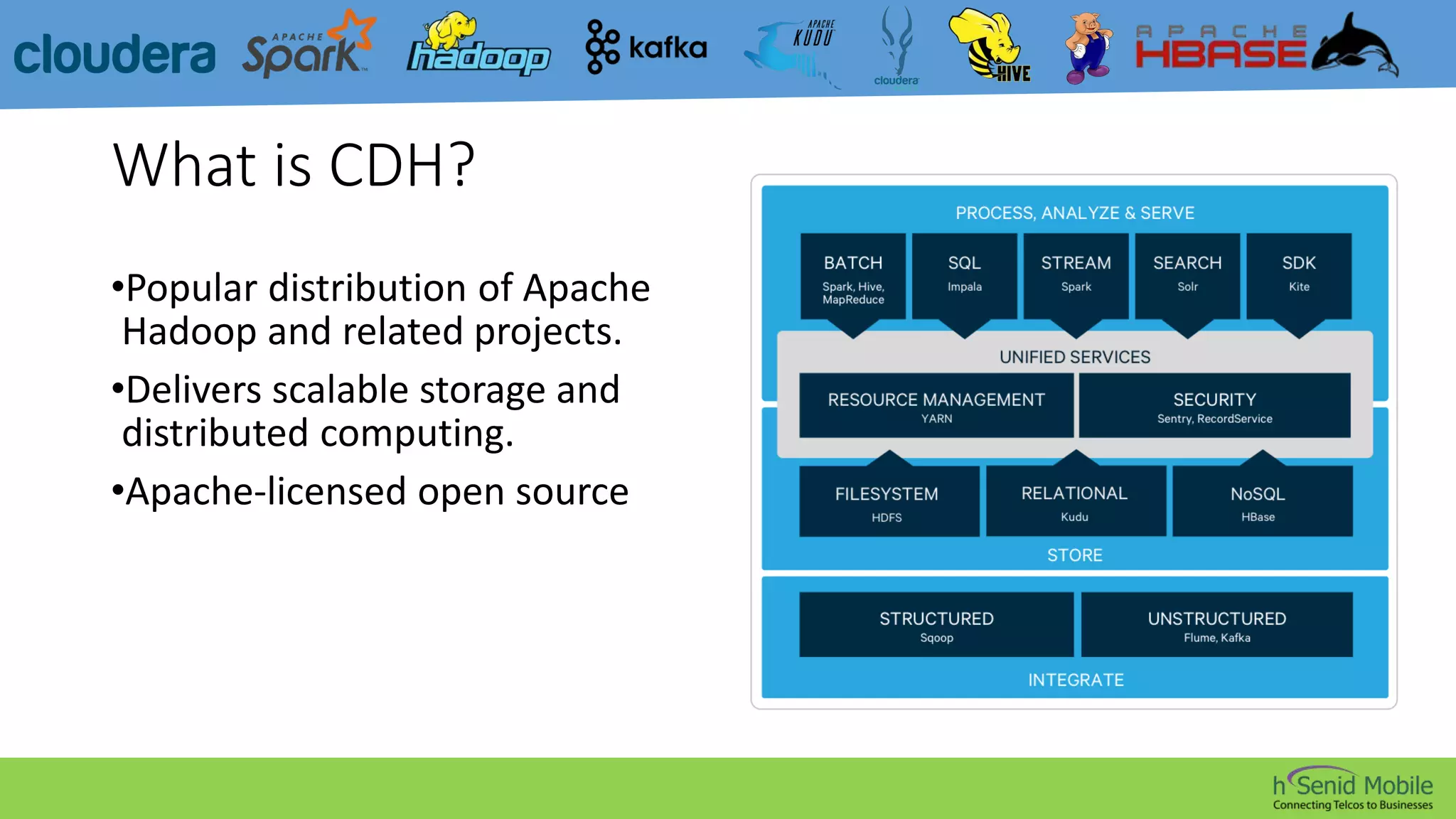
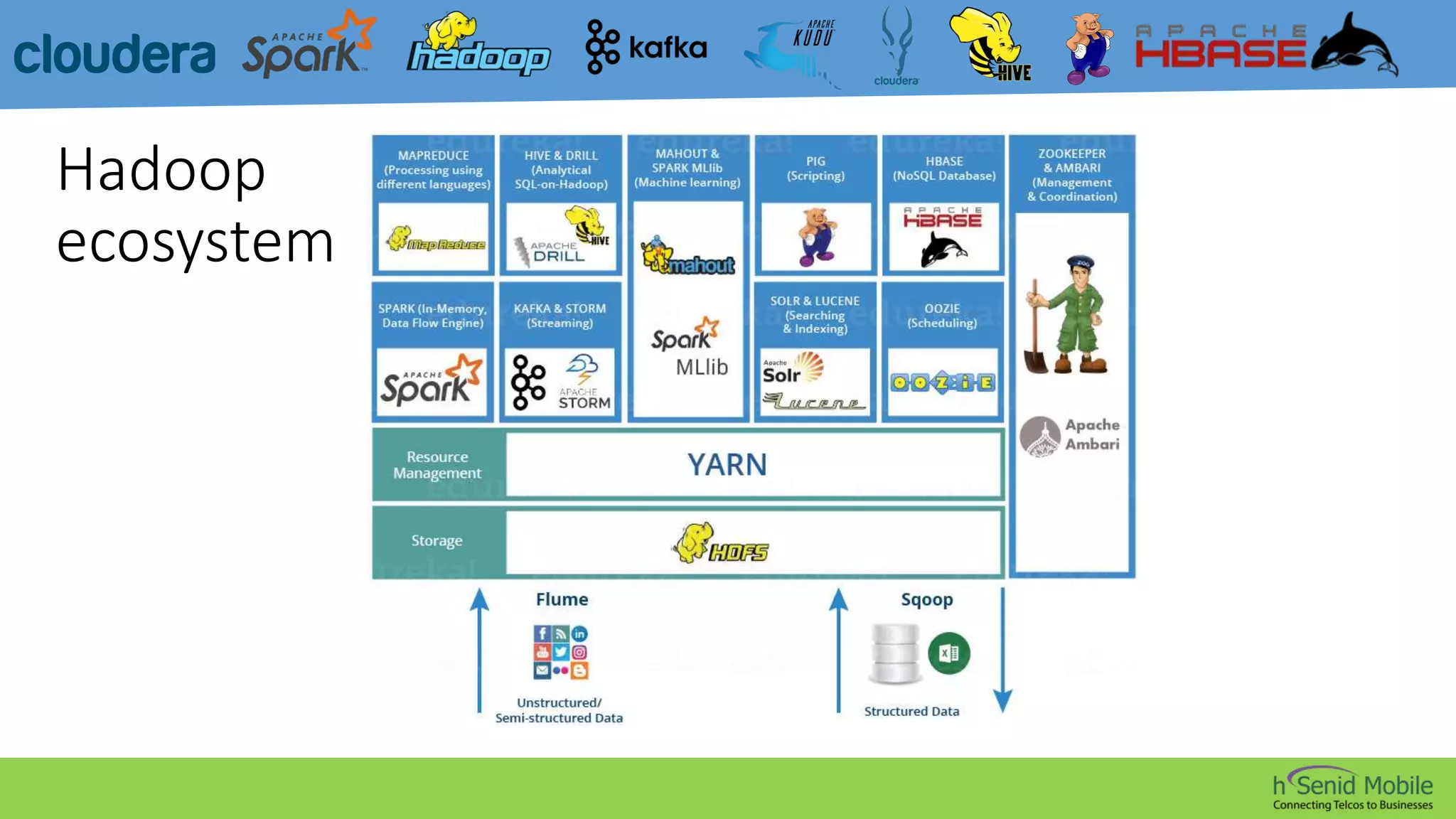
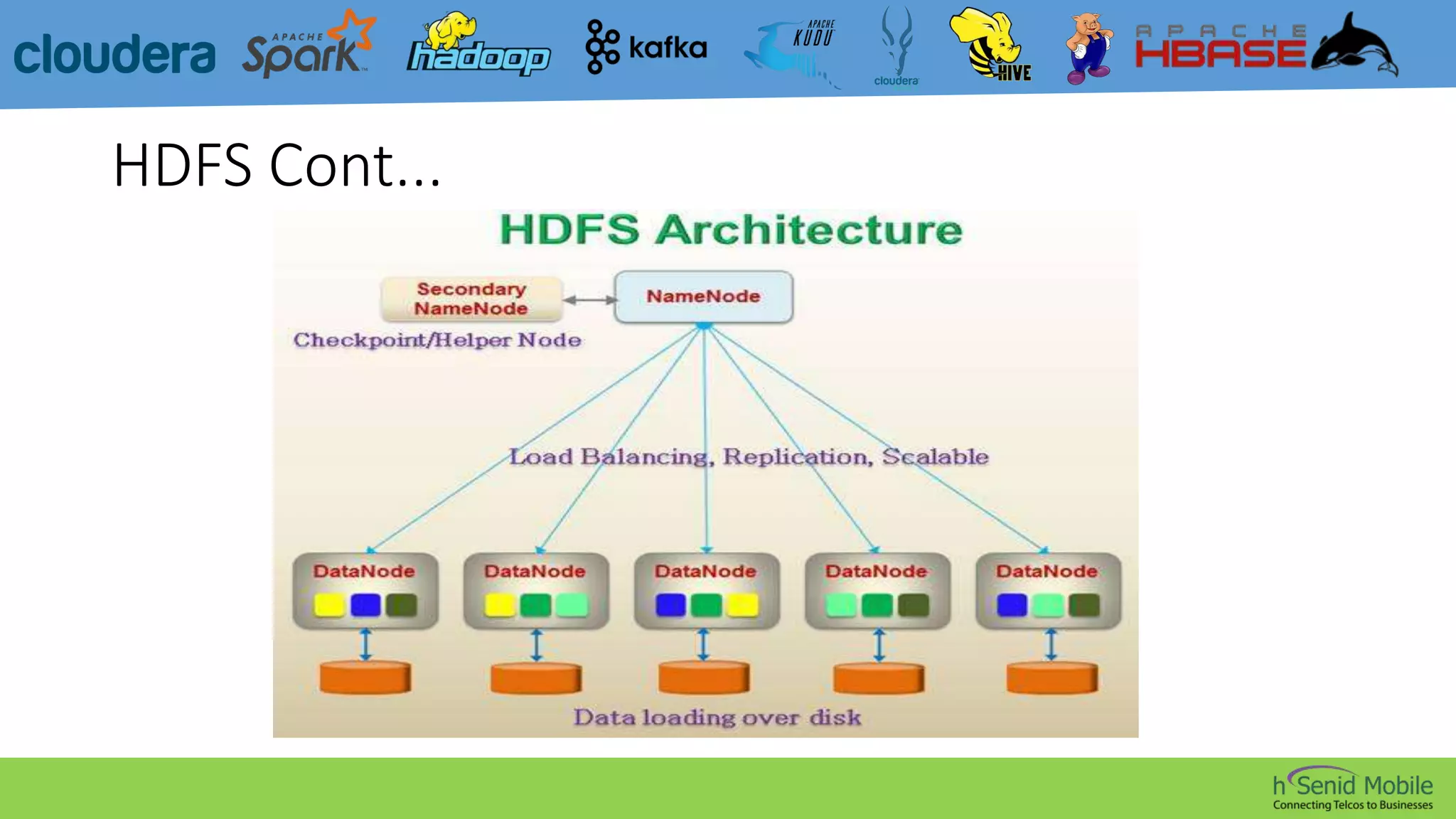
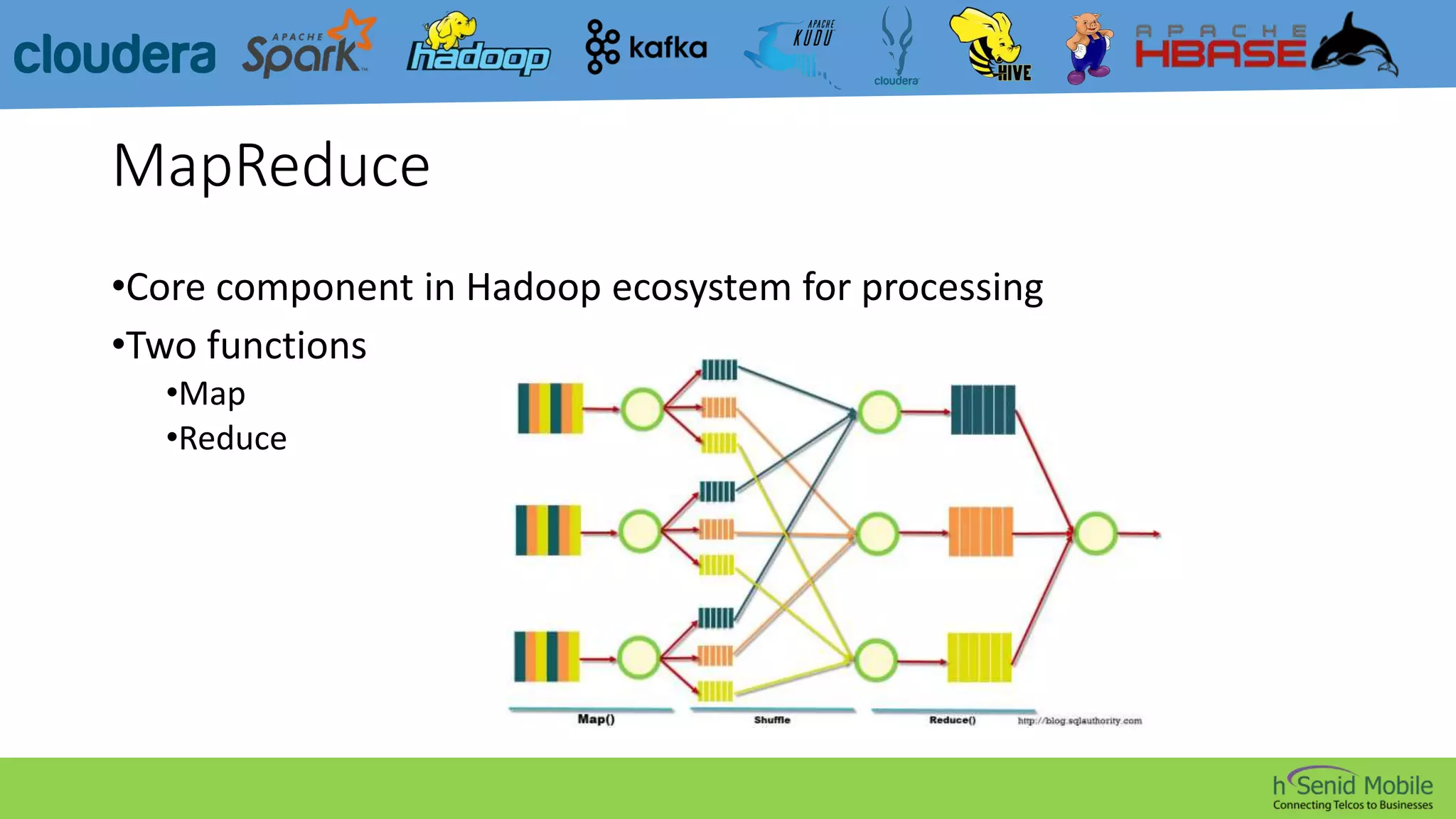
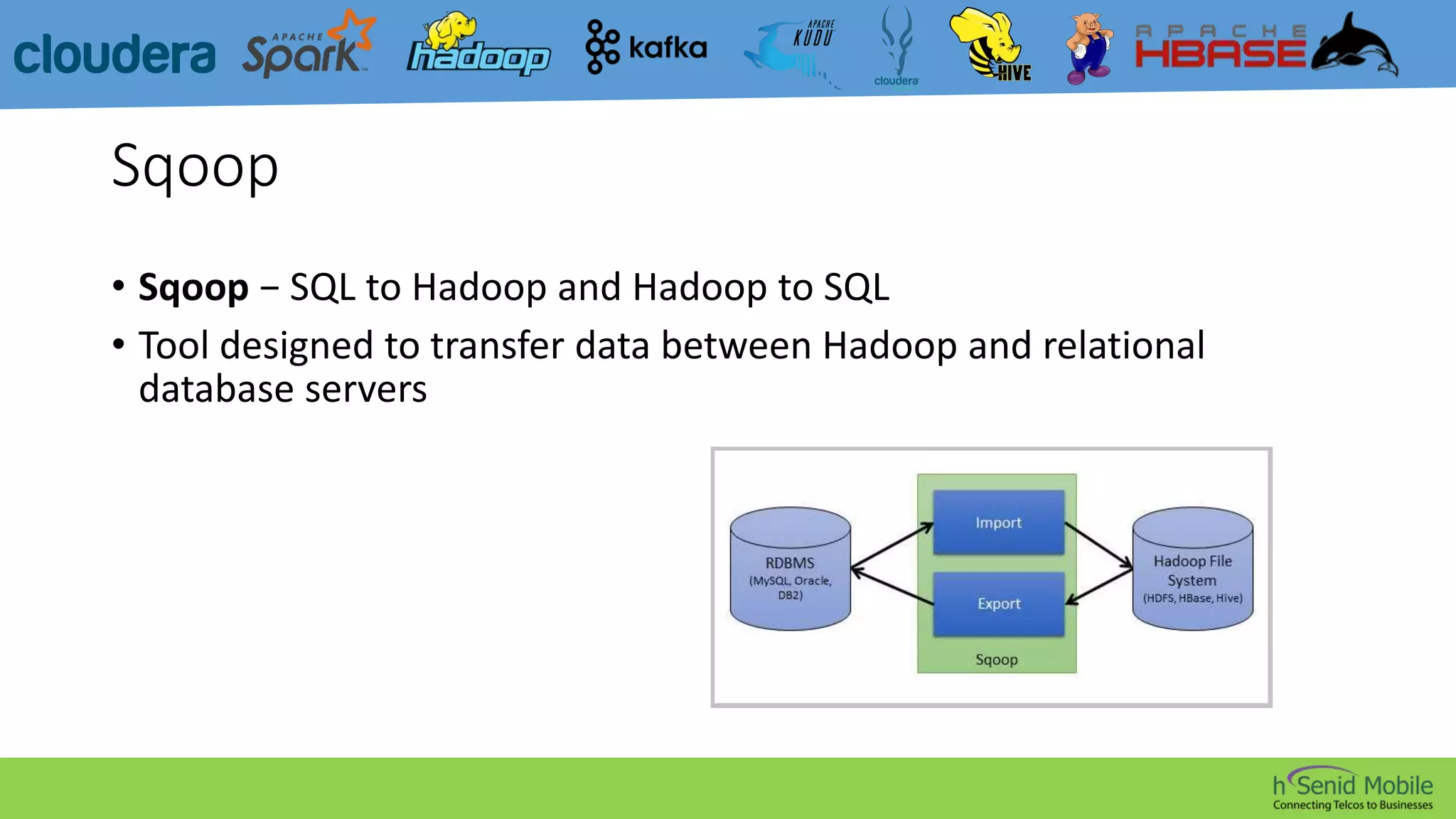
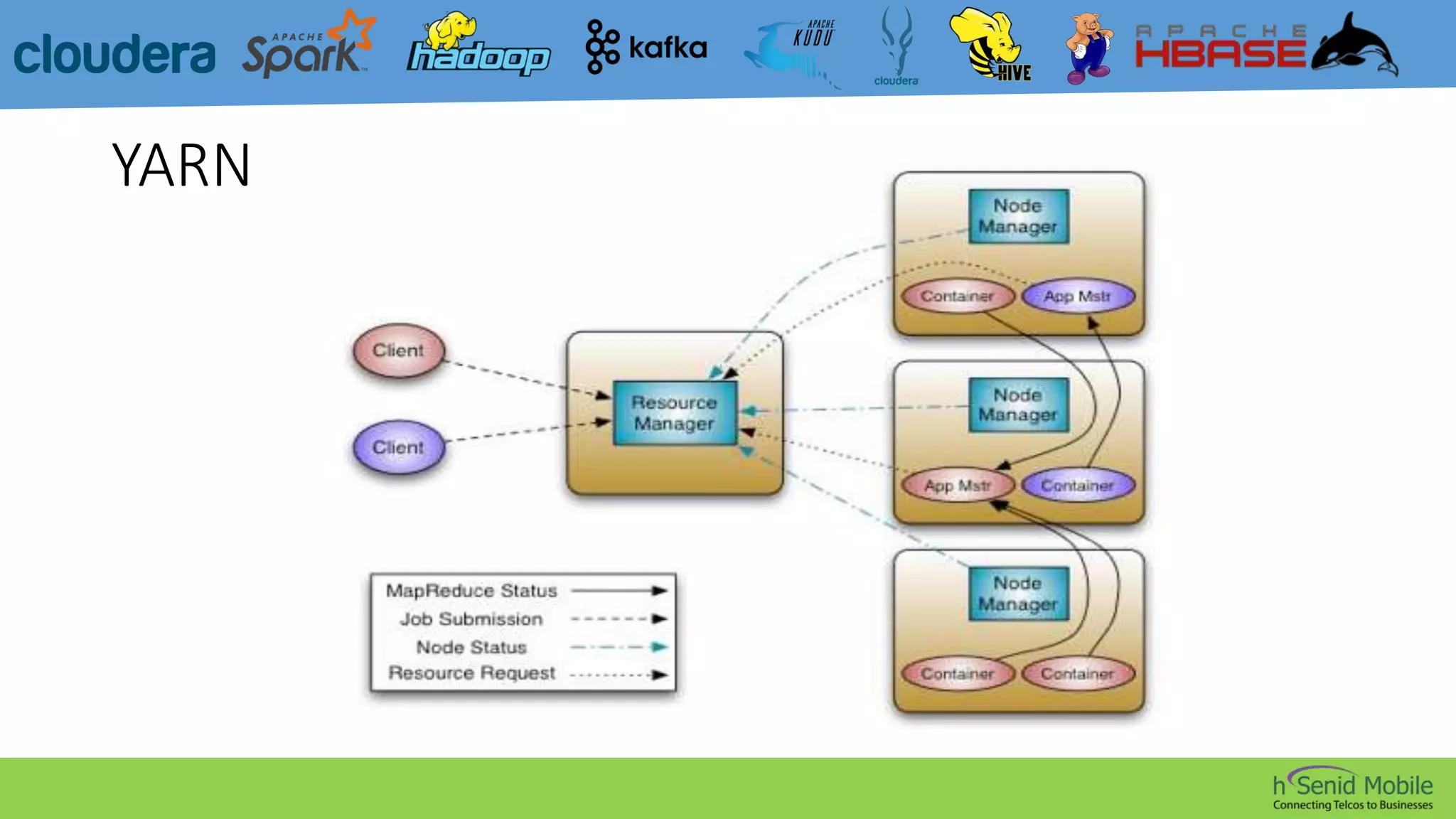
CDH is a popular distribution of Apache Hadoop and related projects that delivers scalable storage and distributed computing through Apache-licensed open source software. It addresses challenges in storing and analyzing large datasets known as Big Data. Hadoop is a framework for distributed processing of large datasets across computer clusters using simple programming models. Its core components are HDFS for storage, MapReduce for processing, and YARN for resource management. The Hadoop ecosystem also includes tools like Kafka, Sqoop, Hive, Pig, Impala, HBase, Spark, Mahout, Solr, Kudu, and Sentry that provide functionality like messaging, data transfer, querying, machine learning, search, and authorization.