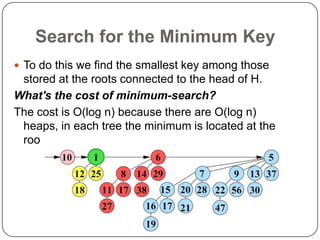
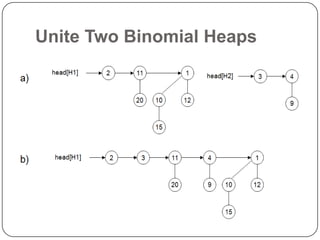
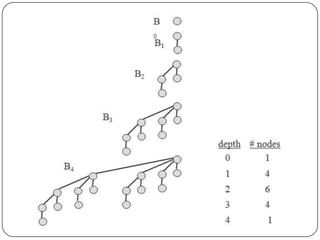
Binomial heaps are a data structure that supports union operations more efficiently than binary heaps. A binomial heap is made up of binomial trees, which are ordered trees built recursively. A binomial heap satisfies properties where no two trees are the same size, each node has a key, and children have smaller keys than their parents. Operations like finding the minimum, inserting, deleting, and uniting heaps take O(log n) time due to the heap being made up of O(log n) trees.





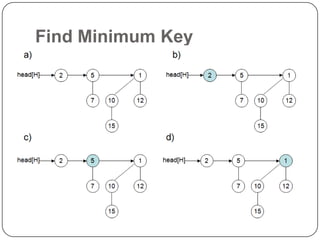
![The roots of the trees are connected so that the sizes of the connected trees are in decreasing order. Also, for a heap H, head [H] points to the head of the list](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/binomialheappresentation-110509113937-phpapp01/85/Binomial-heap-presentation-7-320.jpg)