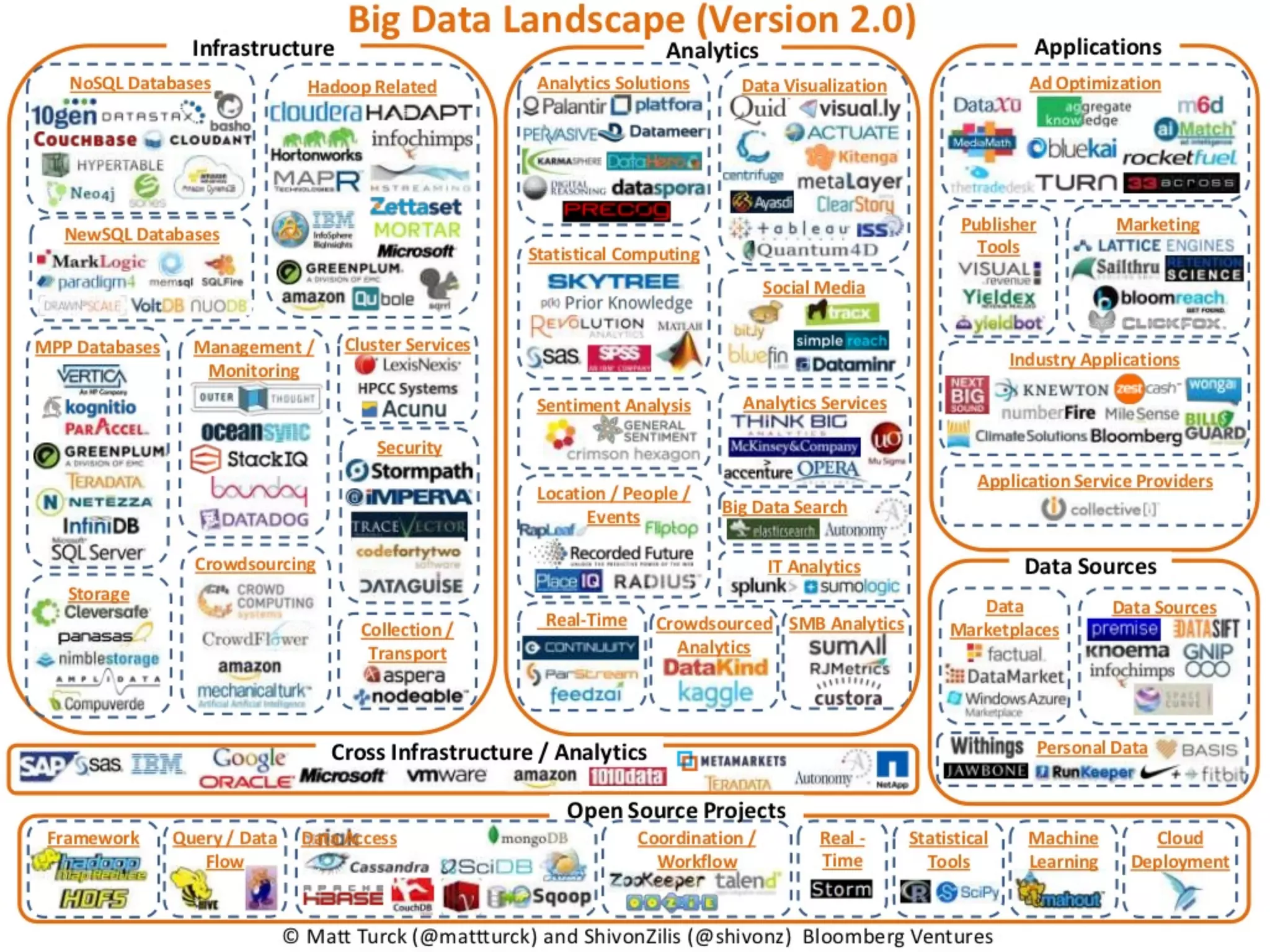
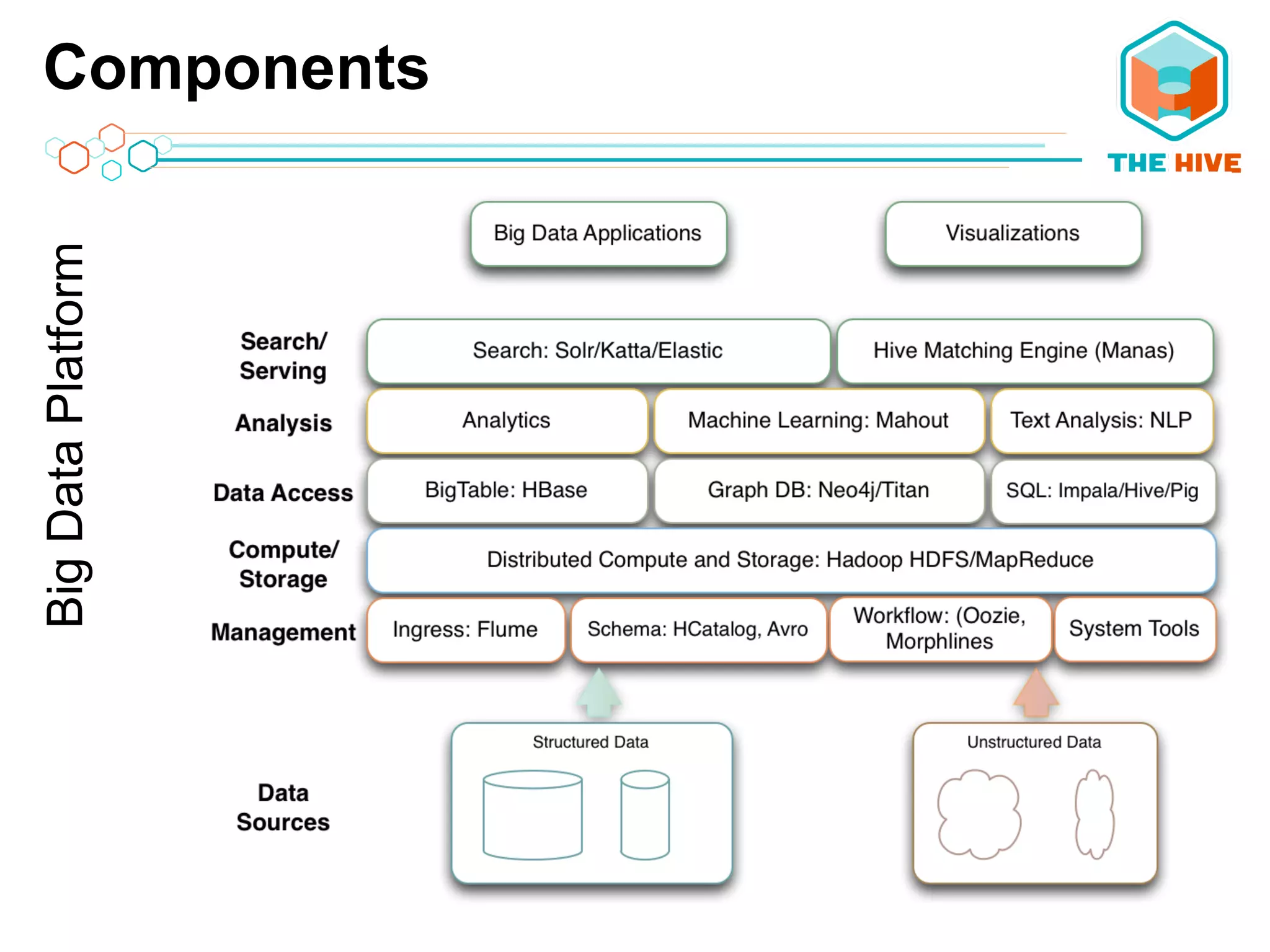
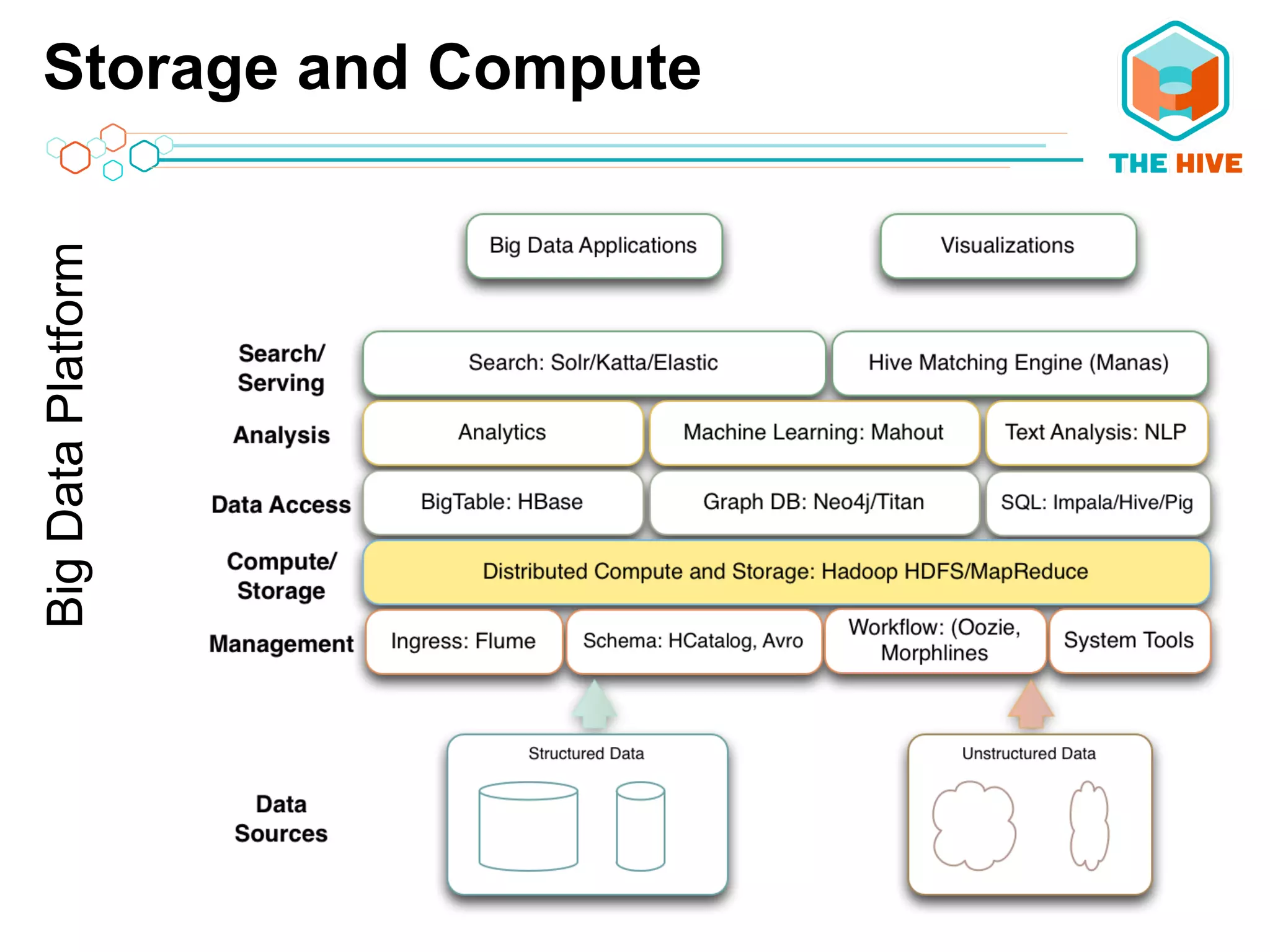
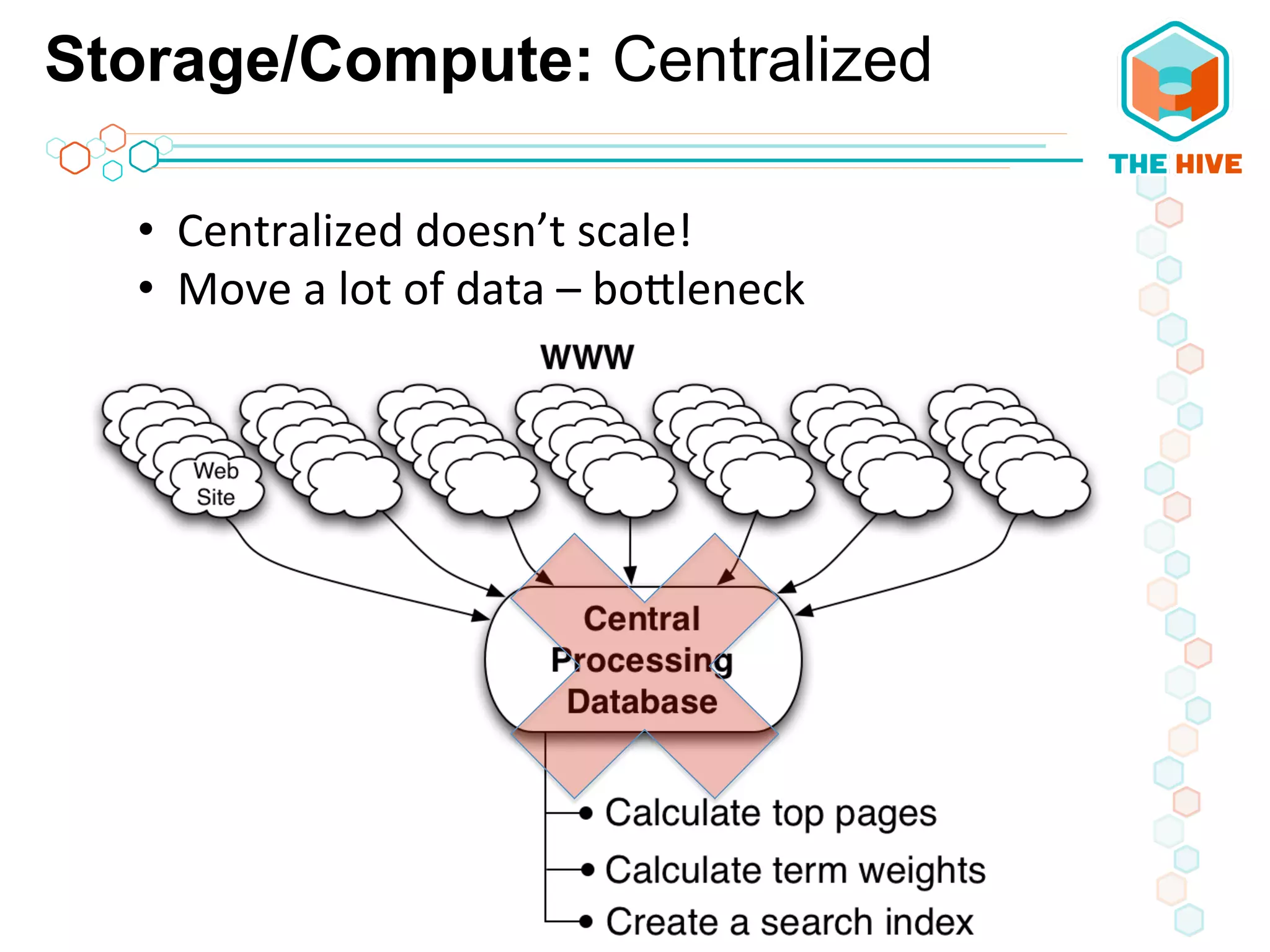
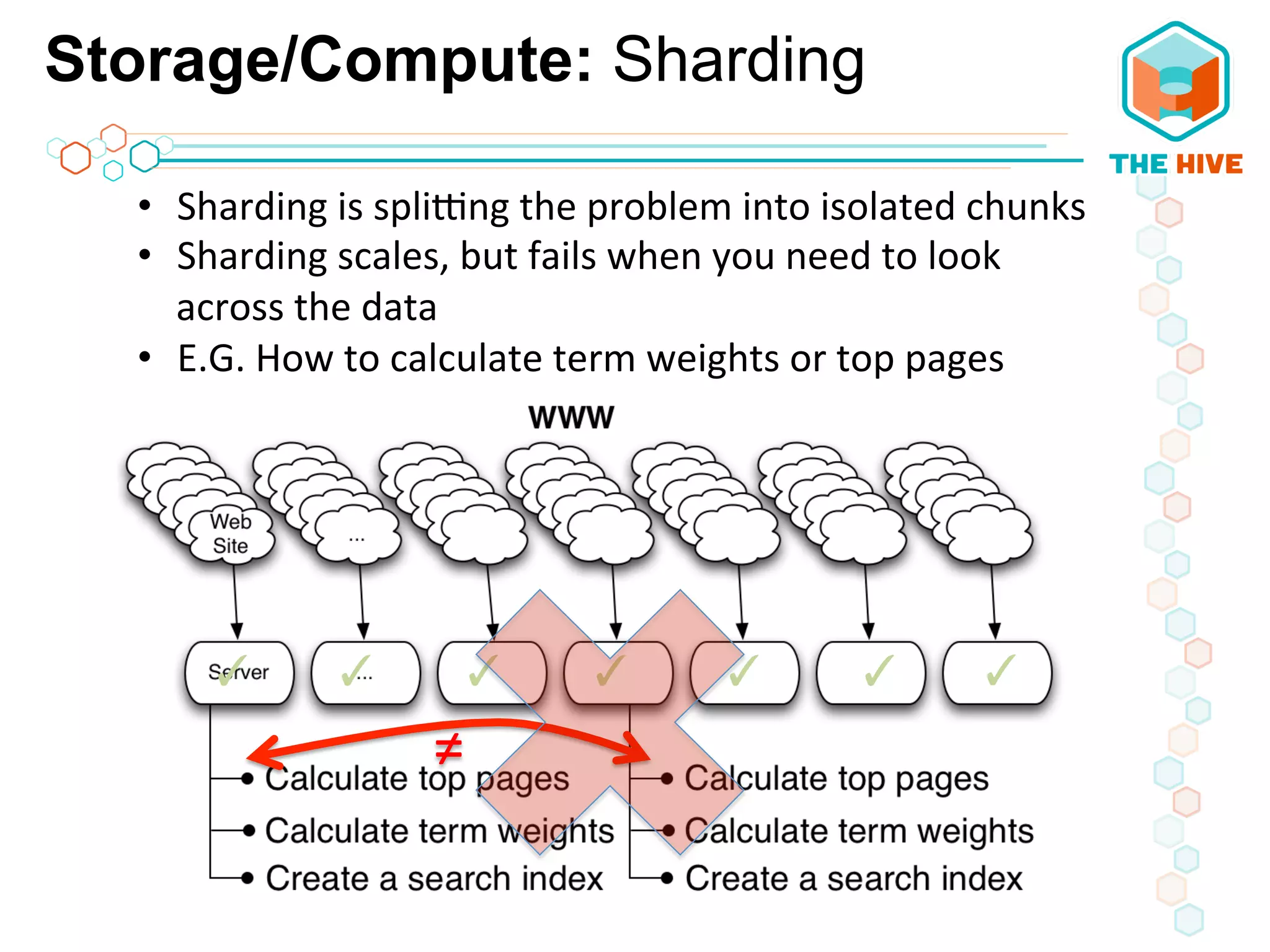
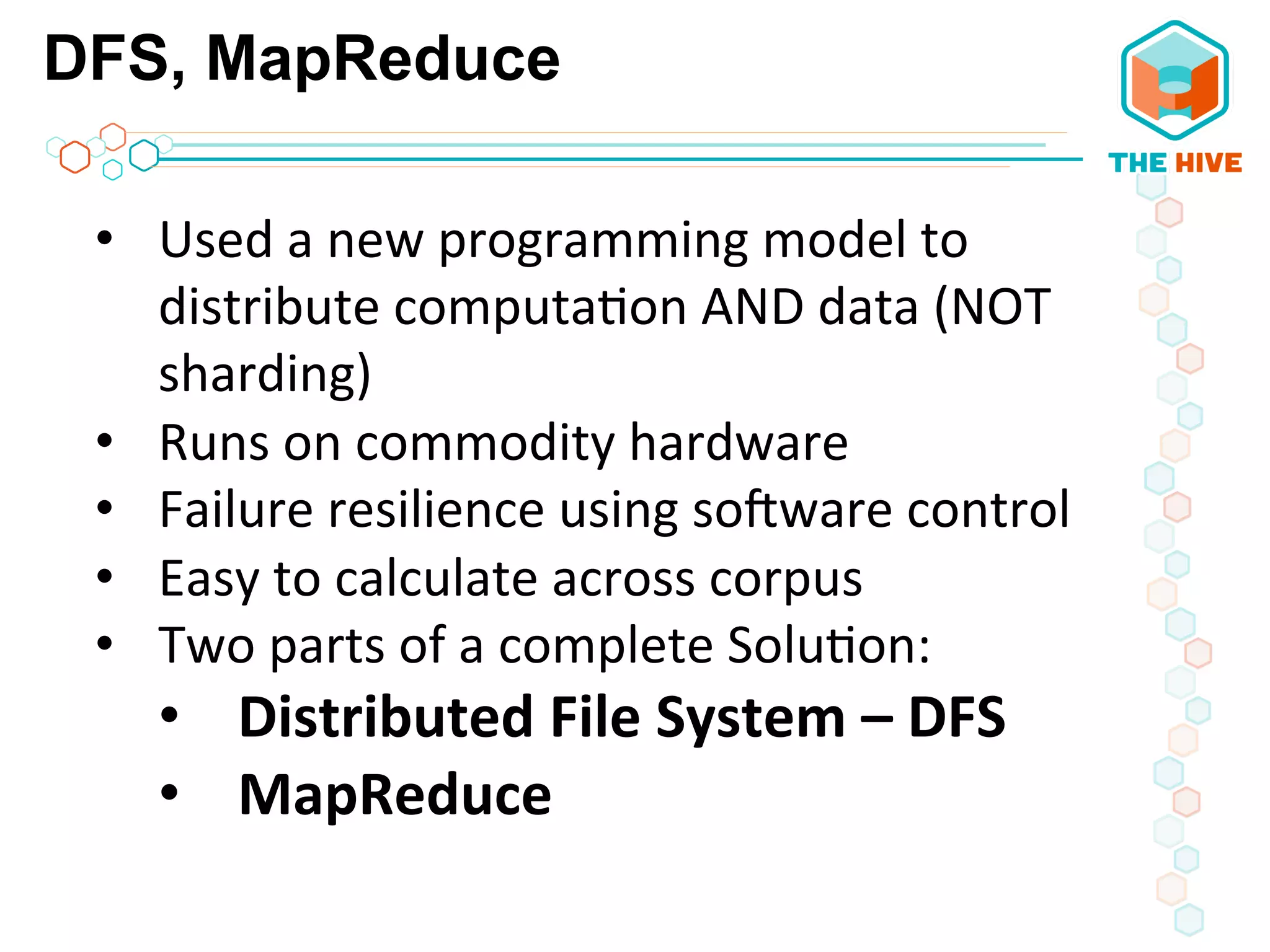
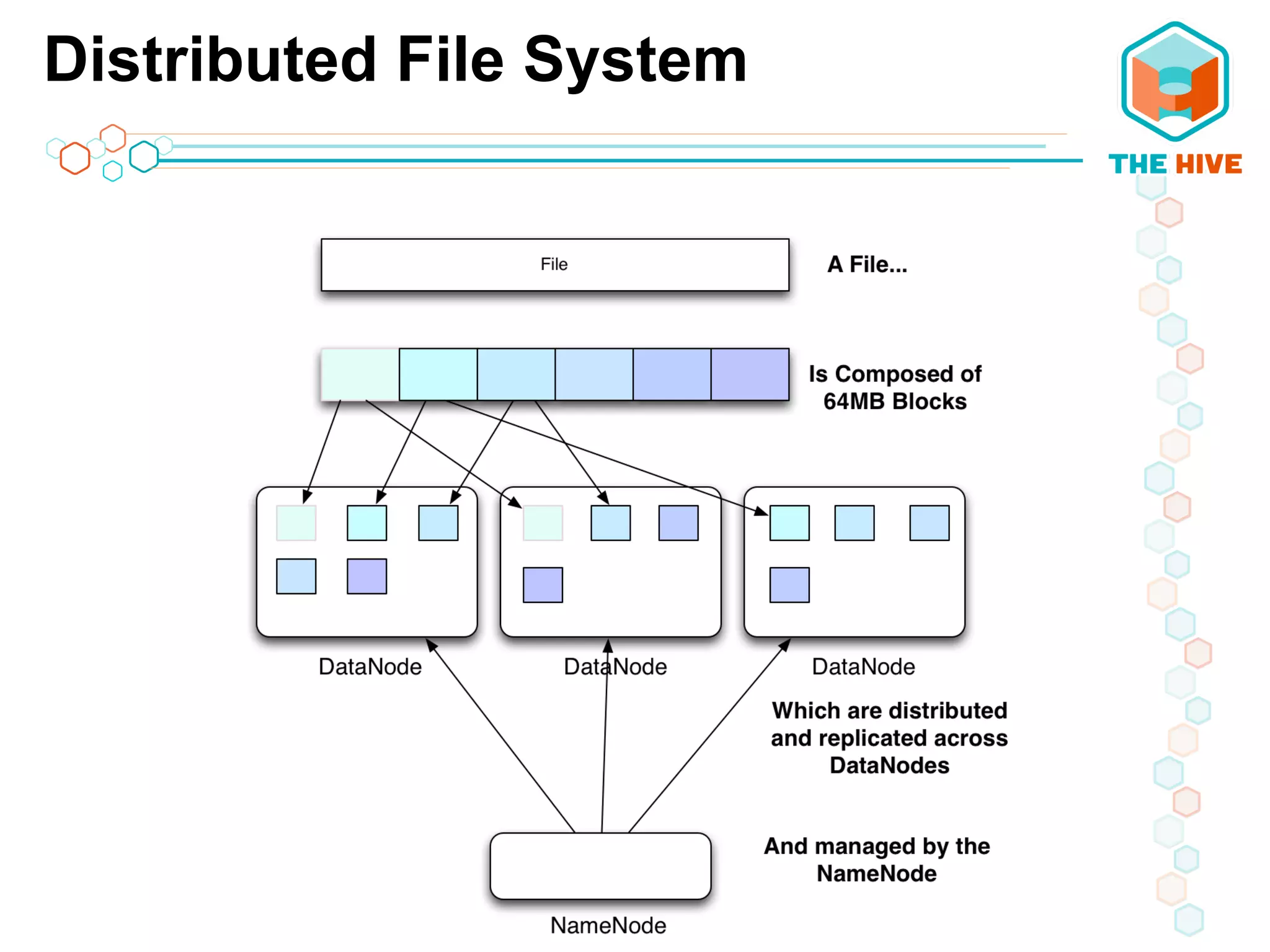
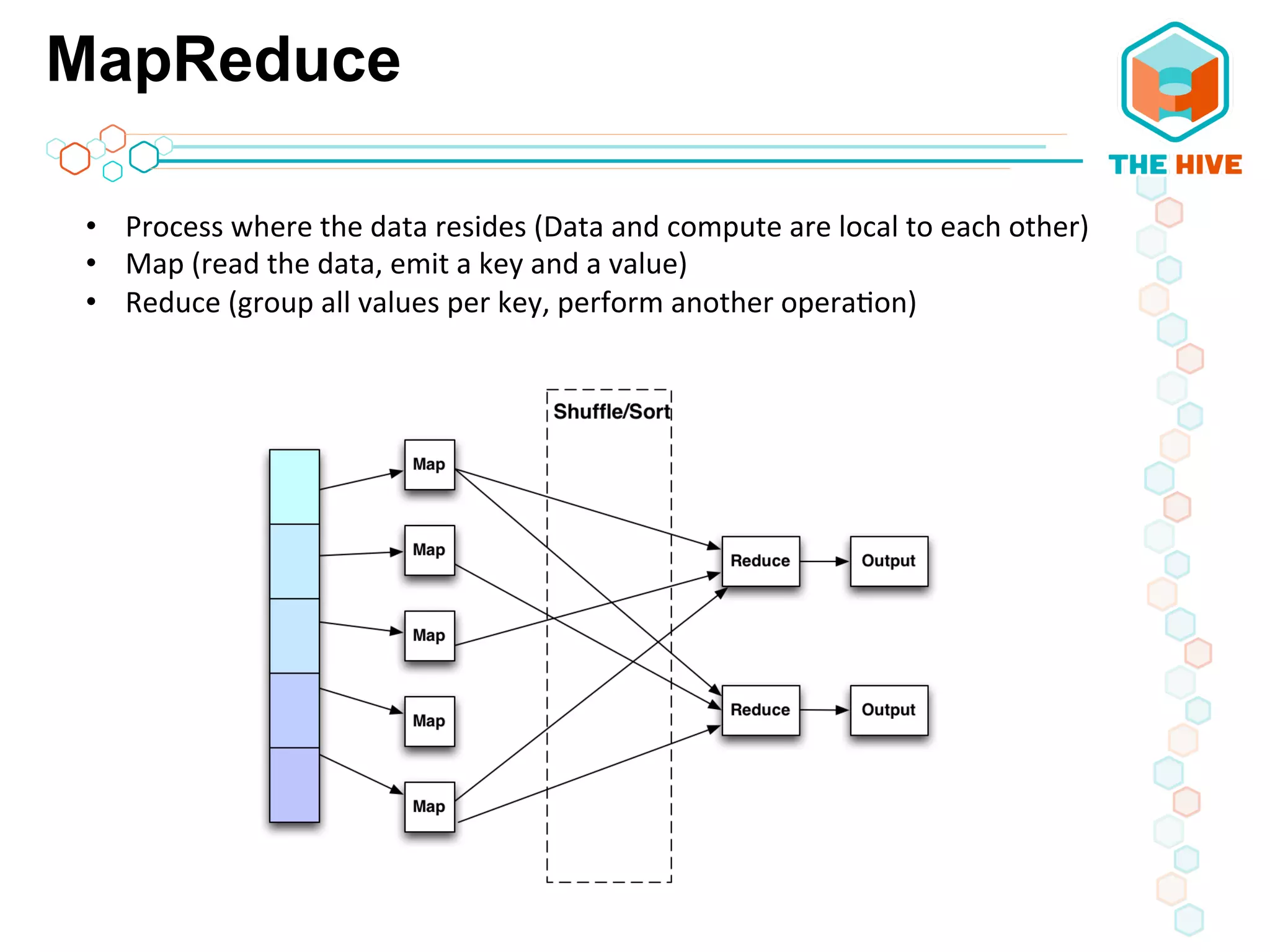
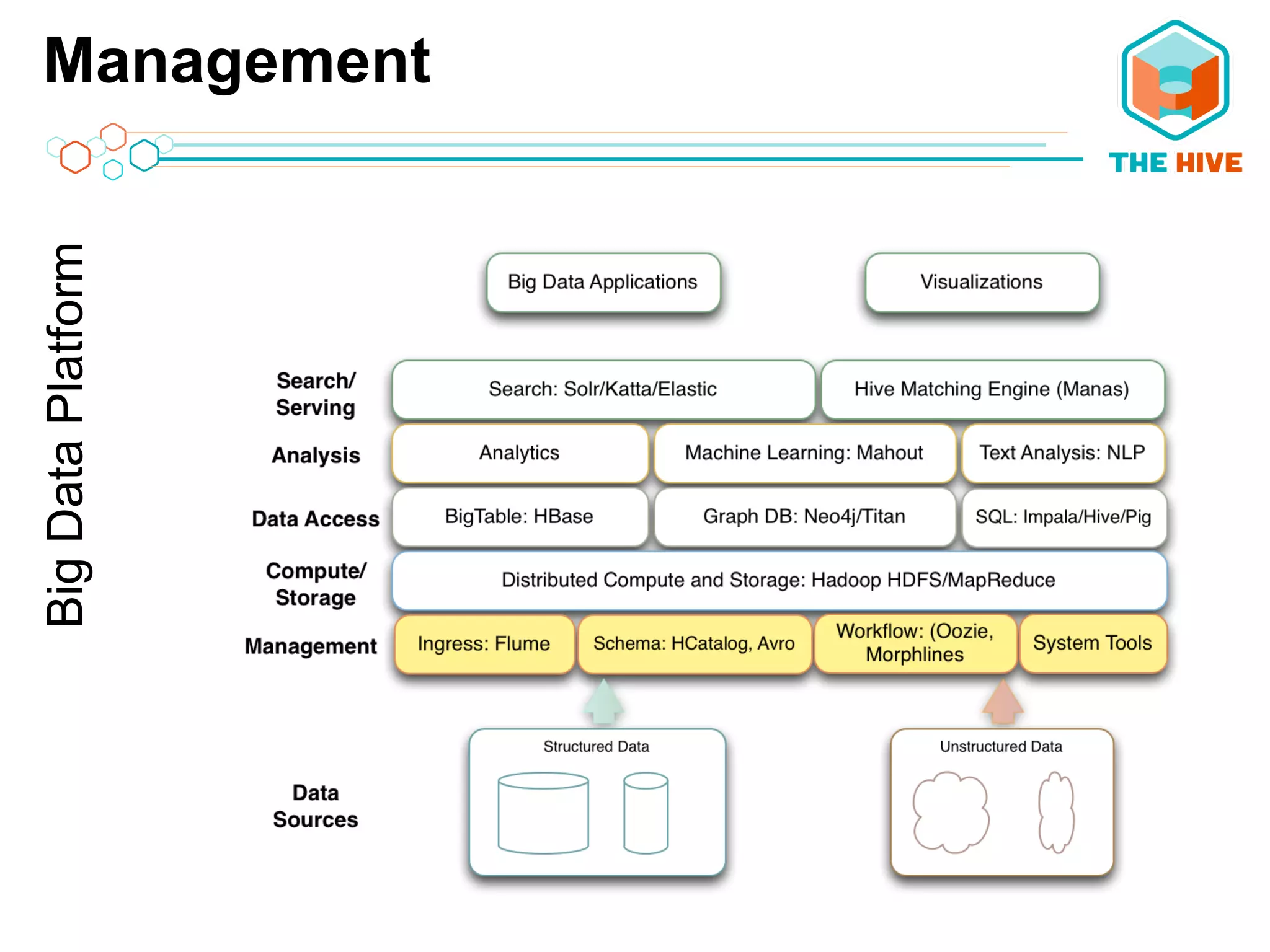
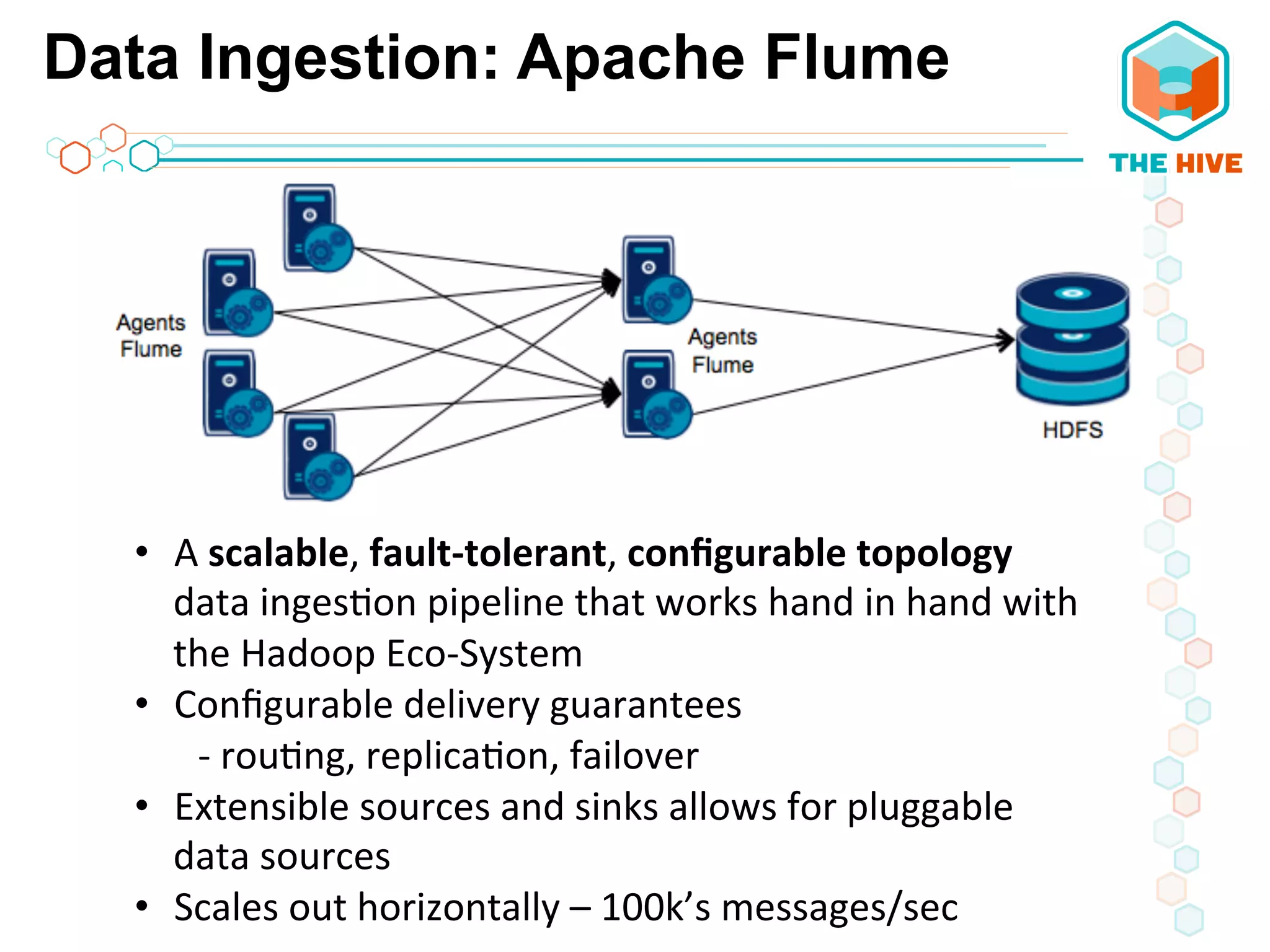
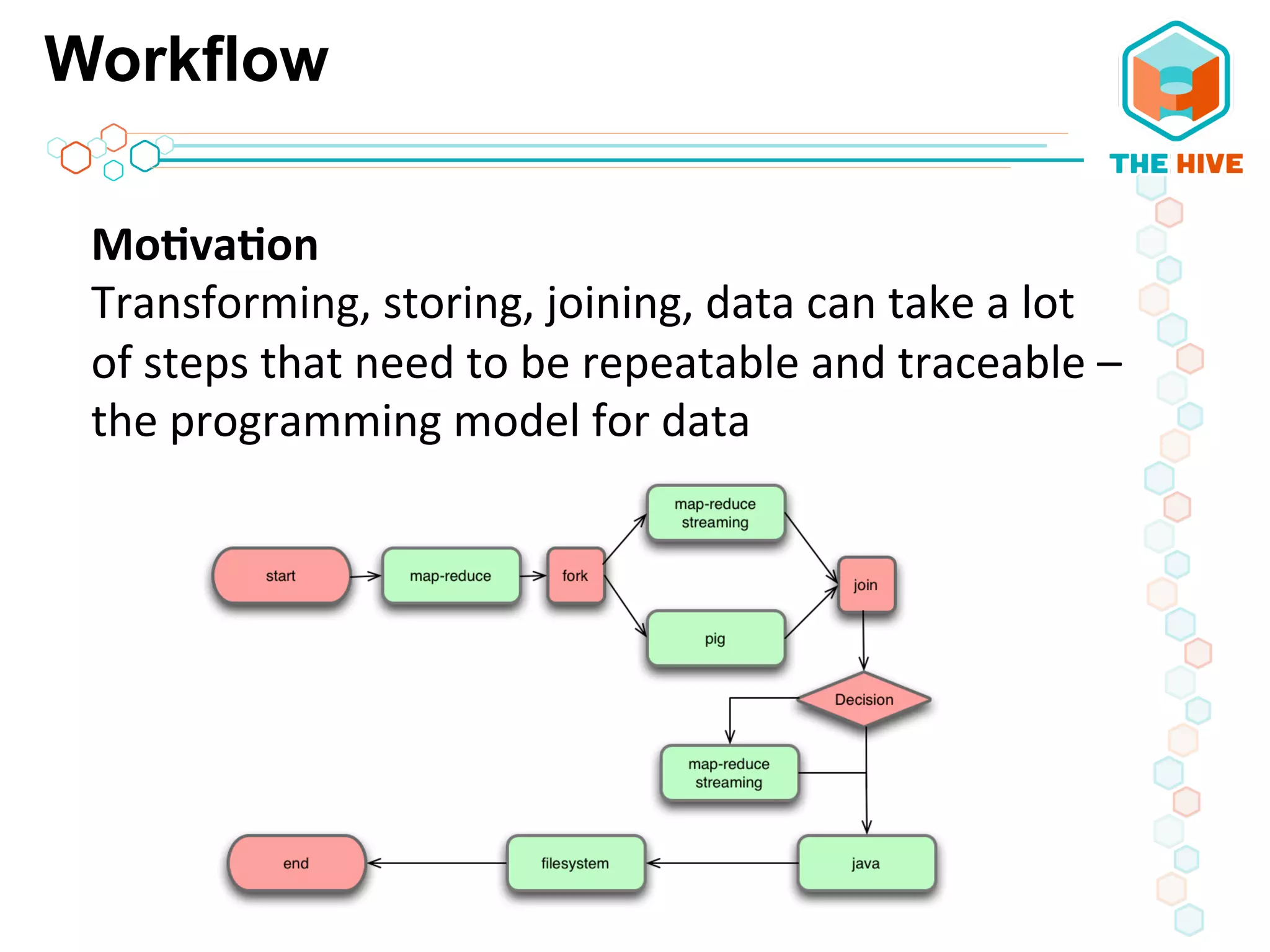
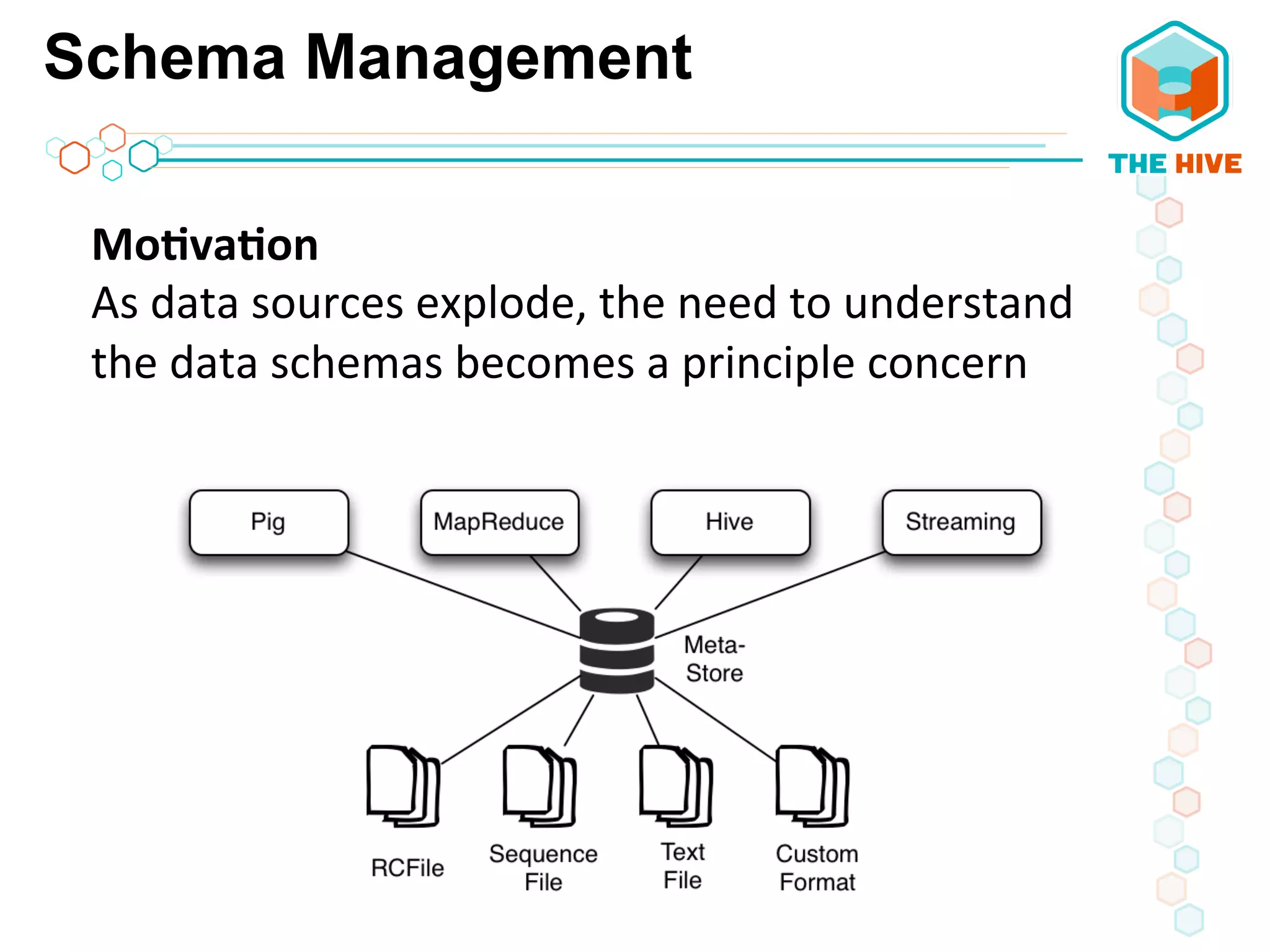
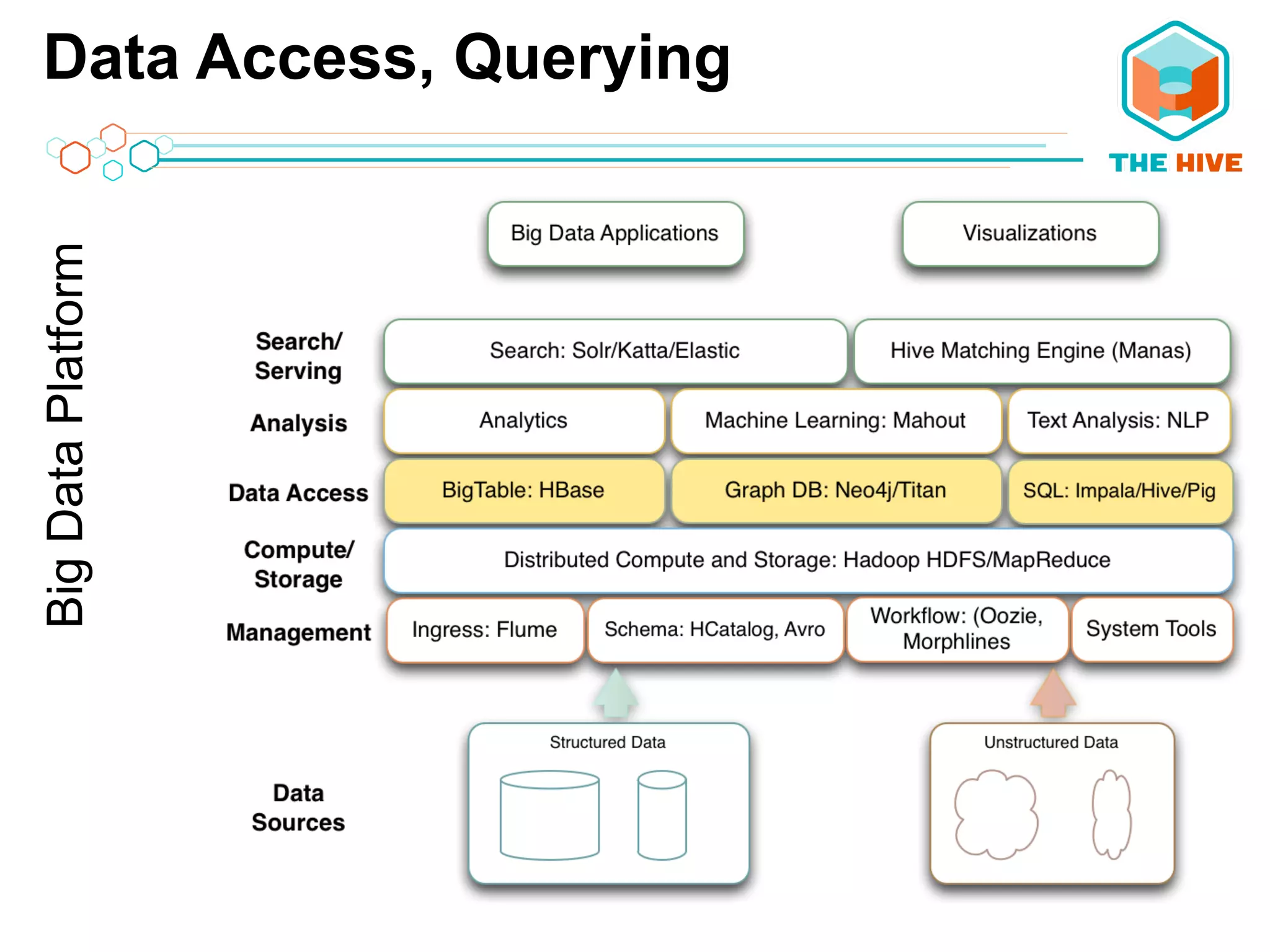
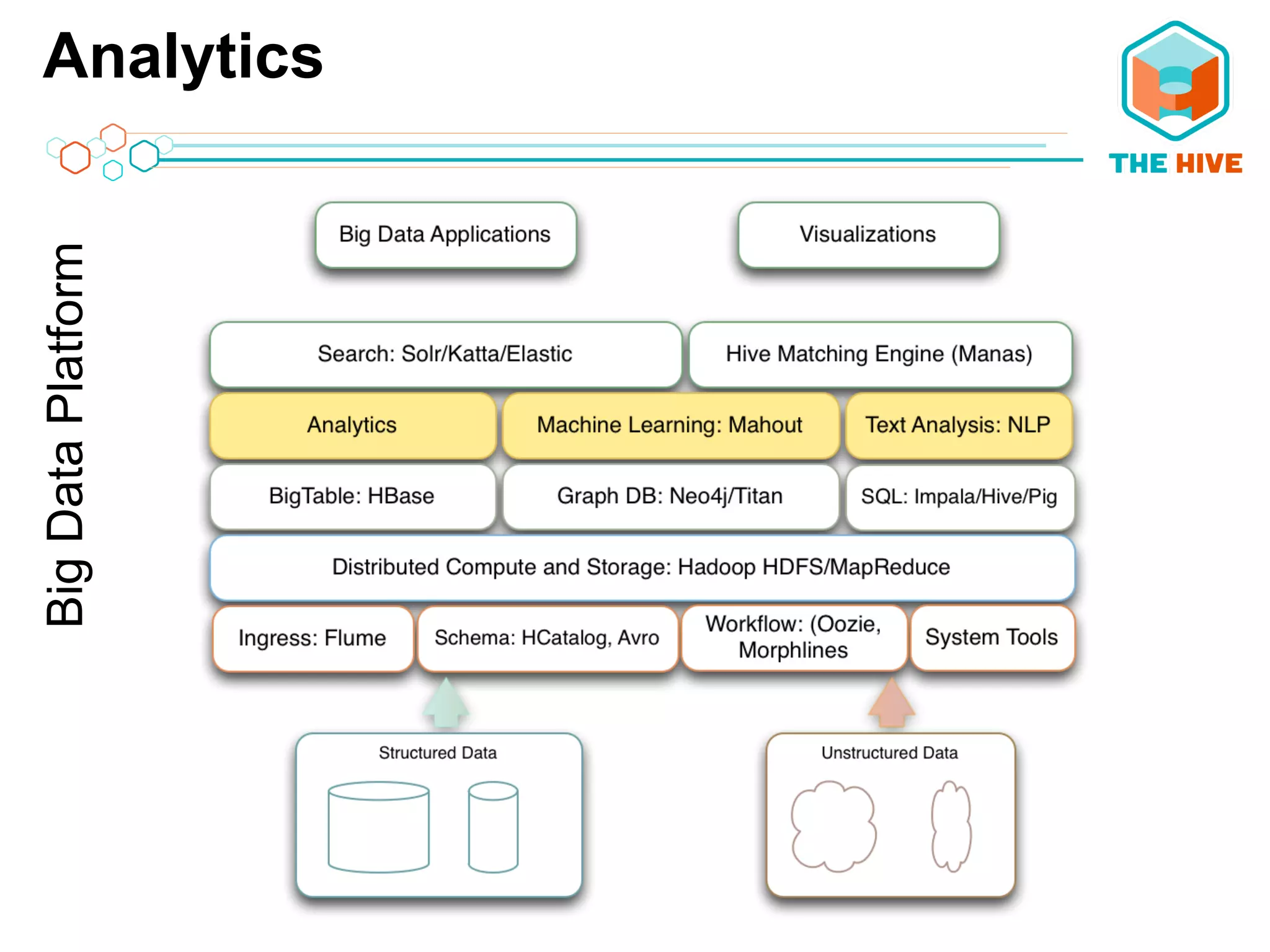
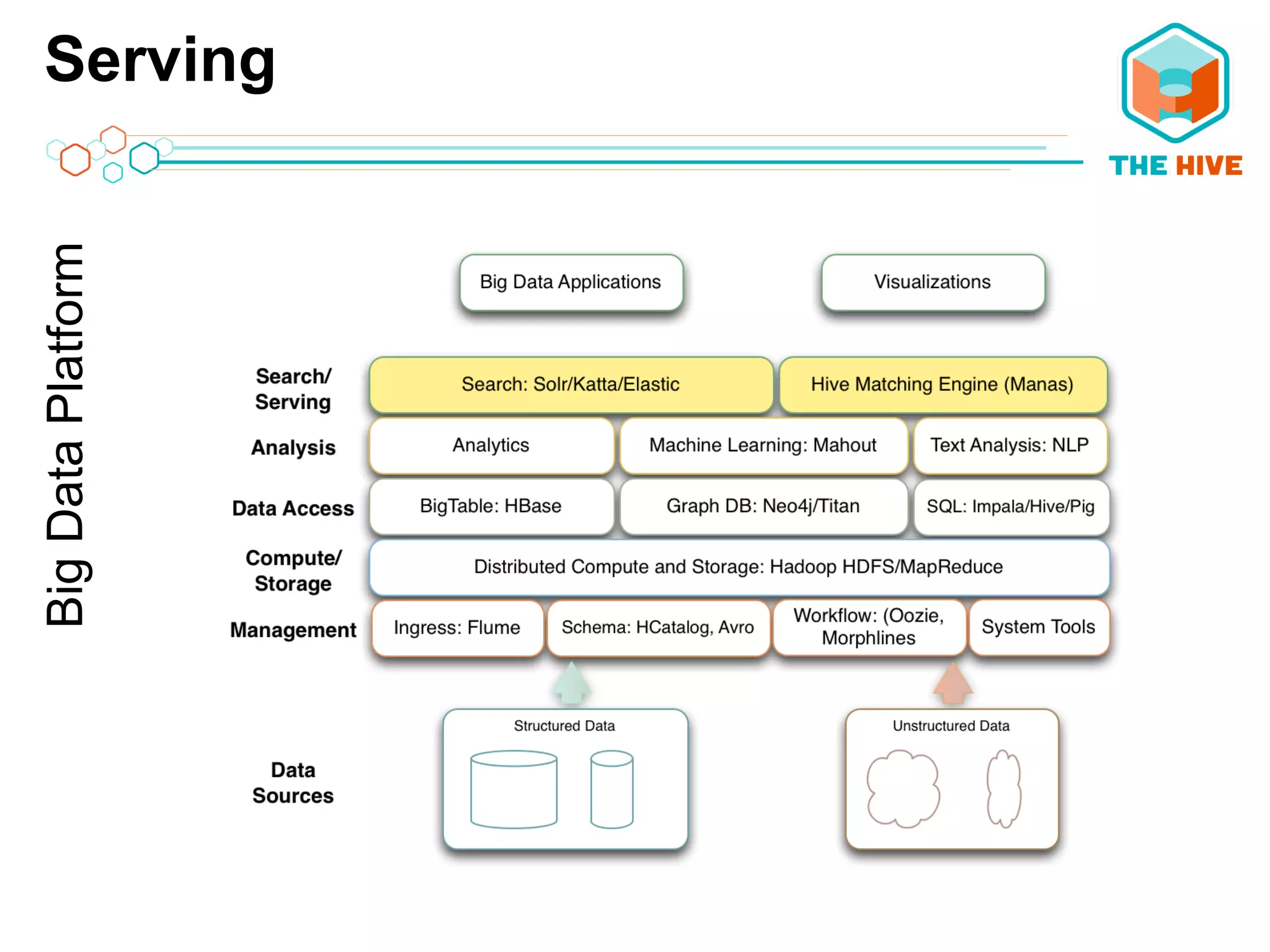
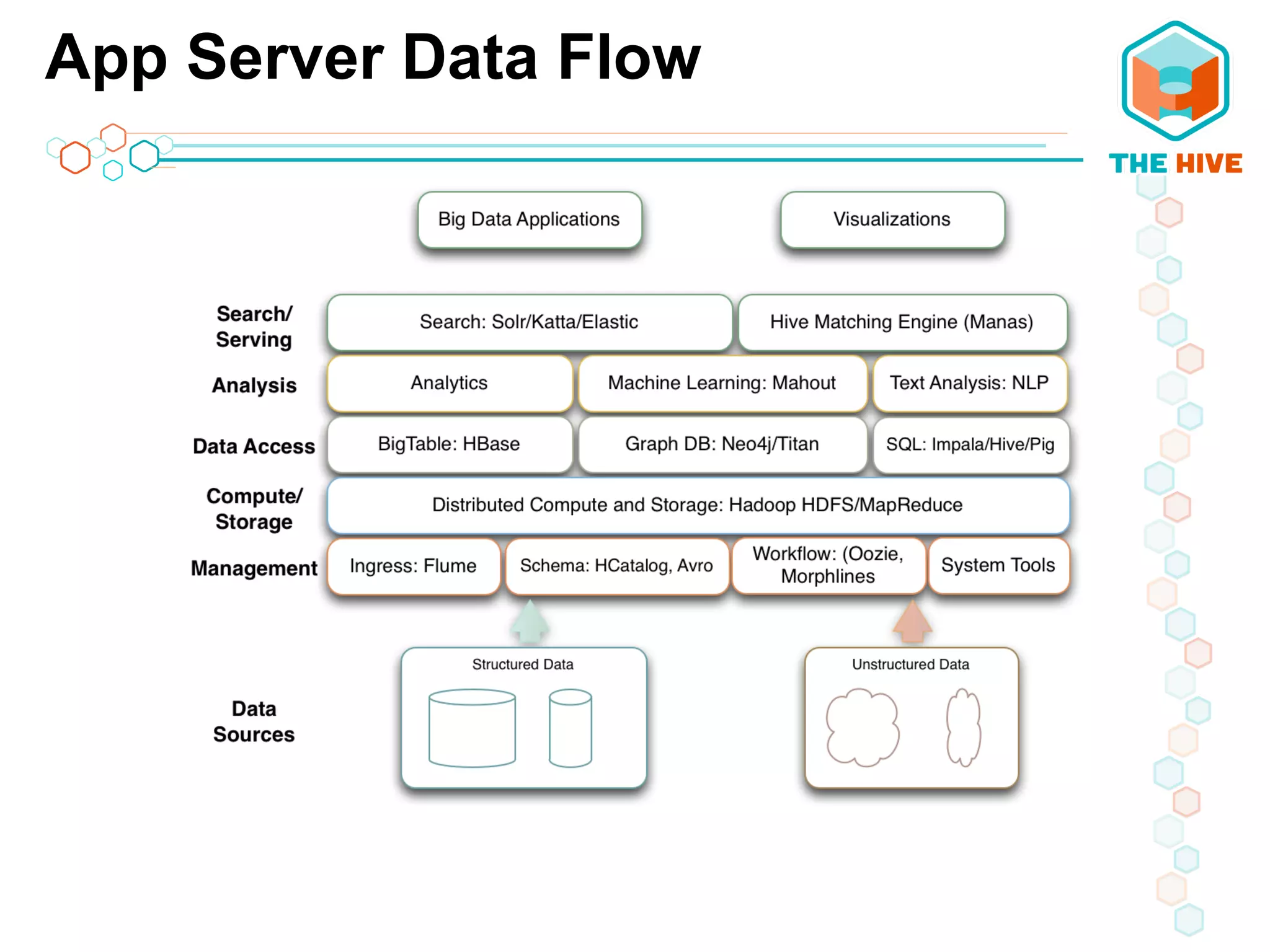
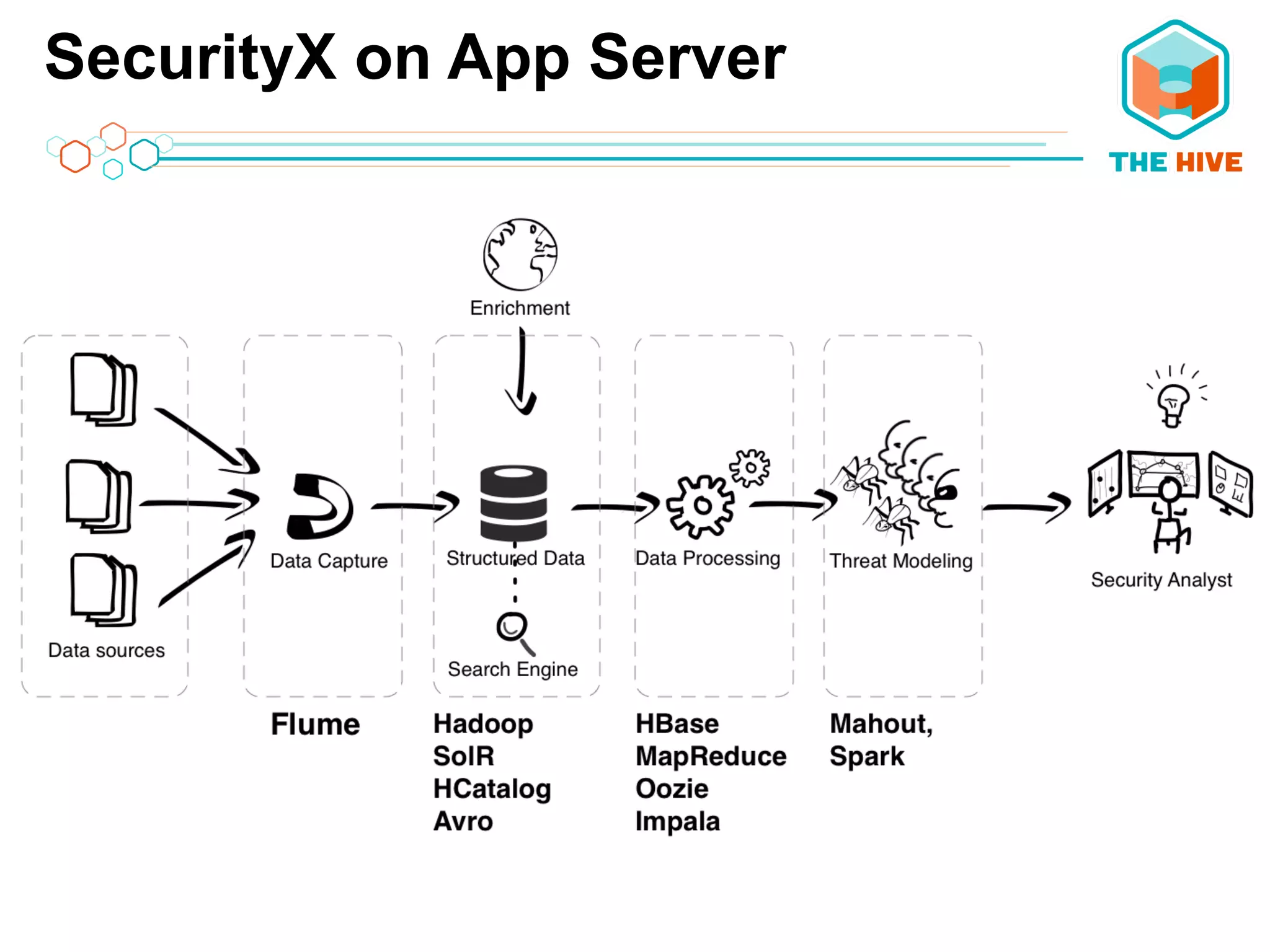
This document describes a big data application server framework for handling large volumes, velocities, and varieties of data to extract value. It discusses use cases like log analytics, security detection, sensor data analytics, and recommendation systems. The document then summarizes several key components of big data platforms, including storage and compute systems like HDFS and MapReduce, data ingestion with Apache Flume, workflow systems like Oozie, schema management with HCatalog and Avro, data access with HBase and SQL querying with Hive and Impala.