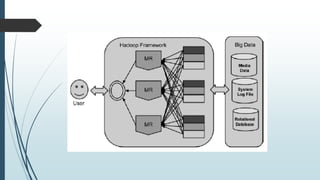
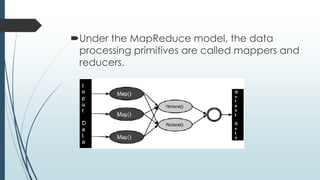
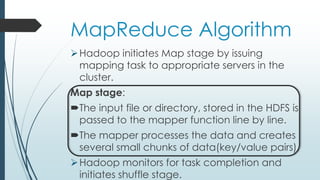
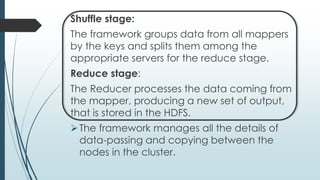
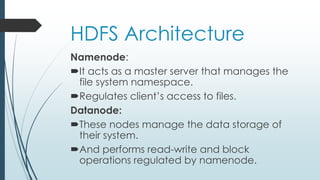
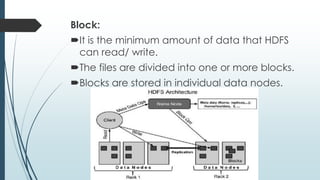
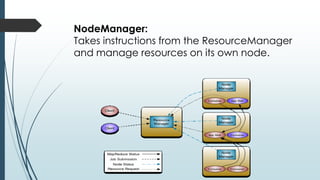
This document defines and describes big data and Hadoop. It states that big data is large datasets that cannot be processed using traditional techniques due to their volume, velocity and variety. It then describes the different types of data (structured, semi-structured, unstructured), challenges of big data, and Hadoop's use of MapReduce as a solution. It provides details on the Hadoop architecture including HDFS for storage and YARN for resource management. Common applications and users of Hadoop are also listed.