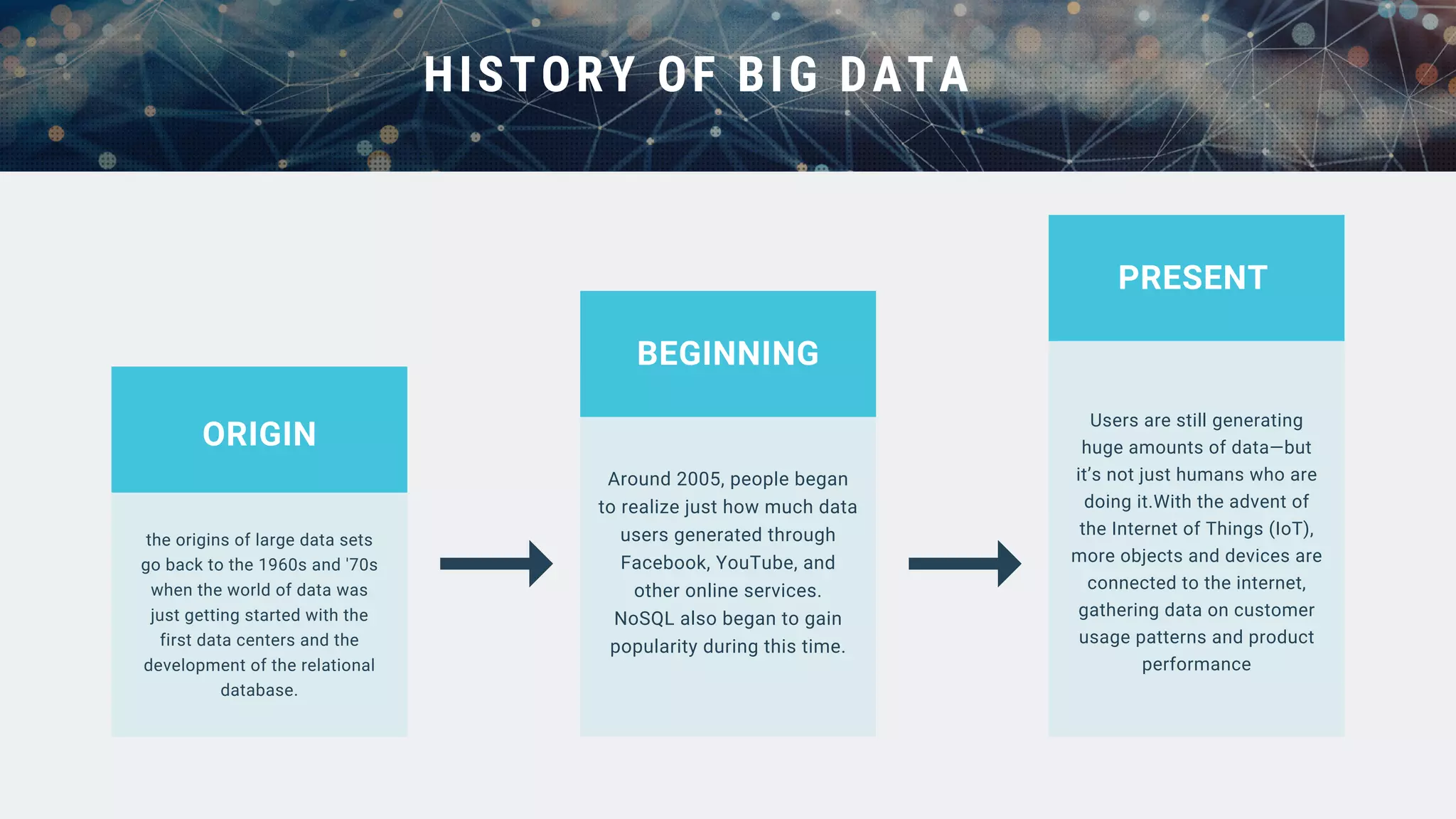
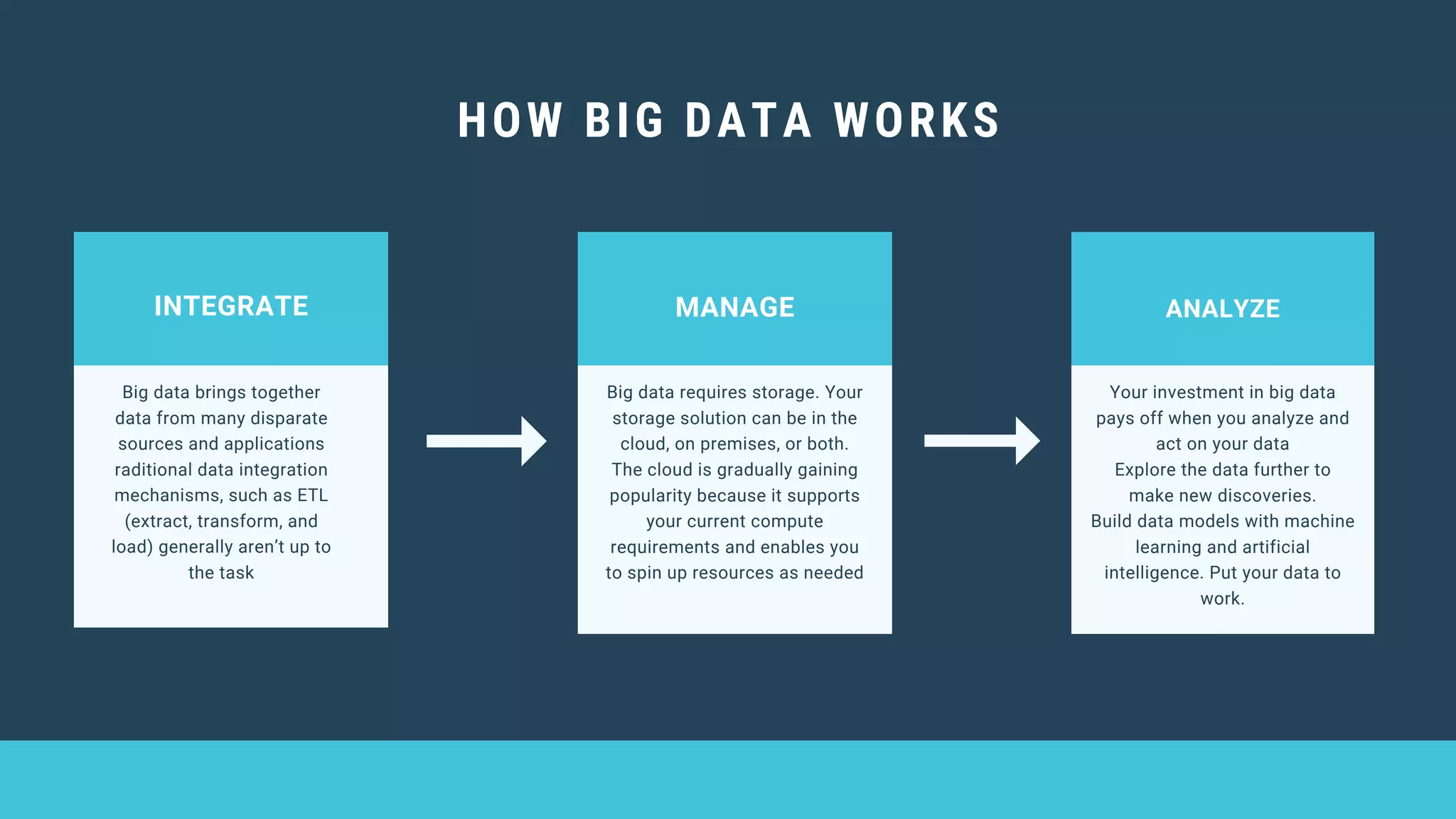
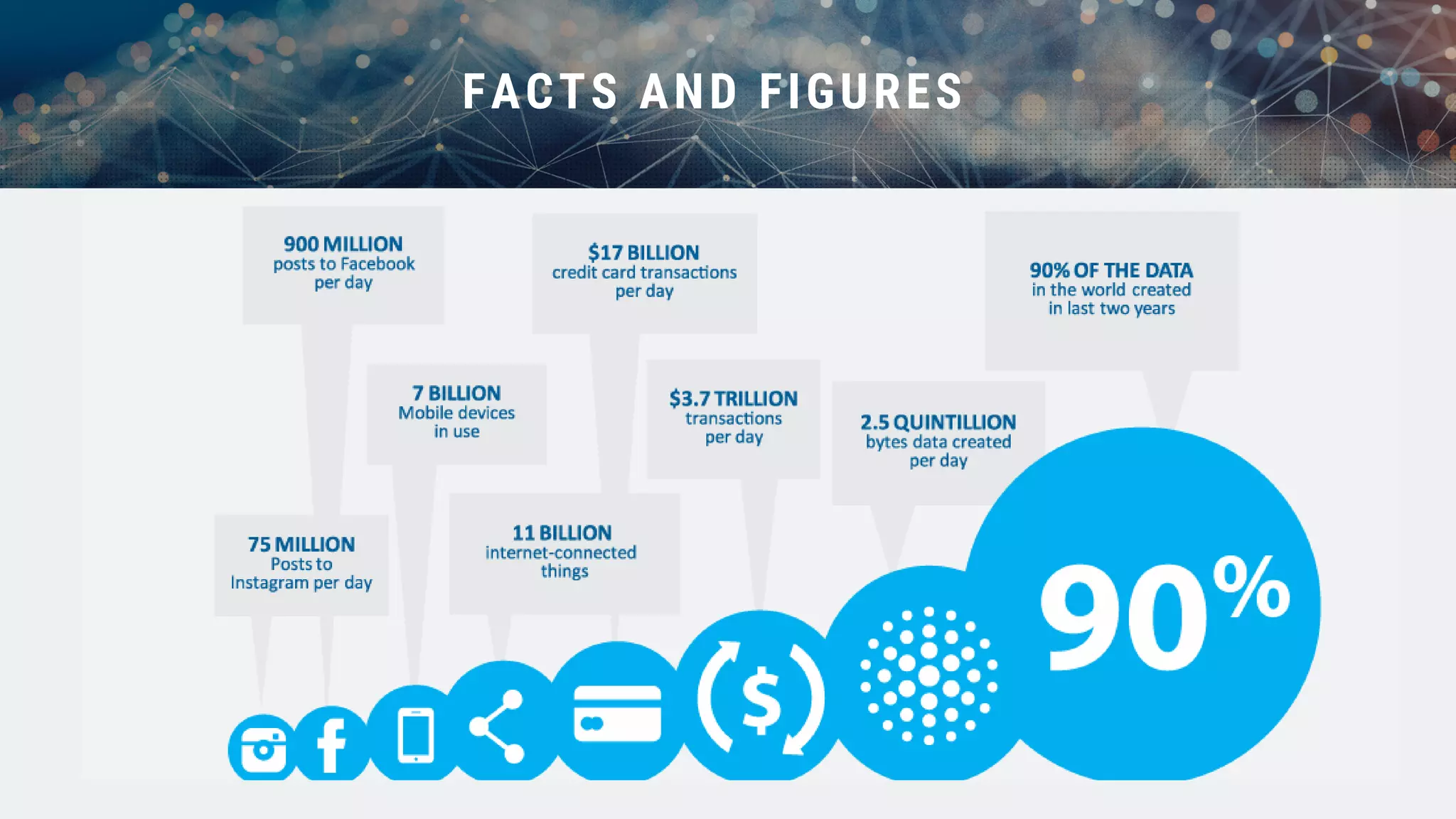
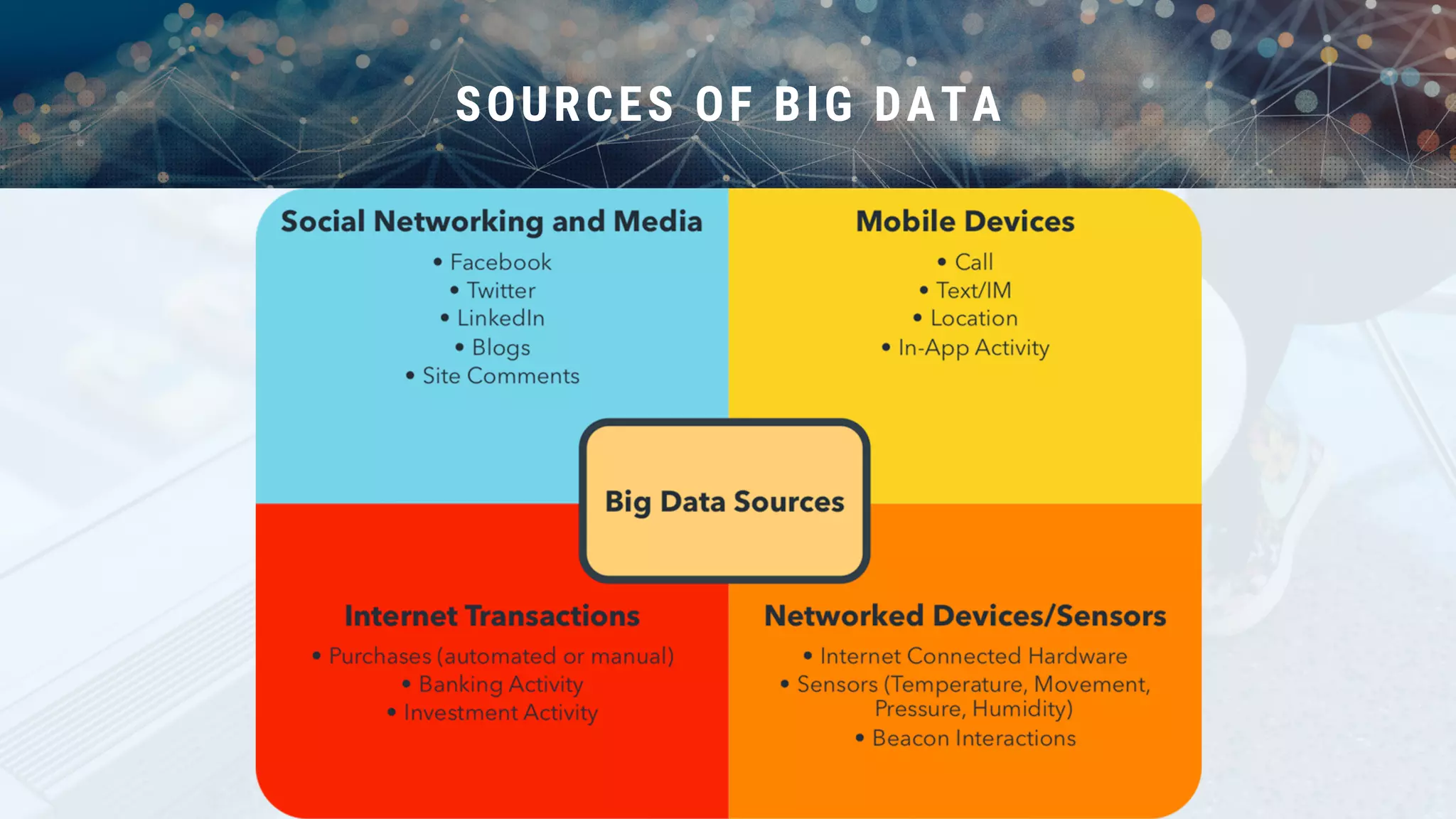
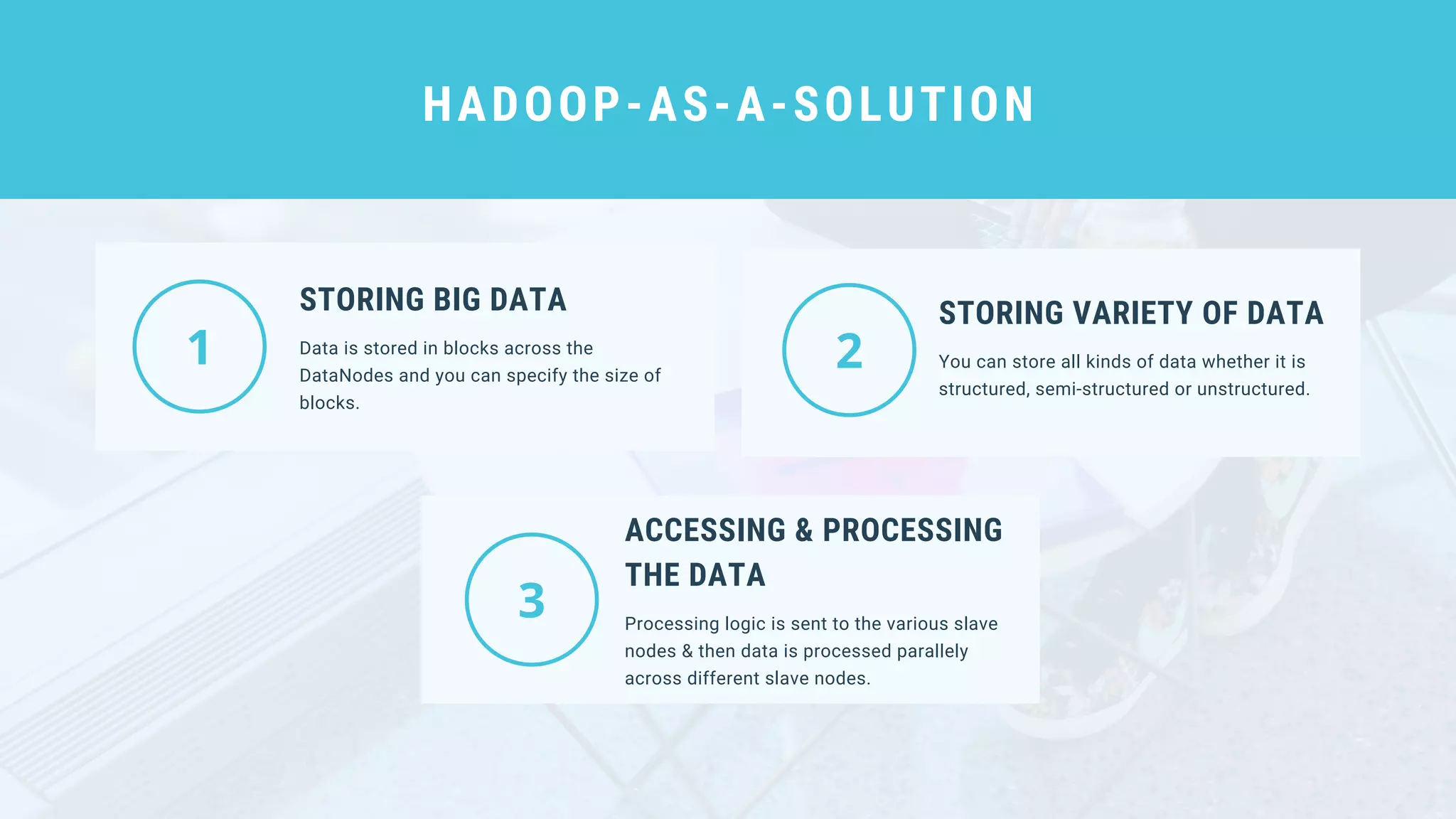
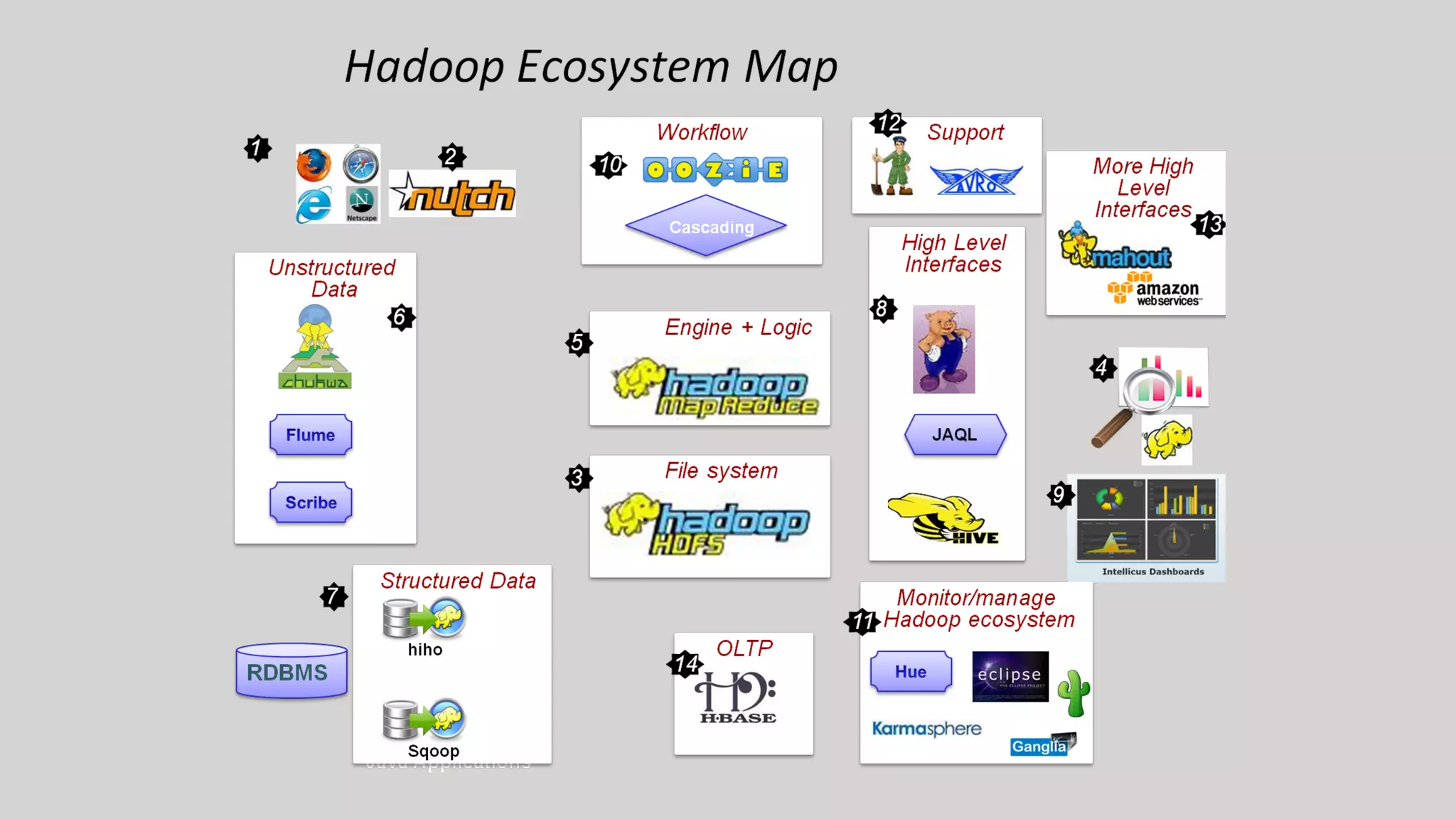
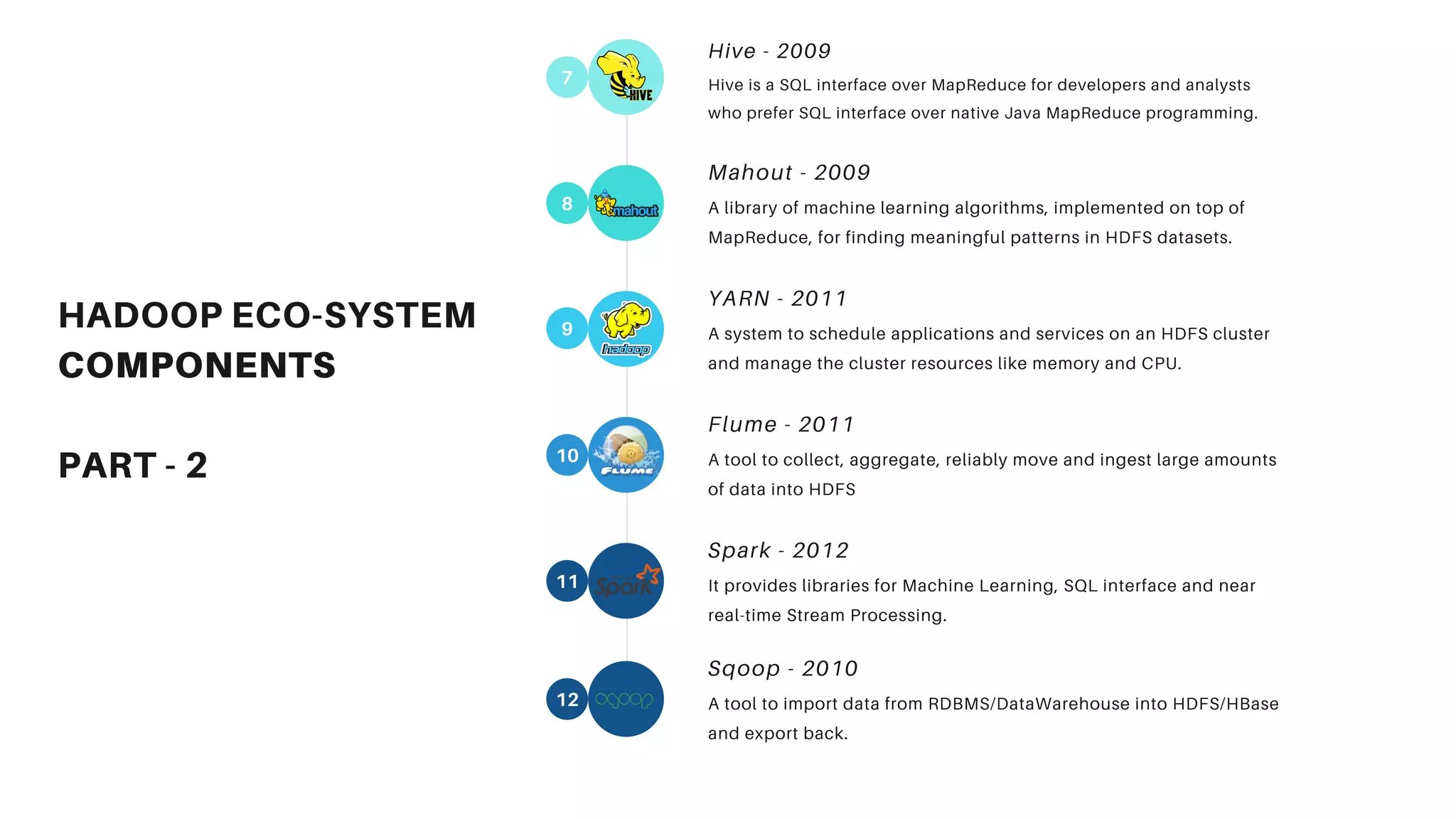
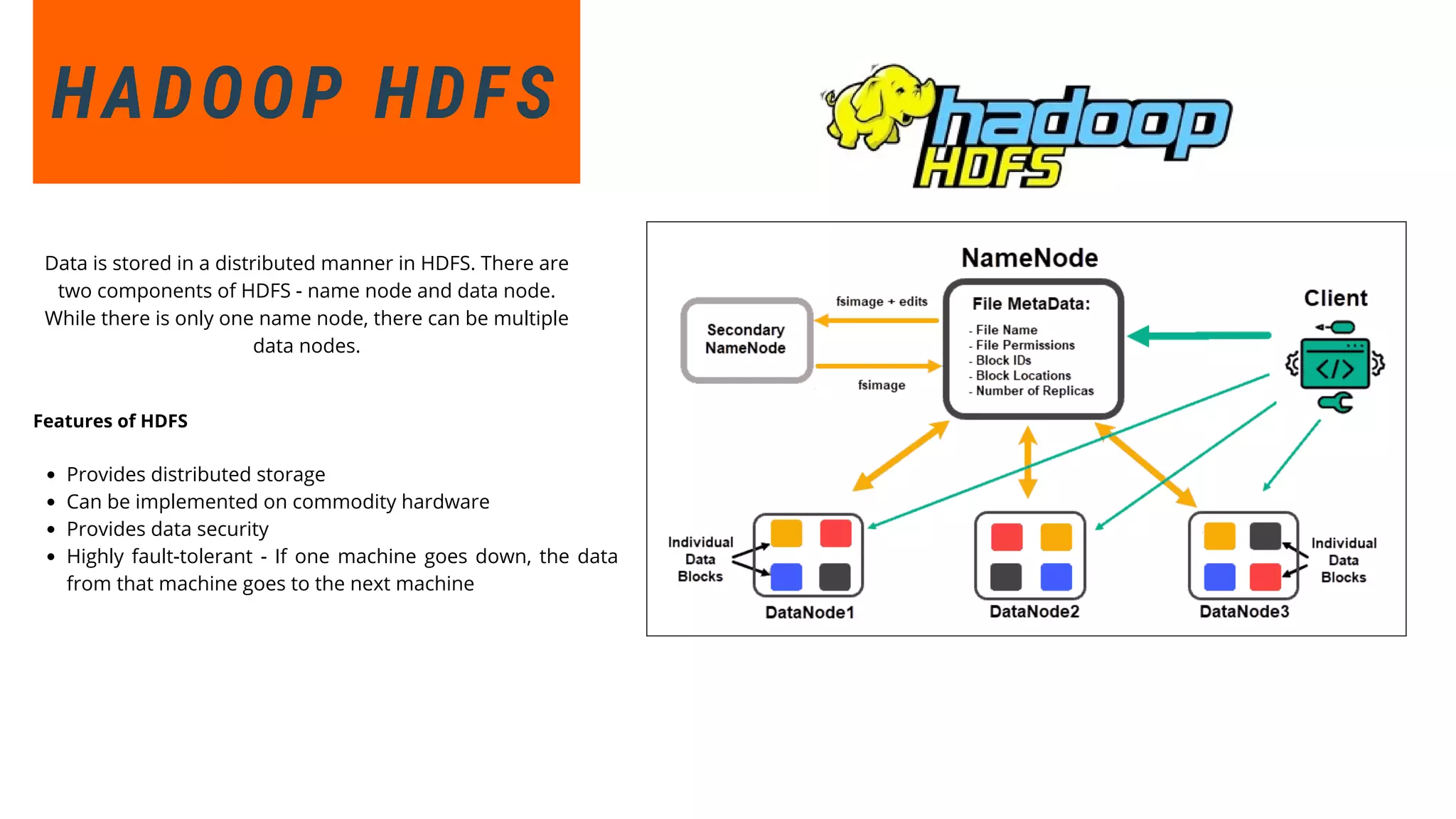
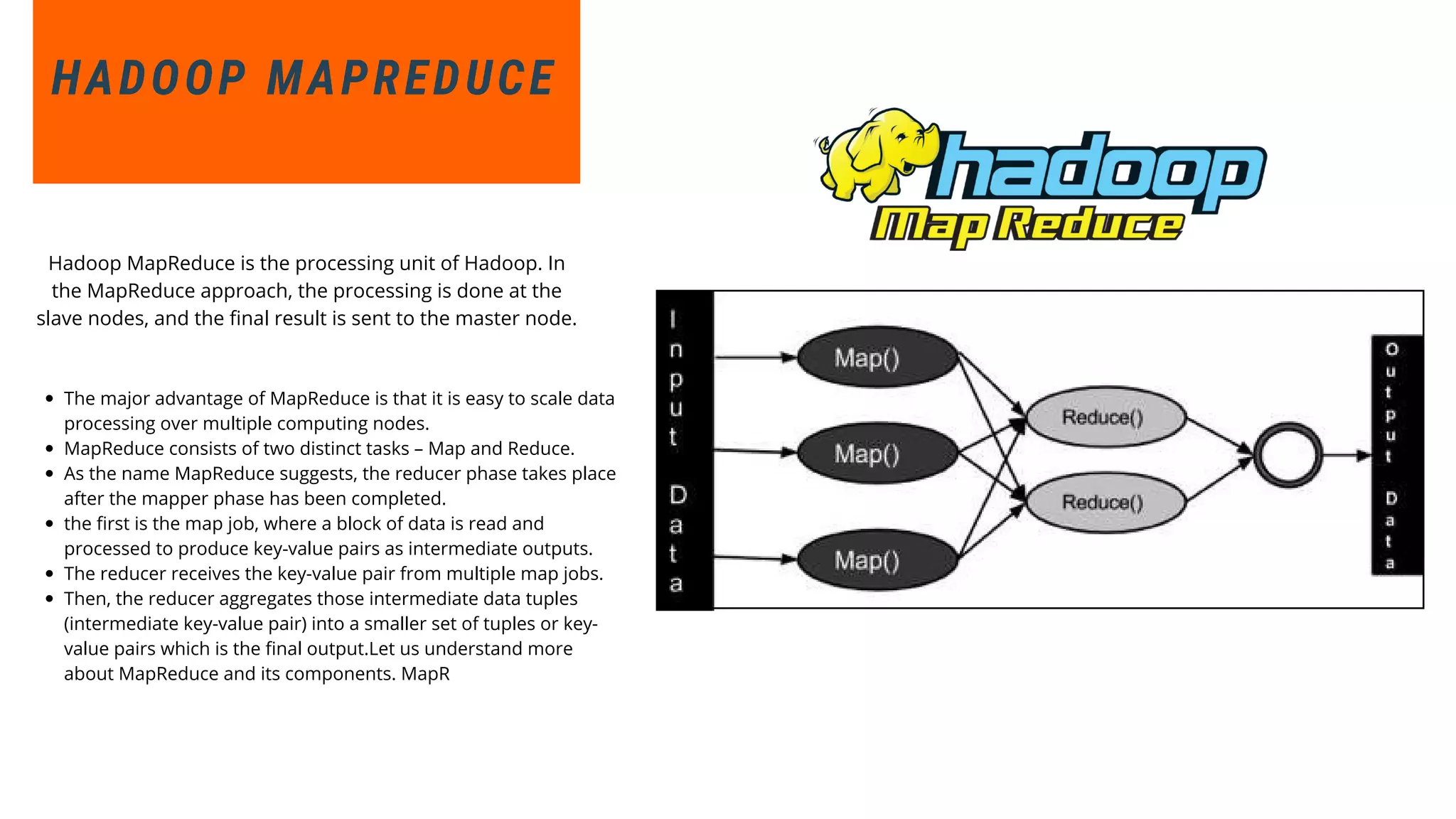
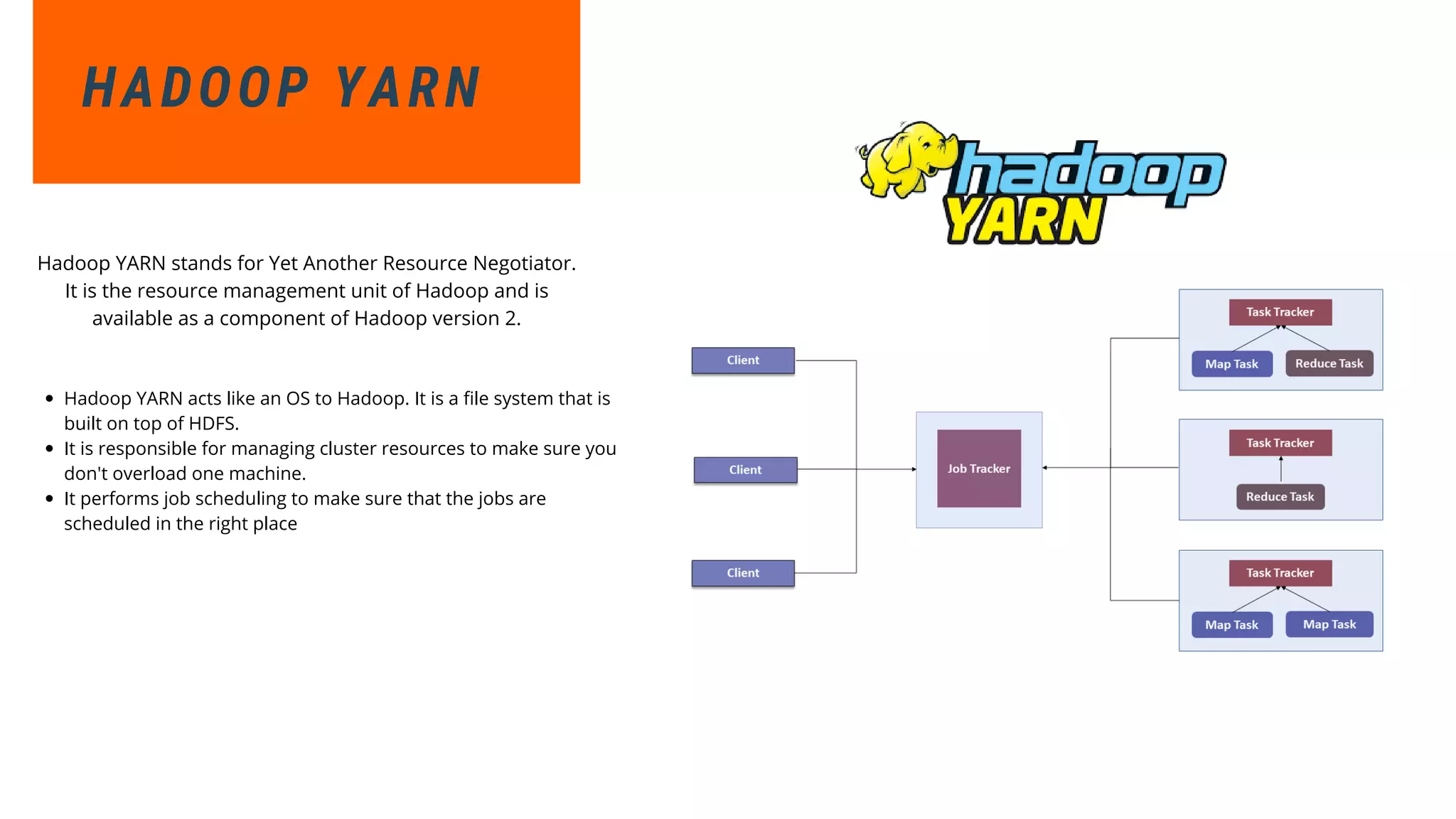
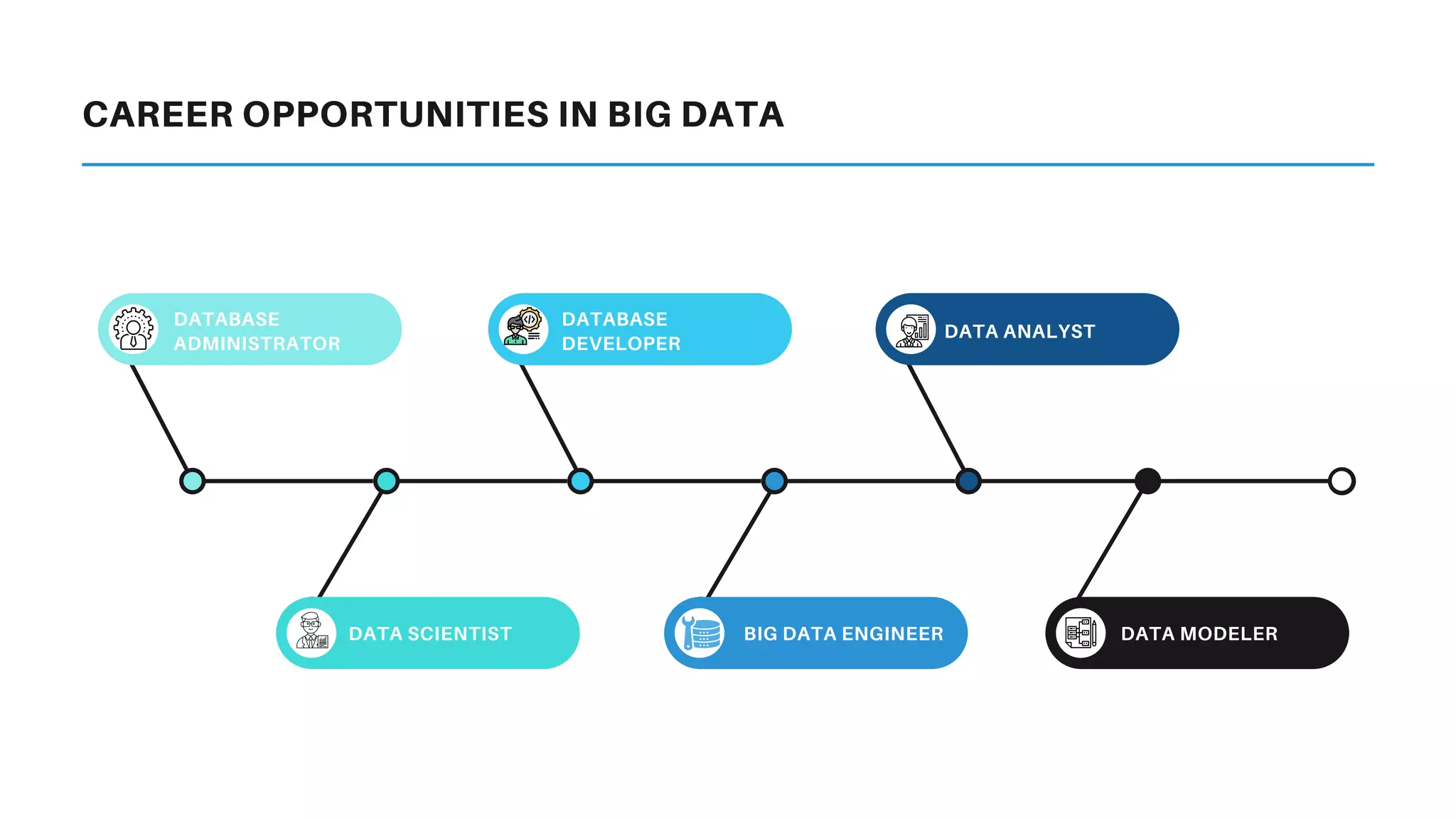
This document provides an overview of big data and Hadoop. It discusses what big data is, its types including structured, semi-structured and unstructured data. Some key sources of big data are also outlined. Hadoop is presented as a solution for managing big data through its core components like HDFS for storage and MapReduce for processing. The Hadoop ecosystem including other related tools like Hive, Pig, Spark and YARN is also summarized. Career opportunities in working with big data are listed in the end.