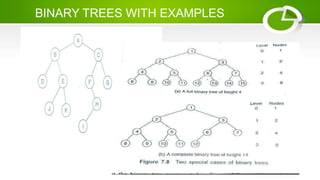
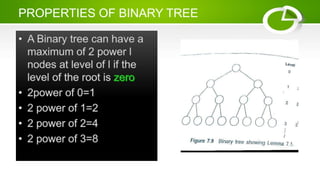
- Binary trees have a root node, child nodes, and properties like maximum/minimum number of nodes based on height.
- They can be represented sequentially using arrays or non-sequentially using linked lists.
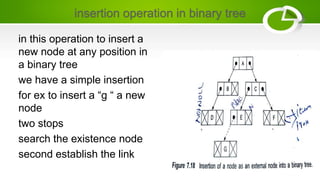
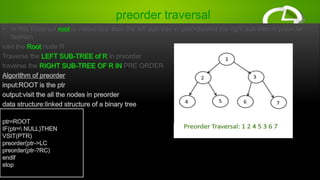
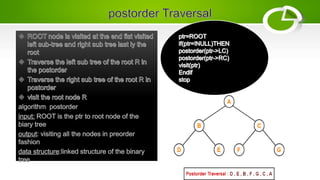
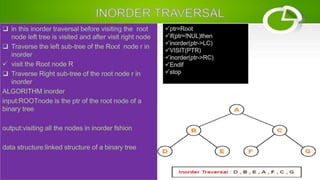
- Common traversal orders are preorder, inorder, and postorder.
- Operations include insertion, deletion, traversal, and merging two trees into one larger tree.
- Algorithms are presented for inserting nodes using linked lists and merging two trees by combining their nodes.






![• The root N of T is stored
in TREE [1]. If a node
occupies TREE [k] then its
is stored in TREE
and its is
stored into TREE](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/binarytreeandoperations1-211105071714/85/Binary-tree-and-operations-9-320.jpg)