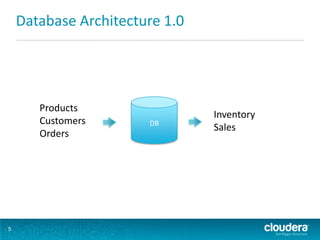
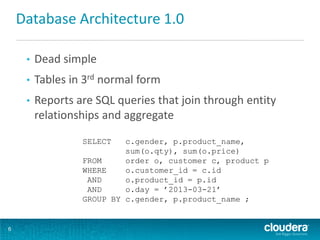
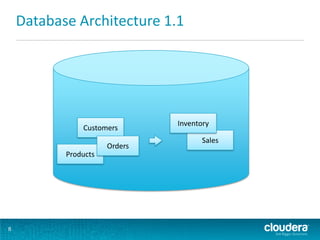
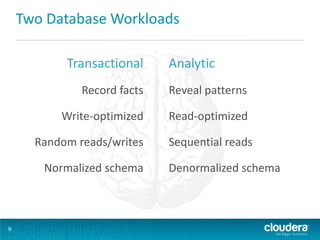
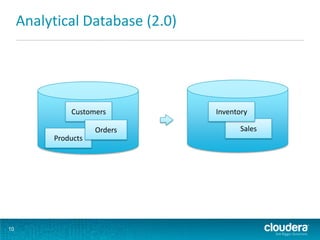
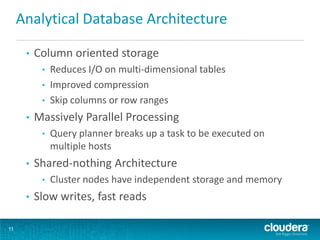
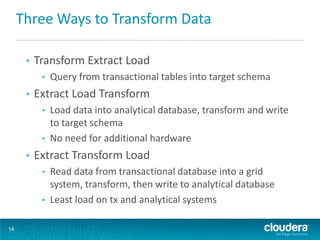
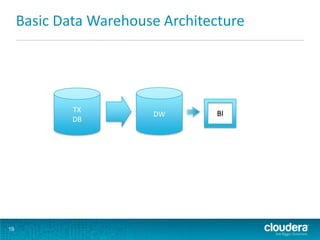
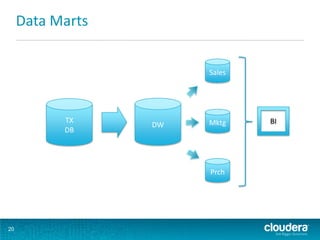
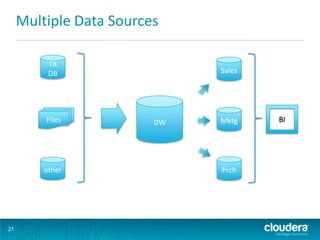
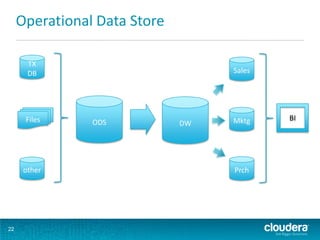
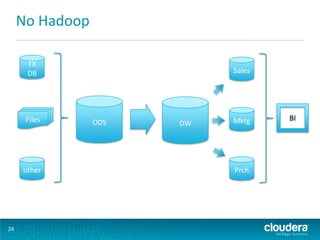
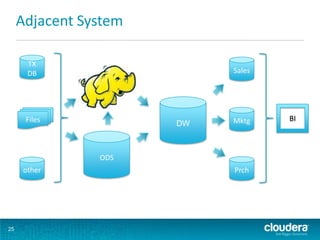
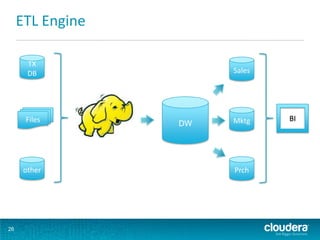
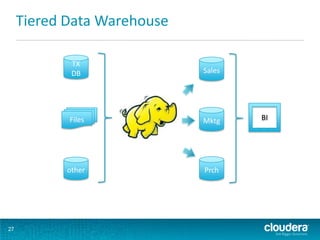
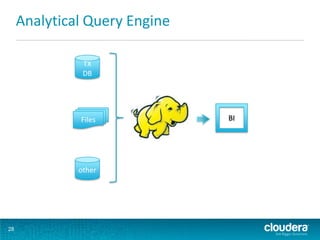
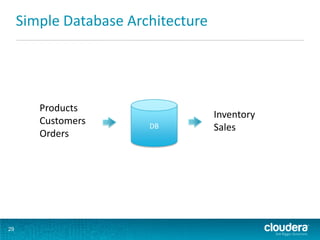
This document discusses how Hadoop can be used in data warehousing and analytics. It begins with an overview of data warehousing and analytical databases. It then describes how organizations traditionally separate transactional and analytical systems and use extract, transform, load processes to move data between them. The document proposes using Hadoop as an alternative to traditional data warehousing architectures by using it for extraction, transformation, loading, and even serving analytical queries.