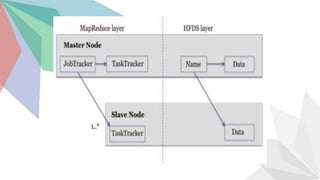
Big data refers to large amounts of data from various sources that is analyzed to solve problems. It is characterized by volume, velocity, and variety. Hadoop is an open source framework used to store and process big data across clusters of computers. Key components of Hadoop include HDFS for storage, MapReduce for processing, and HIVE for querying. Other tools like Pig and HBase provide additional functionality. Together these tools provide a scalable infrastructure to handle the volume, speed, and complexity of big data.